* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Crusades - WordPress.com
Survey
Document related concepts
Church of the Holy Sepulchre wikipedia , lookup
Battle of Nicopolis wikipedia , lookup
Rhineland massacres wikipedia , lookup
Third Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Kingdom of Jerusalem wikipedia , lookup
Savoyard crusade wikipedia , lookup
Siege of Acre (1189–1191) wikipedia , lookup
Northern Crusades wikipedia , lookup
Albigensian Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Fourth Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Siege of Acre (1291) wikipedia , lookup
Despenser's Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Second Crusade wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
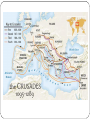
The Crusades Quick Overview of the RC Church The Roman Catholic Church was the main religion of Western Europe during the Medieval period The RC Church had its own hierarchy separate from that of the feudal system The RC Church influenced every aspect of daily life Government/Politics Education Morality Culture The Papacy The decision made by the RC Church impacted everyone in Medieval society - even the kings! The Pope was viewed as God’s representative on Earth If the Pope made a decision regarding anything, everyone had to follow it – not doing so could get you excommunicated Use of “spirituality” and “faith” as a means of political and economic gain Crusades The crusades were holy wars – endorsed by the Pope himself! Fought between European Christians and Middle Eastern Muslims Often advertised to Christians as “pilgrimages” to the Holy Land (Jerusalem). Pilgrimage: A journey to a geographical place with religious significance – search for spirituality The First Crusade started in 1095CE when Pope Urban II wanted access to Christian holy sites in the Middle East The First Crusade The First Crusade started in 1095CE when Pope Urban II wanted access to Christian holy sites in the Middle East Common people were so enthusiastic after the pope’s speech that they headed out towards Jerusalem without the military They believed that they would be protected by God and would not need weapons or have to do any fighting This group did not make it to Jerusalem and instead, attacked Jews in Germany When the actual Crusade army left, they headed toward Jerusalem and fought with the Fatimid Caliphate They were able to conquer the city The Fatimids underestimated the number of Crusaders coming and had their forces divided in another fight The First Crusade was successful European Christians set up small kingdoms along the coast for ease of travel. The Second Crusade After the success of the Europeans of the First Crusade, the Fatimid Caliphate counter attacked the conquered cities Could not take back Jerusalem, but took a nearby city, Edessa People in Europe were unhappy with the capture of a city by the Muslim Caliphate The pope called for another Crusade to take back the lost city France and Germany agreed to go Many soldiers died along the way The Crusaders attacked Damascus but were unsuccessful Third Crusade Muslim military leader Saladin was able to take over Jerusalem Christians in Europe were unhappy again Pope called for another Crusade England, France and Germany headed for Jerusalem King of Germany died along the way; his soldiers went home England captured Cyprus, but from a Christian ruler and made an enemy France got frustrated after laying siege to a Acre and went back France left England alone to attack Jerusalem England could not beat Saladin Saladin and England drafted a peace treaty that allowed access to Jerusalem and promise not to attack each other Fourth Crusade Pope, again, wanted access to Jerusalem and called for another Crusade Kings in Europe mostly ignored the call to Crusade France and England were at war with each other and did not want to go An army was raised and they set out for Jerusalem through ports in Italy Could not afford boats for all the men and equipment Agreed to attack a Byzantine controlled port city as payment Crusaders ended up attacking, conquering and looting Constantinople (the capital of the Byzantine Empire) The Pope was angry that the Crusaders attacked another Christian kingdom instead of Jerusalem Children’s Crusade After the 4th Crusade, two groups of children gathered supporters for another Crusade One boy in France was able to gather 30,000 other children to follow him on a Crusade against Jerusalem They did not get support from the French king or the Pope They got on boats to go to Jerusalem but were never seen again A second boy, from Germany, was about to gather supporters to go ask the Pope if they could go on a Crusade The Pope refused to support it because he was too young Why Jerusalem? Important holy site to the Western religions; Judaism, Christianity, Islam Jews – The place where Abraham tried to sacrifice his son Isaac Christians – where Jesus was crucified Muslims – location of the Dome of the Rock - Believed that the prophet Mohammed ascended to Heaven on that site Significance of the Crusades Exposed Europe to different culture, knowledge and technology An example of the Pope’s influence over people and kings An example of the importance of religion and holy sites in Medieval European culture Acted as a unifying cause for European kingdoms all came together as Christians to fight a common enemy Major conflict between two cultural and religious groups