* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chromosomal abnormalities
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Comparative genomic hybridization wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Birth defect wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
DiGeorge syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Down syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
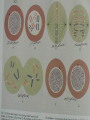
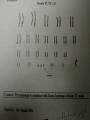
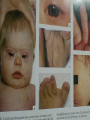
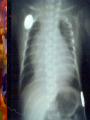
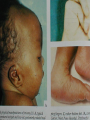
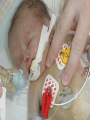
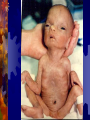
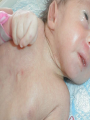
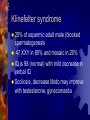
Developmental Chromosomal abnormalities Lecture 7 introduction Normal human cells contain 23 pairs of chromosomes This includes one pair of sex chromosome XX or XY During cell division we can identify chromosomes Lymphocytes incubated for 2-3 days or uncultured bone marrow in 4-24 hours continue Haploid: set of 23 chromosomes Diploid: normal number of 46 chromosomes Aneuploidy: less than an even multiple of 23 usually is 45 or 47 and rarely 48,49 Triploidy: 69 chromosomes Mosaicism Abnormal in deletion and translocation(balanced and unbalanced)Balanced Incidence The earlier the abortion the more likely to be chromosomal 50% of spontanous abortion are chromosomal abnormal Mostly triploidy. 45 XO, trisomy 16 98% of fetus with turner abort Generally 6/1000 the incidence of chromosomal abnormalities When to suspect it Unexplained infertility/ balanced translocation Multiple abortion >2 Prior case of defective baby When to suspect it…continue Presence of congenital anomalies 45% have minor single anomalies 9% 3 minor anomalies 1.5% HAVE major anomaly 2 or more major anomalies may represent genetic syndrome or chromosomal abnormalities(10%). Down Syndrome Incidence 1/700 2/3 of down fetus spontaneously abort Clinical diagnosis depend on gestalt Trisomy 21 in 94% of cases with extra chromosome from mother mostly(95%) Risk correlate with maternal age <25 y/o 1/1600 >40 y/0 1/80 2% are mosaic Other Clinical features Hypotonia without weakness Clinodactaly protruded tongue,small ears,brachycephaly,small up turned nose, depressed nasal bridge. Mental retardation, socially do better with good environment (Happy children) Clinical issues Cardiac and GI Hypothyriodism Transient leukemoid reaction Alzheimer’s disease up to 25% over 40 y/o Early death relate to cardiac dysfunction Trisomy 18 Incidence 1/8000 Overlaps with trisomy 13 Sever Mental retardation >90% dead in 1st year Trisomy 18 Small face with prominant occiput Small sternum and pelvis Flexion deformity of the finger VSD and horseshoe kidney triploidy Complete extra set of chromosomes Mostly miscarriages Fetal wastage skeleton more than cephalic, 2% survive to be recognized Large hydatidiform placenta VSD, ASD, Syndactaly Genital and CNS abnormalities Trisomy 13 Sever developmetal retardation Incidence 1/20000 90% dead in the 1st year Trisomy 13 Midline brain defect Malformed ear Microophalmos and coloboma Scalp defect Turner syndrome Most common abnormality in early abortion Female, short stature, primary amenorrhea, sterility, spares hair and underdeveloped breast Neonatal: wide spaced nipple, lymphedema , shield chest, Coarctation of the aorta Continue turner syndrome Normal IQ scale with difficulty in spatial orientation such as map Present with short stature or delay sex maturation Hormonal therapy continue Mosaisim (15%), remove gonads Recurrent risk is 1-2% Noonan syndrom AD, fresh mutation Pulmonary stenosis, nl stature, microceph, mental retardation Klinefelter syndrome 20% of aspermic adult male (blocked spermatogenesis 47 XXY in 80% and mosaic in 20% IQ is 98 (normal) with mild decrease in verbal IQ Scoliosis, decrease libido may improve with testesterone, gynecomastia Fragile X Syndrome Moderate to sever mental retardation Speech delay, short attention, hyperactivity Poor motor coordination and mouthing objects Poor socialization, temper tantrum Mood disorder (bipolar), schizophrenia Fragile X syndrome Long protruding ears Long face and prominent jaw Flattened nasal bridge High arch palate Macroorchidism Genetic is complex, 80% penetration in male and 30% penetration in female Genetic imprinting Means: as genomes pass through miosis it is normal for part of it to change. During miosis inactive X chromosome become active and changes on fragiloe X gene (imprinting) make it malignant Angelman syndrome Sever mental retardation Inappropriate laughter Decrease pigmentation of choroid or iris (pale blue eyes) Ataxia and jerky eye movement Sever speech proplem Deletion of b15q11q13, maternal in origin Paternal uniparental disomy Prader-willi syndrome (A fat red faced boy in state of somnolency) Charles Diickens Early hypotonia Obesity Short stature as adult Almond shaped blue eyes Mental retardation (mild to moderate) Narrow hands Chromosomal linked disorder Smith Lemli opitz syndrome CHARGE Low cholesterol High 7 dehydrocholesterol Like trsomy 18 Coloboma Heart Atresia of choanae Retarded Genitalia hypoplasia Ear anomalies VATER