* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Advanced Algebra
Survey
Document related concepts
Elementary algebra wikipedia , lookup
Signal-flow graph wikipedia , lookup
History of algebra wikipedia , lookup
Quadratic equation wikipedia , lookup
Factorization of polynomials over finite fields wikipedia , lookup
Cubic function wikipedia , lookup
Quartic function wikipedia , lookup
System of polynomial equations wikipedia , lookup
Exponentiation wikipedia , lookup
Eisenstein's criterion wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
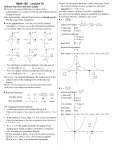
Advanced Algebra Final Formulas and Facts Name:________________________ nth Term of an Arithmetic Sequence for all positive integers n: Sum of the First n Terms of an Arithmetic Series for all positive integers n: tn t1 (n 1)d t t Sn n 1 n 2 nth Term of a Geometric Sequence Sum of the First n Terms of a Geometric Series 1 rn where r 1 Sn t1 1 r tn t1r n 1 where n > 1. logb mn logb m logb n If m, n, and b are positive real numbers and b 1. log b Factoring Sum of Two Cubes a 3 b3 a b a 2 ab b 2 Factoring Difference of Two Cubes a 3 b3 a b a 2 ab b 2 log b m p log b m p m log b m log b n n If m, n, and b are positive real numbers and b 1. If logb x logb y , then x = y log b b x x and blogb x x for x > 0 If b > 0 and b 1 Sum of an Infinite Geometric Series t where r 1 S 1 1 r If m and b are positive real numbers, and p is a real number log b x log a x log a b For any positive real numbers a x>0 Compound Interest r A(t ) P 1 n nt Continuously Compounding Formula: Simple Growth/Decay: A Pe rt A P(1 r )t Rational Root Theorem: Let P be a polynomial function with integer coefficients in standard form. If p is a root q of P ( x ) 0 , then p is a factor of the constant term of P and q is a factor of the leading coefficient of P. Vertical Asymptotes: If (x – a) is a factor of the denominator of a rational function, but not a factor of the numerator, then x = a is a vertical asymptote of the graph of the function. Standard Equation of a Parabola y k a x h 2 Complex Conjugate Root Theorem: If P is a polynomial function with realnumber coefficients and a + bi is a root of P ( x ) 0 , then a – bi is also a root of P ( x ) 0 . 1 , b 1, Horizontal Asymptotes: Let R( x) P be a Q rational function. P and Q are polynomials. - If the degree of P is less than the degree of Q, then y = 0 is the equation of the horizontal asymptote of the graph of R. - If the degree of P is equal to the degree of Q, and a and b are the leading coefficients of P and Q, respectively, then y a is the b Holes: If (x – b) is a factor of the numerator and denominator of a rational function, then there is a hole in the graph at x = b, unless there is a vertical asymptote at x = b. To find the y-value, substitute the x-value into the simplified version of the function. Standard form of the Equation of a Circle or x k a y h 2 b 1, ( x h) y k r 2 2 equation of the horizontal asymptote of the graph of R. - If the degree of P is more than the degree of Q, then graph of R has no horizontal asymptote. Standard Equation of an Ellipse x h 2 a 2 2 y k b 2 2 1 Standard Equation of a Hyperbola 2 2 2 2 x h y k 1 or y k x h 1 a2 b2 b2 a2 Permutations and Combinations n! n! n Pr n Cr r ! n r ! n r ! Probability of A or B: Mutually exclusive: P( A or B) P( A) P ( B ) Inclusive: Probability of the Complement of A: Probability of Independent Events: Conditional Probability P( Aand B) P( B | A) P( A) P( A and B) P( A) P( B) P( Ac ) 1 P( A) y f(x)=bx x y =0 x -1 0 1 y 1/b 1 b P( A or B) P( A) P( B) P( Aand B) y f(x)=logbx x =0 x x 1/b 1 b y -1 0 1