* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evidence of Evolution
Survey
Document related concepts
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
The Selfish Gene wikipedia , lookup
Sociobiology wikipedia , lookup
Kin selection wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of sexual reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Mate choice wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary landscape wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
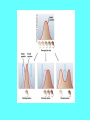
Examples of Evolution http://schoolworkhelper.net/wp-content/uploads/2010/12/cladogram.gif Allele Frequencies There are dominant and recessive alleles. Hardy and Weinberg (scientists) determined that dominant alleles do NOT automatically replace recessive alleles. Alleles in a population only change if selection acts upon them http://campus.murraystate.edu/academic/faculty/terry.derting/bio116/hardy_weinberg.jpg http://www.google.com/imgres?imgurl=http://www.wallsofthewild.com/pterodactyl.jpg&imgrefurl=http://www.wallsofthewild.com/pter.htm&usg=__9caIuOdNvnUNeTtJd_BwijJIK5M=&h=479&w=800&sz=100&hl=en&start=0&zoom=1& nid=vSsuBQ-o-EFlxM:&tbnh=131&tbnw=219&ei=6ahTYjRF6iU0QGo5JSEBQ&prev=/images%3Fq%3Dpterodactyl%26um%3D1%26hl%3Den%26rlz%3D1G1GGLQ_ENUS398%26biw%3D1438%26bih%3D680%26tbm%3Disch&um=1&itbs=1&iact=hc&vpx=1109&vpy=148&dur=1 95&hovh=174&hovw=290&tx=91&ty=85&oei=-6ahTYjRF6iU0QGo5JSEBQ&page=1&ndsp=19&ved=1t:429,r:5,s:0 HARDYWEINBERG PRINCIPLE: The frequencies of alleles in a population do not change unless evolutionary forces act on the population. http://www.maropeng.co.za/images/uploads/fossil_lg.jpg Hardy-Weinberg • Holds true for: • large populations in which members do not mate with relatives AND • as long as evolutionary forces are not acting on the population 5 Evolutionary Forces 1. Mutations 2. Gene Flow 3. Nonrandom mating 4. Genetic drift 5. Natural Selection #1 Mutations • Mutation rates are slow in nature • Not all result in phenotype changes (remember the codon wheel) • Mutation IS the source of variation though & makes evolution possible • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Mkmt odFQbQM #2 Gene Flow • The movement of individuals to or from a population (MIGRATION) creates gene flow. • Immigrants = arriving individuals • Emigrants = departing individuals #3 Nonrandom Mating • In-breeding alters Hardy-Weinberg • Also occurs when organisms choose their mates #4 Genetic drift • Small populations that are isolated from one another can differ greatly because of genetic drift • Fires - landslides - etc. # 5 Natural Selection • The frequency of an allele will increase or decrease depending on the allele’s effects on survival and reproduction • N.S. is one of the most powerful agents of genetic change. http://evolution.berkeley.edu/evolibrary/article/evo_39 Natural Selection affects the Distribution of Phenotypes in 4 Ways! 1 – Stabilizing Selection 2 – Directional Selection 3 – Disruptive Selection 4 - Sexual Selection 1- Stabilizing Selection • Individuals with the average form of a trait have the highest fitness. 2 – Directional Selection • Individuals at one end of the curve have higher fitness and are favored more than individuals in the middle or other end. 3 – Disruptive Selection • Individuals with either extreme variation of a trait have greater fitness than individuals with the average form of the trait. 4 – Sexual Selection • The preferred choice of a mate based on a specific trait. Peacocks -- females choose males based on certain traits V. I .S .T. • V = Variation: All life forms vary genetically within a population. It is this genetic variation upon which selection works. • I = Inheritance: Genetic traits are inherited from parents and passed on to offspring. • S = Selection: Organisms with traits that are favorable to their survival get to live and pass on their genes to the next generation. • T = Time: Evolution takes time. It can happen in a few generations, but major change, such as speciation, often take very long periods of time.