* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1 - Cobb Learning
Electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Electroactive polymers wikipedia , lookup
Hall effect wikipedia , lookup
Magnetoreception wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Induction heater wikipedia , lookup
Electrostatics wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic compatibility wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Faraday paradox wikipedia , lookup
Force between magnets wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic core wikipedia , lookup
Scanning SQUID microscope wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Superconducting magnet wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Induction motor wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Eddy current wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Electric current wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
History of electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
Electricity wikipedia , lookup
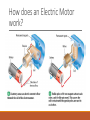
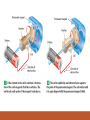
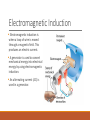
Electricity and Magnetism Electricity and Magnetism how are they related? When an electric current flows through a wire, a magnetic field forms around the wire. The Right Hand Rule Use the Right hand rule to determine the direction of the current and the magnetic field. Imagine your right hand curled around the wire, your thumb points in the direction of the current and your fingers show the direction of the magnetic field What is an Electromagnet? When an electric current is passed through a coil of wire wrapped around a metal core, a very strong magnetic field is produced. This is called an electromagnet. The more coils wrapped around the core, the stronger the magnetic field that is produced. This stronger magnetic field leads to a stronger current. An electromagnet is considered a temporary magnet. What are Electric Motors? An electric motor is a device which changes electrical energy into mechanical energy. A basic electric motor has a power source, a permanent magnet, and an electromagnet that can rotate. How does an Electric Motor work? Electromagnetic Induction Electromagnetic induction is when a loop of wire is moved through a magnetic field. This produces an electric current. A generator is used to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy by using electromagnetic induction. An alternating current (AC) is used in a generator. Electromagnetic Induction vs. Electric Motors The electromagnet in a generator is rotated by some outside source of mechanical energy. Electric motors change electrical energy in to mechanical energy, and generators turn mechanical energy into electrical energy.