* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Telecommunication
Survey
Document related concepts
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Computer security wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Net neutrality law wikipedia , lookup
Recursive InterNetwork Architecture (RINA) wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Zero-configuration networking wikipedia , lookup
Network tap wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
List of wireless community networks by region wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
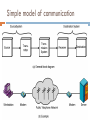
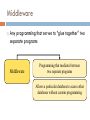
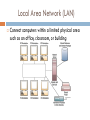
CHAPTER 6 Telecommunications and Networks Learning Objectives 1. 2. 3. 4. Understand the concept of a network. Apply Metcalfe’s law in understanding the value of a network. Identify several major developments and trends in the industries, technologies, and business applications of telecommunications and Internet technologies. Provide examples of the business value of Internet, intranet, and extranet applications. Learning Objectives 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Identify the basic components, functions, and types of telecommunications networks used in business. Explain the functions of major components of telecommunications network hardware, software, media, and services. Explain the concept of client/server networking. Understand the two forms of peer-to-peer networking. Explain the difference between digital and analog signals. Learning Objectives 10. 11. 12. 13. Identify the various transmission media and topologies used in telecommunications networks. Understand the fundamentals of wireless network technologies. Explain the concepts behind TCP/IP. Understand the seven layers of the OSI network model. Network Concept Network: A connected system of objects or people Computer network: A collection of computers and other hardware devices connected together so users can share hardware, software, and data, and electronically communicate Networks range from small private networks to the Internet (largest network in the world) Network Concepts Number of possible connections on a network is N * (N-1) Where N = number of nodes (points of connections on the network) Example, if there are 10 computers on a network, there are 10 * 9 = 90 possible connections Bob Metcalfe’s Law The usefulness (value) of a network equals the square of the number of users If there are only 2 users on the network, it’s not very useful; if there are 200 it’s much more useful. So the Internet with millions of computers is incredibly useful. Telecommunications Telecommunications Exchange of information in any form (voice, data, text, images, audio, video) over networks Telecommunications When we communicate, we are sharing information. This sharing can be local or remote. Local ( usually occurs face to face) or remote ( take place over distance) Data Communications The movement of computer information from one point to another by means of electrical or optical transmission systems. Such systems are often called data communications networks. Telecommunication (which Includes telephony, telegraphy and television ) (tele is Greek for "far“) means communication at a distance Exchange of information in any form (voice, data, text, images, audio, video) over networks Components of data communication 1. Message: data text, number, audio … 2. Sender: device that sends the data – computer, telephone, camera 3. Receiver: device that receives the data – computer, telephone, camera 4. Transmission medium: physical path by which message travels. 5. Rules or Protocols: Set of rules that govern data communications/ an agreement between the communicating devices components of data communication Simple model of communication Simple model of Communication The key elements of this model are: Source generates data to be transmitted Transmitter converts data into transmittable signals Transmission System carries data from source to destination Receiver converts received signal into data Destination takes incoming data Open Systems Information systems that use common standards for hardware, software, applications and networks Open systems provide: Connectivity: Ability of networked computers to easily access and communicate with each other and share information Interoperability: The ability of an open system to enable end user applications to be accomplished using different varieties of computer systems, software packages, and databases provided by a variety of interconnected networks Middleware Any programming that serves to “glue together” two separate programs Middleware Programming that mediates between two separate programs Allows a particular database to access other databases without custom programming Data Transmission Characteristics There are two fundamentally different types of data: Digital data – Computer produced signals that are binary, either on or off. Digital data have discrete states and take discrete values. Analog – Electrical signals which are shaped like the sound waves they transfer. Analog data are continuous and take continuous values 15 Data Transmission Characteristics Signals: Electric representations of information. Can be Analog or Digital An analog signal refers to something that is continuous- a type of signal represented by continuous waves. Analog signals can have an infinite number of values in a range A digital signal refers to something that is discrete –a type of signal where data represented by 0s and 1s digital signals can have only a limited number of values. Transmission can also be Analog or Digital Analog transmission system: continuous signals Digital transmission system: discrete signals 16 encoder/decoder modulator/demodulator Digital Network Technologies Rapid change from analog to digital network technologies Analog: voice-oriented transmission, sound waves Digital: discrete pulse transmission Digital allows: Higher transmission speed Larger amounts of information Lower error rates … Internet2 Next generation of the Internet High-performance network In use at 200 universities, scientific institutions, communications corporations Internet2 may never replace the