* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download US subprime credit crisis and its implications from a corporate
Survey
Document related concepts
Private equity secondary market wikipedia , lookup
Financial history of the Dutch Republic wikipedia , lookup
Derivative (finance) wikipedia , lookup
Private money investing wikipedia , lookup
Systemically important financial institution wikipedia , lookup
Systemic risk wikipedia , lookup
CAMELS rating system wikipedia , lookup
Private equity in the 2000s wikipedia , lookup
Private equity in the 1980s wikipedia , lookup
Synthetic CDO wikipedia , lookup
Federal takeover of Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac wikipedia , lookup
Securitization wikipedia , lookup
Asset-backed security wikipedia , lookup
Financial crisis wikipedia , lookup
Financial crisis of 2007–2008 wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
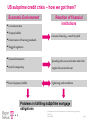
US subprime credit crisis and its implications from a corporate financing point of view Thilo Kusch, Chief Financial Officer 15th CEO Summit Röjtökmuzsaj 24 April, 2008 US subprime credit crisis – how we got there? Economic Environment Reaction of financial institutions Low interest rates Property bubble Deterioration of financing standards Excessive financing – search for yield Sluggish regulation Financial innovation Spreading risks via securitization where the Lack of transparency original risk can not be seen Burst of property bubble Tightening credit conditions Problems in fulfilling subprime mortgage obligations US subprime credit crisis and its implications from a corporate financing point of view Thilo Kusch 24 April, 2008 Page 2 US subprime crisis and its spreading in the global financial system Problems in fulfilling subprime mortgage obligations Losses of financial intermediaries and investors Reassessing risks, and risk-taking (banks, funds, investors) Increase in counter-party risk, losses of confidence Cost of financing has increased Financing possibilities have narrowed Impact on financial markets and real US subprime credit crisis and its implications from a corporate financing point of view economy Thilo Kusch 24 April, 2008 Page 3 Effect on the Capital markets Harder to raise financing both on equity and debt markets: public transactions (IPO, bond issuance) are delayed, because of increased costs and low demand of securities Global debt issuance collapsed in first quarter 2008 In Q1 2008 the number of abandoned IPO’s jumped Investors are strongly selective, but the demand for good quality assets and transactions may even increase: Visa IPO in February 2008 was the USA’s greatest IPO ever, 40% surge in equity price following the official listing on NYSE US subprime credit crisis and its implications from a corporate financing point of view Thilo Kusch 24 April, 2008 Page 4 Impact in the CEE region and Hungary CEE banks did not have significant exposure to US subprime credit market Risk appetite of investors deteriorated: investors partially moved to safe markets from the region Asset prices came under pressure Due to weaker macro-fiscal conditions, heavier equilibrium problems and unstable business environment, Hungary is deeper affected by the financial turmoil than its regional peer-group Overview of the financing environment in Hungary Due to the weak financing capacities of the domestic sectors, the country is strongly exposed to foreign financing Unfavorable global environment Unfavorable local environment: HUF interest rates increase significantly Implication: economic actors who have financing needs, it is more costly to get to funds from the debt market US subprime credit crisis and its implications from a corporate financing point of view Thilo Kusch 24 April, 2008 Page 5 Possible reactions to reduce risks for companies Restructuring the loan portfolio: Shorten the maturity Raise the share of FX loans Raise the share of loans with floating interest rate Cash pooling – optimising the cash balances of group companies Enhancing the working capital management Modifies the risk-taking of a company Possible advantages depend on the current status of efficiency No superior ‘after-crisis solution’ exists. The negative effects of a similar turmoil can be alleviated most efficiently by prudent risk management, well before the emergence of such a credit crunch. US subprime credit crisis and its implications from a corporate financing point of view Thilo Kusch 24 April, 2008 Page 6 Capital structure of Magyar Telekom The company’s strategic priority remains finding further value-creating acquisitions, require a flexible balance sheet net debt ratio in the range of 30-40% Magyar Telekom shares are listed both on BSE and NYSE The net debt ratio 31% EoY 2007 HUF 367 bn) significant debt portfolio (total debt of Financing need of Magyar Telekom arises in connection with the annual dividend payment (HUF 80.2 bn in 2008) maturing components of the loan portfolio decreased by MT Group’s strong cash generation US subprime credit crisis and its implications from a corporate financing point of view Thilo Kusch 24 April, 2008 Page 7 Effects on the financing of Magyar Telekom Bank loans and financing from the international markets has became more expensive The following financing characteristics could help lessen the effects: available shelf facilities in sufficient amount loan portfolio with longer maturity/maturities spread over time only a part of the debt needs to be renewed under the unfavourable (and possible temporary) circumstances significant portion of the debt portfolio in debt instruments bearing fix interest diversified financing sources the turmoil might affect various creditors and investors differently market push on dividend payment more difficult to move towards the optimal capital structure under the changed circumstances Continuous risk management in the past is paying back now, it could decrease the effect of the credit crunch in short or even in medium run. US subprime credit crisis and its implications from a corporate financing point of view Thilo Kusch 24 April, 2008 Page 8 Dive on the M&A market The value of announced M&A in Q1 2008 was down 40 percent from the same period last year, resulting the least active first quarter since 2004 The drop in M&A volumes has been accompanied by a sharp drop in activity in the debt and equity markets The unfavourable stock price levels globally motivate potential sellers to put off deals until market recovery The end of the credit boom and wild swings in the stock market have made M&A deals harder to finance and harder to value The credit squeeze has been particularly felt in private equity deals, whose value has dropped 71 per cent year-on-year For Magyar Telekom the effect is twofold: (i) less acquisition opportunity may arise, but (ii) less competition is expected from the private equities US subprime credit crisis and its implications from a corporate financing point of view Thilo Kusch 24 April, 2008 Page 9 Roundtable discussion topics I. Role of financing – can capital market risks be excluded? II. Is there a balance of power between banks and companies? Why do the companies have to bear the burden of the banks’ excessive risk-taking? Lessons of Magyar Telekom… US subprime credit crisis and its implications from a corporate financing point of view Thilo Kusch 24 April, 2008 Page 10