* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Quiz No.2 ECE 48
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Sound level meter wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Galvanometer wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Peak programme meter wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
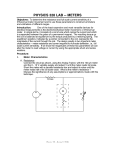
ECE48:INSTRUMENTATION 1 QUIZ No. 2 1. Describe briefly the principle of operation of d'Arsonval meter movement. 2. How can d'Arsonval meter be used to measure: a. Current b. Voltage c. Resistance 3. Calculate the voltage drop developed across d'Arsonval meter movement having an internal resistance of 600Ω and a full-scale deflection current of 100µA. 4. Find the resistance of multiplier required to convert a 200µA meter movement into a 0 to 150Vdc voltmeter, if Rm = 1kΩ. 5. Calculate the half-scale current of a meter movement that has a sensitivity of 20kΩ/V. 6. Calculate the value of resistors R1 through R5 in the circuit shown below. ECE48:INSTRUMENTATION 2 QUIZ No. 2 7. Calculate the value of resistors R1 through R3 in the circuit shown in the figure. 8. In the circuit of the figure shown, a voltmeter A having a sensitivity of 5kΩ/V is connected to points X and Y and indicates 15V on its 30-V range. A voltmeter B is then connected to points X and Y and indicates 16.13V on its 50-V range. a. Find the sensitivity of voltmeter B. b. If R = 40KΩ calculate the error due to voltmeter loading for both meters.