* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch-25-Lessons-One-and-Two
Clostridium difficile infection wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Chagas disease wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
Microbicides for sexually transmitted diseases wikipedia , lookup
Ebola virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Human papillomavirus infection wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Multiple sclerosis wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
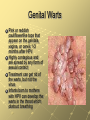
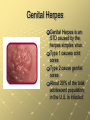
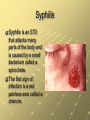
Sexually Transmitted Infections and HIV/AIDS Chapter 25 Lessons One and Two Common STI’s and Risks Pgs 648-56 STIs and STDs STIs and STDs are infectious diseases spread through sexual contact STI is the abbreviation for sexually transmitted infection STD is the abbreviation for sexually transmitted disease A person can have an infection and pass it to others without necessarily having the disease The Hidden Epidemic Epidemics are occurrences of diseases in which many people in the same place at the same time are affected STDs are the most common communicable diseases in the U.S. 65 million people in the U.S. are living with an incurable STD The Hidden Epidemic Many people with STDs are asyptomatic or without symptoms. They infect others unknowingly Even when STDs are diagnosed, they may not be reported to health departments to notify people High Risk Behavior and STDs Teens make up 25% of new STD cases each year Being sexually active with more than one person Having unprotected sex Selecting high-risk partners Using alcohol and other drugs The Consequences of STDs Some STDs are incurable and can remain in the body for life Some STDs cause cancer (liver cancer or cervical cancer) Some STDs can affect the ability to reproduce by damaging reproductive organs Some STDs can be passed from an infected female to her child before, during, or after birth The Importance and Benefits of Abstinence Cause and Effect: Sexual activity is the cause and an STD is the effect Abstinence is the deliberate decision to avoid harmful behaviors including sexual activity before marriage Use refusal skills and choose friends who also support abstinence Human Papillomavirus (HPV) HPV can cause genital warts or asymptomatic infection It is the most common STD in the U.S. CDC estimates that 5075% of sexually active people will acquire HPV sometime in their lives There is no treatment HPV can cause cancer of the cervix, penis, and anus Genital Warts Pink or reddish cauliflowerlike tops that appear on the genitals, vagina, or cervix 1-3 months after HPV Highly contagious and are spread by any form of sexual contact Treatment can get rid of the warts, but not the virus Infants born to mothers with HPV can develop the warts in the throat which obstruct breathing Chlamydia Chlamydia is a bacterial infection that affects the reproductive organs 40% of cases are reported in teens 15 to 19 years old Chlamydia There are no visible symptoms in 75% of females and 50% of males When symptoms are present, males may experience a discharge from the penis or burning during urination. Females may have vaginal discharge, burning during urination, or abdominal pain Chlamydia Chlamydia is diagnosed by lab examination of secretions from the cervix in females and from the urethra in males It can be treated with antibiotics but a person can be infected again Chlamydia often goes unnoticed until serious complications occur such as pelvic inflammatory disease in females and infertility in both genders Infants born to infected mothers may develop eye disease or pneumonia and are often born prematurely Genital Herpes Genital Herpes is an STD caused by the herpes simplex virus Type 1 causes cold sores Type 2 cause genital sores About 20% of the total adolescent population in the U.S. is infected Genital Herpes Most individuals are asymptomatic Typical symptoms are blisterlike sores in the genital area The virus can be spread with or without visible symptoms Medication relieves the symptoms but can’t cure the virus People with herpes are more capable of transmitting or acquiring HIV Gonorrhea “The Clap” Gonorrhea is a bacterial STD that affects mucous membranes Highest rates found in females 15-19 years old and males 20-24 years old Symptoms in males = discharge from the penis and painful urination 50% of females have no symptoms. Some have vaginal discharge and painful urination Gonorrhea Gonorrhea can be treated with antibiotics but people can be reinfected if exposed If untreated, gonorrhea can lead to infertility in both genders The bacteria can spread to the bloodstream and cause permanent joint damage Females can pass it to their babies and babies can be contract eye infection leading to blindness Trichomoniasis Trichomoniasis is an STD caused by a microscopic protozoan that results in infections of the vagina, urethra, and bladder. Females may have no symptoms but the disease may result in vaginitis: an inflammation of the vagina characterized by discharge, odor, irritation, and itching Males usually show no symptoms but may have itching or discharge and burning after urination Syphilis Syphilis is an STD that attacks many parts of the body and is caused by a small bacterium called a spirochete. The first sign of infection is a red painless sore called a chancre. Syphilis A chancre will heal on its own, but left untreated it can spread through the blood to other body parts Eventually it can damage internal organs like the heart, liver, nervous system, and kidneys A person is at risk for paralysis, convulsions, blindness, and heart disease. An infant infected with syphilis can have a damaged nervous system and die Treatment Prevention is every individual’s responsibility Embarrassment should not keep a person from getting medical treatment Only a professional can prescribe the correct treatment Personal information is kept confidential although an infected person should notify all sexual partners (current and past)