* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Cold War
Survey
Document related concepts
1948 Czechoslovak coup d'état wikipedia , lookup
War in Vietnam (1954–59) wikipedia , lookup
South Vietnam wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Cuba–Soviet Union relations wikipedia , lookup
Culture during the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
Role of the United States in the Vietnam War wikipedia , lookup
North Vietnam wikipedia , lookup
Operation Anadyr wikipedia , lookup
Sino-Vietnamese War wikipedia , lookup
Cold War (1947–1953) wikipedia , lookup
Domino theory wikipedia , lookup
Cold War (1953–1962) wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
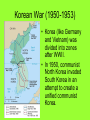
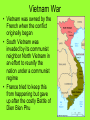
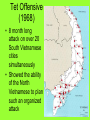
The Cold War Intense competition of nations after WWII WWII Aftermath • Germany (and its capital Berlin) were divided into four occupational zones dominated by four Allied powers. • When Germany was to be reunified, the Soviet Union (Russia) refused to give up its German zones. • This began a four decade long period of intense competition between the U.S. and the Soviet Union that involved many other nations who allied with one of the two superpowers (called the Cold War). Marshall Plan (1947-1951) • AKA – The European Recovery Program • America’s main program for rebuilding Western Europe after WWII to keep the area from falling to communism • European nations were asked how much money they needed to rebuild and the U.S. spent $13 billion for economic and technical assistance for these nearly destroyed democratic nations • The Soviet Union was offered the same aid if they made political reforms but they refused Containment • The policy of the U.S. of preventing the spread of communism to new areas was called containment. It dominated U.S. foreign policy during the Cold War. Communism U.S. Containment - Keeping the lid on Communism • NATO – permanent alliance formed by the United States and many noncommunist European nations to prevent a communist take-over in member nations • The world domination goal of Soviets were viewed as a threat to American security • The Soviet Union began the Warsaw Pact (an alliance of communist nations) Truman Doctrine (1947) • Stated the U.S. would supply any nation with economic and military aid to prevent its fall to communism • It was a direct threat to the Soviet Union Building Cold War Walls • Berlin Wall • Containment • 38th Parallel in Korea Cold War conflicts occurred when these walls were breached. McCarthyism Senator Joseph McCarthy • The Chinese Revolution and the Korean War increased American fears of the spread of communism in the early 1950’s. • A revived “Red Scare” emerged led by Sen. Joseph McCarthy who claimed that the U.S. government and military was full of communists. • The civil rights of those who were communist, those who were believed to be communists, and those who supposedly knew communists were violated. HUAC • Special House Committee on Un-American Activities that investigated the film and entertainment industries for Communist supporters or spies to be placed on blacklists • Investigated the State Department member Alger Hiss as a communist spy but failed to prove his guilt – sentenced to 5 years in prison for perjury Alger Hiss before HUAC Korean War (1950-1953) • Korea (like Germany and Vietnam) was divided into zones after WWII. • In 1950, communist North Korea invaded South Korea in an attempt to create a unified communist Korea. • North Korea was aided by the new communist superpower, China. • The U.S. was bound by our containment policy to assist South Korea to prevent the spread of communism. • The U.S. troops drove the North Koreans back across the border (38th parallel). • Gen. Douglas MacArthur then attempted (without Pres. Truman’s consent) to drive the communists completely out of Korea into China. • When the American troops approached the Chinese border, the Chinese attacked forcing the U.S. to retreat back to the 38th parallel which still remains the border between North and South Korea. • Gen. MacArthur was fired by Truman for not following his orders. Cuba’s Role in the Cold War • Fidel Castro – led the Cuban Revolution and became the Prime Minister in 1957 with American support • The U.S. turned against Castro when he allied Cuba with the Soviet Union, suspended all elections, and named himself president for life Bay of Pigs Invasion (1961) • 1,500 Cuban exiles were armed and trained by the CIA to invade Cuba at the Bay of Pigs and remove Castro from power • The invasion was leaked to Castro and the invasion was crushed • President Kennedy refused to involve U.S. troops to help them • 1200 were captured and the U.S. had to give $53 million in food and supplies to Cuba for their release • Soviets became bold when Cuban Missile they were convinced that Kennedy would not engage Crisis U.S. troops in Cuba after the Bay of Pigs invasion • Soviets began to install nuclear missile bases in Cuba aimed at targets in the U.S. claiming they would be used if another American invasion occurred • U.S. spy planes took photos of the missile sites and President Kennedy immediately responded • U.S. naval forces completely surrounded Cuba and demanded that the missiles be removed by the Soviet Union or there would be another massive invasion (by U.S. forces this time) • After a tense thirteen day standoff, the Soviet Union finally agreed to remove the nuclear missiles in Cuba if the U.S. removed their missile sites in Turkey aimed at the U.S.S.R. • Both nations removed their threatening missile bases Sputnik I • Americans feared the Soviets might use rockets to launch nuclear weapons from space • The Soviet Union launched the first artificial satellite (Sputnik I) into space in 1957 • This started the “space race” of the Cold War period • Americans feared we had fallen behind the Soviets in science and technology • Federal funds for education (especially math and science) were increased as well as national military defense programs Vietnam War • Vietnam was owned by the French when the conflict originally began • South Vietnam was invaded by its communist neighbor North Vietnam in an effort to reunify the nation under a communist regime • France tried to keep this from happening but gave up after the costly Battle of Dien Bien Phu • In the 1950’s, the U.S. (because of our containment policy) decided to send military advisors and economic aid to the South Vietnamese forces • In the early 1960’s, President Lyndon Johnson reported the Tonkin Gulf Incident to the Congress and asked them for permission to actually fight in the war • Congress allowed more involvement in the war with the Tonkin Gulf Resolution • South Vietnam and the U.S. fought North Vietnamese troops and the Viet Cong for nearly a decade • The U.S. troops had a difficult time in this war because it was difficult to identify the enemy and fight in the dense tropical rainforests • Domino Theory – the belief that if one nation in an area fell to Communism the others would fall as well (The fall of Vietnam could lead to the rest of Southeast Asia becoming communist) Tet Offensive (1968) • 8 month long attack on over 20 South Vietnamese cities simultaneously • Showed the ability of the North Vietnamese to plan such an organized attack Tet Offensive (cont’d.) • It was the largest and most damaging attack of the war; it ultimately failed • Many people began to question Pres. Johnson’s speeches claiming our victory in the war was near Anti-War Movement • After the Tet Offensive, many Americans began to openly protest the Vietnam War • College campuses were particularly known for forming groups to protest the war • Most anti-war groups favored… – ending the military draft – removing all American troops from Vietnam Anti-Vietnam War Movement • Used many of the same tactics as Civil Rights groups including sit-ins, marches, and public demonstrations • Later protesters became more radical, burning their draft cards, going to prison rather than Vietnam, and even fleeing to Canada Ending Vietnam • In the election of 1968, Richard Nixon promised vaguely to end the Vietnam War which helped him to win the presidency • Vietnamization – Nixon’s plan to remove U.S. troops from the war respectably (“Peace with honor”); called for the gradual withdrawal of troops as South Vietnamese troops were trained to take over their combat roles South Vietnam’s Defeat • March, 1975 – North Vietnam launched a massive invasion of South Vietnam • South Vietnam appealed to the U.S. for help and they received only economic aid (no troops) • April 30, 1975 – Saigon (capital of South Vietnam) was captured to end the war • Vietnam was reunified as a communist nation