* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What is Biology?
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Taxonomy (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Regeneration in humans wikipedia , lookup
Natural environment wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of sexual reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
History of biology wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Sexual reproduction wikipedia , lookup
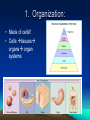
What is Biology? Chapter 1 Characteristics of life outline Biology: Organisms: 1. Organization cells -> ___ ___ ___ specialization 2. Reproduction asexual sexual 3. Growth Development 4. Adjust Stimulus/Response Homeostasis 5. Adapt/Evolve • Biology: –study of life • Organisms: –living things What determines life? • 5 characteristics that all living things must have! 1. Organization: • Made of cells!! • Cells tissues organs organ systems • Single-cell organisms have everything they need to be self-sufficient. In multicellular organisms, specialization increases until some cells do only certain things. 2. Reproduction: • must occur for a species to survive Species ·Organisms that look alike and can mate among themselves. Same Species Not Same Species Reproduction can be: --Asexual: One parent makes identical offspring. • Sexual – two parents, offspring is hybrid of those parents 3. Growth/ Development: • Growth: –Increase in size • Development: –Changes from embryo to adult 4. Adjust to Surroundings: • Stimulus: triggers a reaction • Response: the reaction to the stimulus. • Homeostasis: – Regulate internal environment – Ex. Sweating when hot, shivering when cold 5. Adapt/ Evolve: • Adaptations are traits giving an organism an advantage in a certain external environment. Ex. Polar bears have thick fur, fish have gills • Survival of the fittest! Locomotion (Movement): • Not all organisms move (ex. Sponge is an animal that is sessile; mushroom is fungi that does not move from place to place.)