Internet. May remain a scientific and government network. Business Value of Telecommunication Networks The Internet Over 46 million servers (2004) 710 – 945 million users (2004) No central computer system No governing body No one owns it Internet Service Provider ISP A company that specializes in providing easy access to the Internet For a monthly fee, you get software, user name, password and access ISPs are connect to one another through network access points Popular uses of the Internet An Intranet A network inside an organization That uses Internet technologies (such as Web browsers and servers, TCP/IP protocols, HTML, etc.) To provide an Internet-like environment within the organization For information sharing, communications, collaboration and support of business processes Can be accessed by authorized users through the Internet Enterprise Information Portal Intranets provide an enterprise information portal. Extranet Network links that use Internet technologies To connect the Intranet of a business With the Intranets of its customers, suppliers or other business partners Intranet that is at least partially accessible to authorized outsiders Types of Communications Networks Wide Area Local Area Communication Networks Peer-to-Peer Virtual Private Client/Server Wide Area Network (WAN) Telecommunications network that covers a large geographic area Source: Courtesy of Cisco Systems Inc. Local Area Network (LAN) Connect computers within a limited physical area such as an office, classroom, or building Virtual Private Networks (VPN) A secure network that uses the Internet as its backbone but relies on firewalls, encryption and other security A pipe traveling through the Internet VPN Client/Server networks Clients: End user personal computers or networked computers Interconnected by LANs Servers: manage networks Processing shared between clients and servers Network Computing Thin client means that very little processing is done on the client. Most the processing is done on the server. Three-tier model includes thin clients, application servers and database servers Two tiered client server includes just client and server Peer-to-Peer Networks Central Server Architecture P2P file-sharing software connects all PCs to a central server that contains a directory of all online users The server sends the requesting PC a list of links to all active peers who have the file Clicking a link connects the two PCs and automatically transfers the file to the requesting PC Peer-to-Peer Networks Pure Peer-to-Peer Architecture No central directory or server File-sharing software connects one PC to another online user When you request a file, the software searches every online user, then sends you a list of active file names Clicking a link automatically transfers the file from that user’s hard drive to yours Peer-to-Peer Network Diagrams Telecommunications Media Source: Phil Degginger/Getty Images. Wireless Technologies microwave Earthbound microwave systems that transmit high-speed radio signals in a line-of-sight path Between relay systems spaced approximately 30-miles apart Communications satellites Satellite serves as relay stations for communications signals Uses microwave radio signals Wireless Technologies Cellular and PCS telephone and pager systems Divide the geographic area into small areas or cells Each cell has transmitter or radio relay antenna to send message from one cell to another Wireless LANs Radio signals within an office or building Connect PCs to networks Bluetooth Short-range wireless technology To connect PC to peripherals such as printer Wireless Web Connect portable communications devices to the Internet Telecommunications Processors Modems Convert digital signals from a computer into Analog frequencies that can be transmitted over ordinary telephone lines Comparing modem and other technologies Internetwork Processors Switch – makes connections between telecommunications circuits in a network Router – intelligent communications processor that interconnects networks based on different protocols Hub – a port switching communications processor Gateway – connects networks using different communications architectures Telecommunications Processors Multiplexer… allows a single communications channel to carry simultaneous data transmissions from many terminals Telecommunications Software Used by servers and other computers to manage network performance Network Operating Systems Middleware Network management functions Traffic Management – manage network resources and traffic to avoid congestion and optimize service levels to users Security – provide authentication, encryption, firewall, auditing and enforcement Network Monitoring – troubleshoot and watch over the network, informing network administrators of potential problems before they occur Capacity Planning – survey network resources and traffic patterns and users’ needs to determine how best to accommodate the needs of the network as it grows and changes Network Topologies Topology: structure of a network Star: ties end user computers to a central computer Ring: ties local computer processors together in a ring on a relatively equal basis Bus: local processors share the same communications channel Network Topologies OSI & TCP/IP Models Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) Model A seven-layer model that serves as a standard model for network architectures Model for how messages should be transmitted between two points in a network Each layer adds functions Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) A five layer telecommunications protocol used by the Internet OSI & TCP/IP Models Internet Telephony Using an Internet connection to pass voice data using IP Voice over IP (VoIP) Skips standard long-distance phone charges Bandwidth Bandwidth Frequency range of a telecommunications channel Determines transmission rate Classified in bits per second (bps) Transmission Rates: Narrow-band – low-speed Broadband – high-speed Transmission Speeds Switching Alternatives Circuit Switching Switch opens a circuit to establish a link between a sender and receiver it remains open until the communication session is completed Packet Switching Break messages into groups called packets Transmit packets separately