* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Post WWII Europe
Survey
Document related concepts
Cold War (1962–1979) wikipedia , lookup
1948 Czechoslovak coup d'état wikipedia , lookup
Berlin Blockade wikipedia , lookup
West Germany wikipedia , lookup
Western betrayal wikipedia , lookup
Eastern Bloc media and propaganda wikipedia , lookup
Czechoslovak Socialist Republic wikipedia , lookup
Origins of the Cold War wikipedia , lookup
East Germany wikipedia , lookup
Berlin Crisis of 1961 wikipedia , lookup
Iron Curtain wikipedia , lookup
Containment wikipedia , lookup
Aftermath of World War II wikipedia , lookup
Consequences of Nazism wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
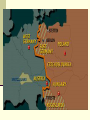
Post WWII Europe Potsdam Conference-Summer 1945 Temporarily divide Germany into 4 zones Divide Berlin Rid Germany of any remnants of Nazi party Reparations Soviets would receive largest share Soviets wanted a buffer zone of friendly governments in Eastern Europe Iron Curtain https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=S2PUI QpAEAQ From Stettin in the Baltic to Trieste in the Adriatic, an iron curtain has descended across the continent. Behind that line lie all the capitals of the ancient states of Central and Eastern Europe. Warsaw, Berlin, Prague, Vienna, Budapest, Belgrade, Bucharest and Sofia, all these famous cities and the populations around them lie in what I must call the Soviet sphere, and all are subject in one form or another, not only to Soviet influence but to a very high and, in some cases, increasing measure of control from Moscow. Athens alone Greece with its immortal glories is free to decide its future at an election under British, American and French observation. - Winston Churchill (3/1946) Germany post WWII Origins of Cold War Define?? Ideological Conflict War is out of the question in 1945 Proxy wars Put me Into Chronological Order BERLIN BLOCKADE/AIRLIFT MARSHALL PLAN POTSDAM Formation of Federal Republic of Germany WARSAW PACT TRUMAN DOCTRINE NATO Formation of German Democratic Republic RESPONSES Potsdam (7/45) TRUMAN DOCTRINE (3/1947) MARSHALL PLAN (1947) BERLIN BLOCKADE/AIRLIFT (June 1948May 1949) Formation of Federal Republic of Germany (WG) (1949) Formation of German Democratic Republic (EG) (1949) NATO (1949) WARSAW PACT (1955) U.N…..Implications…? FRG vs. GDR After Berlin Blockade is over In August 1949 the three Western zones joined together to form the FRG (Federal Republic of Germany). In response, the Soviet zone became the German Democratic Republic (GDR). Hot Spots With the creation of the Truman Doctrine and the Policy of Containment…the stage was set for points of Conflict Korean WAR-Hot Spot Clash between Communist North Korean and Democratic South Korea… USSR supports North, US supports South 1950-1953 Stalemate-North Korea remained communist South Korea-ally of the west CAUSES • Disagreements between the Allies during World War II • Differing U.S. and Soviet political and economic systems • Differing goals for postwar Germany and Eastern Europe • Soviet expansion of communism in Eastern Europe • Resistance to Soviet aggression by United States EFFECTS • Political and military struggles around the world • Increased military spending, leading to an arms race • The ever-present danger of nuclear war