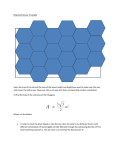
* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download View the Semester Catalog (DOCX 15.6KB)
Telecommunications engineering wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic compatibility wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Portable appliance testing wikipedia , lookup
Mechanical filter wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Anastasios Venetsanopoulos wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Mechanical-electrical analogies wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
London Electrical Engineers wikipedia , lookup
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Electrical wiring in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Electrical wiring wikipedia , lookup
Electrical engineering wikipedia , lookup
Electrical Technology (AS) The Electrical Technology program prepares students for ever increasing career opportunities within the electrical field. From the designing of construction projects in residential, commercial, and industrial areas to the completion of these projects, students experience all phases of an electrical project. A ten-hour OSHA certificate provides students with an understanding of job site safety. The Electrical Technology Associate Degree Program at BFIT fulfills the Massachusetts Board of State Examiners of Electrician’s academic requirements for Journeyman Electrician licensure by providing 600 hours of class room instruction in accordance with 237 CMR 13.06 and 22.01. Experienced personnel in the trades, as well as state regulators, such as the Board of Electricians and the Division of Apprentice Training, assures that the program is aggressive and ever-changing, with new methods and technology. In addition, our material is constantly updated to conform to the National Electrical Code, which changes every three years. Graduates of our program have many entry level career options in the electrical industry including a direct pathway toward obtaining a Journeyman Electrician license, electrical contractor, and electrical support positions such as estimator, product sales representative, and designer. Curriculum The curriculum is structured to provide educational hours in both the classroom and laboratory setting. Students are offered a broad range of courses in the electrical field. Some of these courses include: DC and AC Circuit Theory, electrical design and layout, electrical machinery, photovoltaics and renewable energy, and low voltage systems and controls. Laboratory projects accompany most classes. Facilities The Electrical Department has three laboratories, which are equipped to provide students ample and meaningful hands-on experience in the electrical field. The three labs provide students with the opportunity to learn the basics of wiring, as well as the proper methods of application to the many theoretical principles of motors, transformers, and renewable energies. Outcomes Upon successful completion of the Associate Degree in Electrical Technology, the graduate will be able to: Comprehend and utilize current Electrical Industry Standards, including the National Electrical Code (NFPA 70), Massachusetts Electrical Code (527 CMR 12.00), and Standards for Electrical Safety in the Workplace (NFPA 70E). Identify and install electrical devices and equipment, utilizing a variety of wiring methods and practicing safe work habits. Design, analyze and install various electrical circuits and diagrams related to residential, commercial, and industrial applications. Perform electrical calculations, including Ohm’s law, wire sizing, branch-circuit overcurrent protection sizing, voltage drop, and residential service entrance. Design, analyze, and troubleshoot motor circuits and motor controls. Understand the need for renewable energies and evaluate alternative energy technologies. Faculty Tracey Arvin, Chair Instructor Staff: Thomas DeCosta, Charles Palmieri, Christopher Villano Degree Requirements: Electrical Technology 66 Credits TECHNICAL COURSES: 45 CREDITS Course # Course Credits Lecture Lab BT115 ............ AutoCAD for Electrical Applications ................................... 3 .................... 1 .................... 4 EL110* .......... Circuit Theory I (DC) .......................................................... 4 .................... 3 .................... 2 EL127* .......... Design & Layout I/National Elec. Code I ............................ 5 .................... 4 .................... 2 EL129* .......... Design & Layout II/National Elec. Code II .......................... 5 .................... 4 .................... 2 EL213* ........... Circuit Theory II (AC) ......................................................... 4 .................... 3 .................... 2 EL214* .......... Low Voltage Systems & Controls ....................................... 4 .................... 4 .................... 0 EL222* .......... Design & Layout III/National Elec. Code III......................... 4 .................... 3 .................... 2 EL229* .......... Design & Layout IV/National Elec. Code IV ........................ 4 .................... 3 .................... 2 EL240* .......... Electrical Machinery I ......................................................... 4 .................... 3 .................... 2 EL241* .......... Electrical Machinery II ........................................................ 4 .................... 3 .................... 2 EL243* .......... Photovoltaics & Renewable Energy ................................... 4 .................... 2 .................... 3 * These courses count towards the academic hours required by the Massachusetts State Board of Electrical Examiners GENERAL STUDIES COURSES: 21 CREDITS Course # Course Credits Lecture Lab EN130 ............ College Composition I ........................................................ 3 .................... 3 .................... 0 EN140 ............ College Composition II ....................................................... 3 .................... 3 .................... 0 HU/SS ............ Elective .............................................................................. 3 .................... 3 .................... 0 HU/SS ............ Elective .............................................................................. 3 .................... 3 .................... 0 MA120 ........... College Algebra and Trigonometry ..................................... 3 ................... 3 ................... 0 MA130 .......... Pre-Calculus ...................................................................... 3 .................... 3 .................... 0 or MA270 .......... Statistics ............................................................................ 3 .................... 3 .................... 0 TS201 ............ Environmental Science ...................................................... 3 .................... 3 .................... 0 Typical Course Sequence for Electrical Technology SEMESTER 1 EL091 Success in Electrical Technology EL110 Circuit Theory I (DC) EL127 Design & Layout I/ NEC I EN130 College Composition I MA120 Algebra & Trigonometry SEMESTER 2 EL129 Design & Layout II/ NEC II EL213 Circuit Theory II (AC) EN140 College Composition II MA MA130 or MA270 SEMESTER 3 EL214 Low Voltage Sys & Controls EL222 Design & Layout III/ NEC III EL240 Electrical Machinery I HU/SS Elective TS201 Environmental Science SEMESTER 4 BT115 AutoCAD for Electrical Applications EL229 Design & Layout IV/NEC IV EL241 Electrical Machinery II EL243 Photovoltaics & Renewable Energy HU/SS Elective