* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Energy
William Flynn Martin wikipedia , lookup
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
United States energy law wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
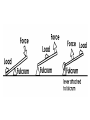
Energy Energy • Is energy involved in the following things? – Chewing gum – Wind blowing – Water flowing down a creek – Sitting still in your desk – Lighted street lamp Energy • Energy – Every change occurring requires energy – Energy is the ability to cause change Energy Different forms or energy: • • • • • • • • Mechanical Thermal Radiant Electrical Chemical Nuclear Sound Gravitational Kinetic Energy • Kinetic Energy – Energy a moving object has because of its motion – KE = ½ mv² – Standard unit is the Joule Potential Energy • Potential Energy – Energy doesn’t have to involve motion – Stored energy – Kinetic vs. Potential Energy Elastic Potential Energy • Elastic Potential Energy – Energy stored in something that can stretch or spring – Rubber bands or springs Chemical Potential Energy • Chemical Potential Energy – Energy stored between chemical bonds – Food and gasoline Gravitational Potential Energy • Gravitational Potential Energy – Anything that can fall, has potential energy – Energy of an object due to their position above the earth’s surface – GPE = mgh What exactly is a Joule? • Joule – Standard unit of measurement for energy – 1 J = 1 kg m²/s² – 1 J = energy to lift a small apple 1 meter straight up Energy Word Problems 1. What is the kinetic energy of a baseball moving at a speed of 40 m/s if the baseball as a mass of 0.15 kg? 2. What is the gravitational potential energy of a ceiling fan that has a mass of 7 kg and is 4 m above the ground? 3. A car is moving at a speed of 20 m/s has a kinetic energy of 300,000 J. What is the car’s mass? Conservation of Energy • Energy is constantly being transformed from one form to another – Light bulbs transform electrical energy to heat and light energy – Gasoline is transformed into kinetic and heat energy • What types of energy can the sun transform into? Conservation of Energy • Law of Conservation of Energy – Energy cannot be created or destroyed – Energy is constantly being changed from one form to another Conversion of Energy • Mechanical energy – Potential energy + Kinetic energy present in a mechanical system – Due to the position and the motion of objects Work and Energy • Work – Transfer of energy that occurs when a force makes an object move – Motion MUST be in the same direction as the force – No movement, NO work – Force is perpendicular to motion, NO work No Work is Being Done!! • No movement • Force perpendicular to motion Work is Being Done! • Work is being done IF: – Object moves – Motion is in the same direction as the force Calculating Work • Calculating work – W = force x distance – Standard unit = Newton meter OR Joule – Energy, Work and Power • How much work is the girl doing on the bicycle? Power • Power – Amount of work done in one second – Rate at which work is done – P = Work ÷ Time – Unit is the Watt – Power – Watts – 1 horsepower = 746 watts Machines • Machines – Device that makes doing work easier 1. Increases force 2. Changes direction of the force Machines • Input force – Force applied to the machine • Output force – Force applied by the machine • Mechanical Advantage – Ratio of the output force to the input force – MA = Output force ÷ Input force Machines • Efficiency – Measure of the amount of work put into the machine is changed to useful output – Efficiency = • (Output ÷ input) X 100% Simple Machines • Levers – Bar that is free to pivot about a fixed point – 1st Class – 2nd Class – 3rd Class Examples of Levers • Examples of Levers – – – – – – Screwdriver Wheelbarrow Baseball bat Our elbow Seesaw Scissors Simple Machines • Pulleys – Grooved wheel with a rope, chain or cable running along the groove – Examples of machines that use pulleys • Flag poles • Sail boats • Weight machines Simple Machines • Wheel and Axle – Shaft or axle attached to the center of a wheel – Examples: • Wheel and axle of a car • Wheel and axle of a bicycle • Handle of a pencil sharpener Examples of Wheel and Axles Simple Machine • Incline Plane – Sloping surface – Examples include: • Stairs • Ramps Simple Machine • Screw – Incline plane wrapped around a cylindrical post – Examples: • Jar lid • Wood screw • Light bulb Simple Machine • Wedge – Inclined plane with one or two sloping sides – Examples: • Knife • Scissors blade • Ax Identify the following simple machines Identify the following simple machines Identify the following simple machines • Compound Machines – Two or more simple machines combined