* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Venture_Capital_ENG_
Survey
Document related concepts
Individual Savings Account wikipedia , lookup
Syndicated loan wikipedia , lookup
Private equity wikipedia , lookup
Present value wikipedia , lookup
Fundraising wikipedia , lookup
Money supply wikipedia , lookup
Private equity secondary market wikipedia , lookup
Public finance wikipedia , lookup
Stock valuation wikipedia , lookup
Investment management wikipedia , lookup
Private equity in the 1980s wikipedia , lookup
Land banking wikipedia , lookup
Venture capital wikipedia , lookup
Stock selection criterion wikipedia , lookup
Global saving glut wikipedia , lookup
Investment fund wikipedia , lookup
Internal rate of return wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
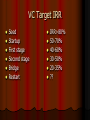
Venture Capital Is It For You? Is Your Venture Ready? by Barry G. Bisson P.Eng (NB) 3 Principles of Sound Finance The business is adequately capitalized The capital structure of the business has an appropriate mix of debt and equity The financing need is addressed with the appropriate type of financing “Money is Time” The source of funds for your business is money from customers, ie. SALES! The best “outsider” money for your business is “smart money” Consider “Bootstrapping” Options Convert “fixed costs” (incurred whether or not a sale is made) to “variable costs” (incurred only when a sale is made) Outsourcing – reduce capital needs Universities – expertise, pro bono work Suppliers – terms, loans, leads, etc. Factors – advance money, reduce collection risk Consider “Bootstrapping” Options Public relations – free advertising, eg. Obama and his Blackberry Government – loans, grants, tax incentives Incubators – lower start-up costs Barter Testing – before entering a large market, gain insights Licensing Consider “Bootstrapping” Options Per Inquiry Ads - pay % of sales generated by ad Pricing – get it right, don’t leave precious cash on the table Staging – try to leave as many options open as possible, try to defer investments if possible Mentors free advice from experienced skilled people Consider “Bootstrapping” Options Relationship building – in every facet of your business Selling – persuading people to take a favorable action for all parties Be the CEO – “Chief Everything Officer” Conventional Financing Assets Inventory & receivables Land & buildings Equipment & vehicles Other Liabilities & Equities Operating line of credit Mortgage Term loan Share capital & retained earnings VC Financing Fills the cash gap between cash needs to finance high growth and cash available from earnings and conventional financing Giving up a piece of the pie to grow a bigger pie Capital Markets Playing Field Phase I Knowledge Acquisition Phase II Concept Investigation Basic Design Phase III Prototype Building Market Entry Manufacturing Ramp-up Government Programs Public Issues Commercial Banks Non-Financial Corporations Seed Funds Venture Capital Funds Wealthy Family Funds Private Investors Faminly and Friends Personal Savings 10 The Business Life Cycle Typical SME Growth Profiles 60 High-Growth Firm Sales ($ millions) 50 40 30 Moderate-Growth Firm 20 VC Prospects 10 Low-Growth Firm 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 Years 7 8 9 10 Magnitude of Investment Typically >$1.0 million for institutional Small deals too costly Typically less than $10 million in Canada Most deals $1.0-$3.0 Based on business plan pro formas Investment Time Horizon 4-7 years How long will it take to create value? Years to cash flow breakeven? “Money is time” The VC Life Cycle Submit business plan Preliminary assessment Meet the people Light due diligence Term sheet Heavy due diligence Investment memorandum Commitment letter Shareholder’s agreement Grow the company Exit in 4-7 years VC Investment Criteria Exponential growth potential Attractive industry Sustainable advantage platform Excellent team “execution” Owners receptive to involvement of outsiders Owners willing to share the wealth creation Credible exit alternatives (4-7 years out) Ingredients-The Value Proposition Why will/do our customers buy or product? Ease the Pain Improve Revenue/ Productivity/Profitability The Ingredients-The Business Model Implies having a well defined business model that says, “I know who my customers are, what they need, how I will meet their needs, how I will reach them, how I will service them, how I will continue to best my competition and how I will make money”. Revenue sources, cost drivers, critical success factors, investment requirements alll make sense Internal Rate of Return (IRR) VC Investments and IRR % Ownership Required VC Target IRR Seed Startup First stage Second stage Bridge Restart IRR>80% 50-70% 40-60% 30-50% 20-35% ?? “The Golden Rule” of Venture Capital “He who has the gold rules”