* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BIODIVERSITY OF PLANTS
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
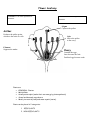
Flower Anatomy STAMEN: The male reproductive structure. PISTAL: The female reproductive structure. Stigma Captures the pollen. Anther Produces the pollen grains which are the male sex cells. Style Moves the pollen to the ovary. Filament Supports the anther. Ovary Contains the eggs. Later becomes the fruit. Fertilized eggs become seeds. OVERVIEW OF PLANT STRUCTURE Plants are: KINGDOM - Plantae Multicellular Usually autotrophic (make their own energy by photosynthesis) Sexual and Asexual reproducers Mostly terrestrial (land) and some aquatic (water) Plants can be placed in 2 categories: 1. SEED PLANTS 2. NON SEED PLANTS Seed Plant / Non Seed Plant Concept Map SEED PLANTS SEEDLESS PLANTS GYMNOSPERMS PRODUCE SEEDS THAT ARE NOT ENCLOSED Seeds that are exposed on the surface of cones; Includes conifers such as pines, firs, spruce and cedar trees ANGIOSPERMS Produce enclosed SEEDS contained in fruit Vascular; Reproduce using flowers, called FLOWERING PLANTS MOST ABUNDANT PLANT ON EARTH MONOCOTS Produce seeds in which the embryo has only 1 cotyledon or seed leaf (structure that helps nourish the plant) Examples: corn, onions, orchids MOSSES NON SEED PLANTS WITHOUT A VASCULAR SYSTEM Dependent on diffusion and osmosis for nutrients; No roots; Rhizoids (rootlike structures) DICOTS Produce seeds in which the embryo has 2 cotyledon or seed leaf Examples: dandelions, maple trees CHARACTERISTICS OF MONOCOTS AND DICOTS FERNS NON SEED PLANTS WITH A VASCULAR SYSTEM PLANT TISSUES There are 4 types of plant tissue: 1. Meristematic Tissue 2. Dermal Tissue 3. Ground Tissue 4. Vascular Tissue MERISTEMATIC TISSUE Cells divided by mitosis; These cells differentiate into other plant cell types; 1) Apical Meristems Found at the tips of roots and shoots Responsible for primary growth (lengthening shoots and roots) 2) Lateral Meristems (Cambium) Cylindrical regions which increase the diameter of roots and shoots (secondary growth) 3) Vascular Cambium Produces the cells for new xylem (water) and phloem (food) DERMAL TISSUE Outermost cell layers Function: o protection from cuts; o microorganism invasion; o water loss; Examples o Leaves and stems may produce wax (prevent water loss) or fine hairs or painful irritants (to discourage herbivores) o Epidermal root tissues develop root hairs to increase water and nutrient absorption o Woody plants produce bark for further protection (bark consists of dead cells) GROUND TISSUE All internal cells except vascular tissues Function o Storage o Support o Photosynthesis Examples o Fleshy portion of apples, pears, potatoes VASCULAR TISSUE For transport of substances in the plants Xylem o Transports water and dissolved minerals from roots to the rest of the plant o These cells die at maturity and become hollow o Appearance – thick walls, may be long and thin or shorter with open ends o When arranged end to end they make continuous tubes for transport o Wood is 100% xylem tissue good support for trees Phloem o Transports sugar and other nutrients from the leaves (site of photosynthesis) to the rest of the plant o Living cells o Sieve tube element Long thin cells with pores at the ends of their cell walls No nuclei, mitochondria or vacuoles Arranged end to end to form tubes o Companion cells Found beside sieve-tube elements Have all the cell organelles that the sieve-tube is lacking Control the functions of the sieve tube DIAGRAMS OF THE VASCULAR TISSUE ROOTS Usually below the ground Serves 5 functions o Anchor the plant to the ground o Absorbs water and minerals o Store extra sugar during photosynthesis o Transport water, sugar, minerals and hormones to the remainder of the plant o Produces some hormones Edible roots include: o Carrots, radishes, sweet potatoes 2 forms: 1. Tap root o Large tapering main root o Example - carrot 2. Fibrous root o Many smaller roots of equal size that grow out of the bottom of the plant o Example – grass ROOT AND SHOOT SYSTEM FLOWERING PLANTS CONSIST OF 2 MAJOR REGIONS: THE ROOT SYSTEM Usually below the ground Serves 5 functions o Anchor the plant