* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Dependency Theory
Survey
Document related concepts
Inclusive Democracy wikipedia , lookup
Pensions crisis wikipedia , lookup
Participatory economics wikipedia , lookup
Welfare capitalism wikipedia , lookup
Economics of fascism wikipedia , lookup
Ragnar Nurkse's balanced growth theory wikipedia , lookup
Marx's theory of history wikipedia , lookup
Rostow's stages of growth wikipedia , lookup
Production for use wikipedia , lookup
Post–World War II economic expansion wikipedia , lookup
Economic democracy wikipedia , lookup
State capitalism wikipedia , lookup
Perspectives on capitalism by school of thought wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
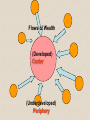
Dependency Theory Towards a Critique of Developmentalist: Dependency Theory 1960s-- United Nations Economic Commission for Latin America. Main Authors: Fernando H. Cardoso, Faletto, Theotonio Dos Santos. Main Thesis: Underdevelopment is not the product of the persistence of “traditional” society; instead, it is generated by the particular fashion the expansion of capitalism assumes in the “periphery.” Developmentalist approaches are wrong. The expansion of the market does not necessarily produce either modernization or development. On the contrary, capitalism makes societies look like “feudal” in the periphery. Development and underdevelopment constitute the two sides of the same coin: capitalism. The periphery is underdeveloped because of the development of the center. Flows of Wealth (Developed) Center (Underdeveloped) Periphery Unequal and Combined Development: The play between Center and Periphery reproduces in all scales (fractal structure) Center Periphery Center-Periphery Center-Periphery Center-Periphery-Center-Periphery Center-Periphery Center-Periphery Sovereign States Center (Ex: England, the U.S.) Elites DEPENDENT DEVELOPMENT The State and the Nation split apart (capitalist) (popular) Nonsovereign States WORLD MARKET CENTER PERIPHERY SOCIAL EXCLUSION (POVERTY) Against Rostow, Huntington, Moore, and... Marx, Cardoso and Faletto argue that... Modernization, Industrialization, Urbanization, to Development do not lead in the periphery. Instead, they foster Underdevelopment, a “caricature” of the central societies. For theorists of dependency, such as Cardoso and Faletto... In the periphery, the development of capitalism leads to... • Dependent and unequal development (distorted, uneven, and pathological form of modernization). • Increasing dependency. Politically... • (economic and social • (economic and social integration fosters) exclusion fosters) Democracies, extended Dictatorships (or Formal citizenship, and the Democracies), State rule of law, which violence, limited PREVAIL in the Center citizenship, and the Free market + Democracy (un)rule of law, which PREVAIL in the Periphery. Alliance: the State + Corporations Free market + Repression Cardoso & Faletto: • “The same fundamental alliance which constitutes a dependent industrial capitalist state may organize itself institutionally within a context of authoritarianism, restricted democracy, or totalitarianism.” SOLUTION: BREAK UP THE BONDS OF DEPENDENCY Since Dependency = Capitalism, Breaking with dependency= Socialism Cardoso & Faletto identify three main strategies to break the dependency bonds (target: the State) 1. Guerrilla movements organized against military dictatorships (ex: Argentina 19691975) 2. The Democratic Path: Salvador Allende’s government (1970-1973) 3. Military Reformism (ex: Perú) Importance of politics. C & F: “the political struggle revolving around the state shows what is essential in this form of dependency: the style of development of the possibility of alternatives depends upon the resolution of this question of the state.” South East Asia... • The explosive economic growth in South East Asia at the beginning of the 1980s was considered by most scholars the demise of the dependency theory. – Argument: the dependency theory cannot explain such a process of growth. Wallerstein – The World-System • Our concepts and the units of analysis we choose do not allow us to understand the real organization of the world. • Problem: the developmentalist perspective consecrates the nation state as the main unit of analysis. Instead, from a holistic perspective... • The notion of “mode of production” appears as central. – (def.) “the way in which decisions are made about dividing up productive tasks, about quantities of goods to be produced and labour-time to be invested, about quantitites of goods to be consumed or accumulated, about the distribution of the goods produced.” (345) Modes of Production • “Reciprocal-lineage.” • “World-systems” – “World-Empire” – -“World-Economy” “Reciprocal-lineage.” • Limited and elementary specialization of tasks and forms of exchange. Based on human labor. Limited growth. Minisystems, short-lived (6 generations). “World-systems”1: “World-Empire.” – Based upon agriculture. Surplus allows to maintain artisans and an “administrative” class. Extra-economic foundation (tribute, force, the power of the sword). Technological advance is not desirable per se. Everthing is “fixed” in the system. Political unity of the economy • Interest of the powerful on the survival of the subjected sectors. “World-systems”2: “World-Economy.” Single division of labor within a system which “has no overarching political structure.” World-market, multiplicity of nationstates. Capitalism. No limits to profit. Starvation may be necessary for profit. Appearance of “the poor.” Markets became dominant in the “World-Economy” • System economically unified and politically fragmented (World-market + Nation-States). • Different nation-states cushion and reinforce the effects of the market. • Importance of the role of the State... Critical and “dependencista” approaches lead towards... • An increasing focus on the role of the State. • Lane: “Bringing the State Back In.”