* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 11
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Chemical potential wikipedia , lookup
Chemistry: A Volatile History wikipedia , lookup
Supramolecular catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Chemical plant wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Photoredox catalysis wikipedia , lookup
California Green Chemistry Initiative wikipedia , lookup
Debye–Hückel equation wikipedia , lookup
Spinodal decomposition wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical industry wikipedia , lookup
Organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals wikipedia , lookup
Process chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Determination of equilibrium constants wikipedia , lookup
Inorganic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Safety data sheet wikipedia , lookup
Double layer forces wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen-bond catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Bioorthogonal chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Rate equation wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Click chemistry wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
VX (nerve agent) wikipedia , lookup
Lewis acid catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Chemical reaction wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
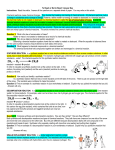
Chapter 11 Chemical Reactions Chapter 11 Section 1 Describing chemical reactions Chemical equations ►A chemical reaction is one or more substances changing to one or more new substances ► The starting substances are called reactants ► The ending substances are called products ► Reactants Products Writing Equations ► Any chemical reaction will have the reactants to the left of the arrow separated by plus signs and the products to the right of the arrow separated by plus signs. ► Word equation- elements or compounds are represented by words Example – Iron + oxygen Iron(III)oxide Chemical equation ► Written the same way, but elements and compounds are represented by symbols and formulas. Example – Fe + O2 Fe2O3 ► Skeleton equation- does not include the relative amounts of the reactants and products. Catalyst ► Speeds up a chemical reaction but is not used up in the reaction. ► Catalysts are neither reactants or products. ► The formula for the catalyst may be written above the arrow in a chemical equation. Balancing equations ► In a chemical equation, each side of the equation must have the same number of atoms of each element. ► Equations are balanced by placing coefficients to the left of the formulas. Example Balanced Fe + O2 Fe2O3 Not balanced 4Fe + 3O2 2Fe2O3 Chapter 11 Section 2 Types of Chemical Reactions Classifying Reactions ► There are five general types of reactions Combination Decomposition Single replacement Double replacement Combustion Combination reactions ► Two or more substances react to form one new substance. ► A + B AB ► The final product will always be a single compound. Decomposition Reaction ►A single compound breaks down into two or more simpler products. ► AB A + B ► Decomposition reactions will always start with a single reactant. Most require energy. ► These are the opposite of combination reactions. Single replacement reaction ► One element replaces a second element in a compound. ► A +BC AC + B ► Both the reactants and the products will contain one element and one compound. ► A metal can only be replaced by a metal that is more reactive than the original. Double replacement reaction ► An exchange of positive ions between two compounds. ► AB + CD CB + AD ► These reactions often take place in aqueous solutions (dissolved in water). Combustion Reaction ► An element or compound reacts with oxygen producing energy. ► CH4 + O2 CO2 + H2O ► Mg + O2 MgO Predicting Reactions ► Combustion contain O2 in reactants. ► Combination combines two to form one ► Decomposition breaks one into two ► Single replacement has one compound and one element on both sides of the equation. ► Double replacement involves two compounds on both sides of the equation. Chapter 11 Section 3 Reactions in Aqueous Solution Net Ionic Equations ► Complete ionic equation- an equation that shows dissolved ionic compounds as dissociated free ions. ► Net Ionic- an equation for a reaction in solution that shows only those particles that are directly involved in the chemical change. ► Spectator ion- An ion that appears on both sides of an equation and is not directly involved in the reaction. Complete ionic equation ► Aqueous silver chloride reacts with aqueous sodium bromide to produce aqueous silver bromide and solid sodium chloride. ► Chemical equation► AgCl(aq) + NaBr(aq) AgBr(aq)+ NaCl(s) ► Complete ionic equation ► Ag+ + Cl- + Na+ + Br- Ag+ ► Net ionic equation ► Na+(aq) + Cl-(aq) NaCl(s) + Br- + NaCl(s)