to the ground o Absorbs water and minerals o Store extra sugar during photosynthesis o Transport water, sugar, minerals and hormones to the remainder of the plant o Produces some hormones THE SHOOT SYSTEM Usually found above the ground Consists of stems, leaves, buds, flowers and fruits Serves 4 functions o Photosynthesis o Transport of materials between leaves, flowers, fruit and roots o Reproduction o Production of some hormones ROOT GROWTH AND DIFFERENTIATION Root Cap o Protective layer of cells at the tip of the root Apical Meristem Zone of Elongation o Newly divided cells from the apical meristem increase in length Zone of Maturation o Root cells differentiate and mature; region with root hairs STEMS Provide support for the above ground portion of the plant; Connect roots with the remainder of the plant; Store water and food; Transportation system – xylem and phloem are located in the stems Examples – potatoes 2 types 1. Woody o Stems are hard and not easy to bend; strong o Composed of dead xylem tissue 2. Non-woody o Soft and bend easily; weak o Height limits Vascular Cambium and Phloem Cells New Xylem matures into wood; Annual Ring is the amount of xylem produced in 1 year LEAVES Green leaves (chlorophyll) are the site of photosynthesis Veins – an extension of the vascular tissue from the stem Node – the attachment site of the leaf to the stem Internode – the space between nodes on the stem SIMPLE AND COMPOUND LEAVES Simple Leaf – continuous undivided blade Compound Leaf – leaf that is divided into 2 or more leaflet successive LEAF STRUCTURE Epidermal Cells 1 cell layer of cells covering the upper and lower surfaces of the leaf blade Palisade Mesophyll Layer Cells at right angle to the leaf surface; rich in chloroplasts; site of photosynthesis Spongy Mesophyll Layer Loosely packed cells with large air spaces; air spaces allow for efficient gas exchange; site of photosynthesis; leaf veins run through this layer Stoma A small opening in the surface of the leaf which permits the exchange of gases Transpiration – process of water loss through evaporation out of the leaf when the stoma are open Guard Cells Control the opening and closing of the stoma; a pair of crescent shaped cells that surround the pore opening SEEDS AND FRUIT Most of the species we eat are angiosperms. Most commonly the seeds and fruit are used to feed the 6 billion (+) people on the planet. SEEDS The worlds’ 3 most important crops are: 1. Wheat 2. Corn 3. Rice Other important crops are soybeans or other beans. The edible portion of these crops are the seeds The seeds of these plants are high in protein, carbohydrates and fibre. FRUIT Structure that develops in the ovary of a pollinated angiosperm Fruits help the plant spread its seeds o Maple keys, dandelion fluff are examples of fruits with a form that helps them spread o Consumed in animals and pass through the digestive tract unharmed and are deposited in another location Many vegetables are actually fruits – cucumbers, pumpkin, tomatoes, zucchini, squash Other common fruits include bananas, mangoes, apples SEEDS AND FRUIT Most of the species we eat are angiosperms. Most commonly the seeds and fruit are used to feed the 7 billion (+) people on the planet. SEEDS The worlds’ 3 most important crops are: 1. Wheat 2. Corn 3. Rice Other important crops are soybeans or other beans. The edible portion of these crops are the seeds The seeds of these plants are high in protein, carbohydrates and fibre. FRUIT Structure that develops in the ovary of a pollinated angiosperm Fruits help the plant spread its seeds o Maple keys, dandelion fluff are examples of fruits with a form that helps them spread o Consumed in animals and pass through the digestive tract unharmed and are deposited in another location Many vegetables are actually fruits – cucumbers, pumpkin, tomatoes, zucchini, squash Other common fruits include bananas, mangoes, apples POLLINATION Process by which pollen is moved from the anther (portion of male reproductive structure – STAMEN) to the female egg cells and fertilizes these cells. Some plants can fertilize themselves and others need pollen from a different plant. Some plants even have separate male plants and female plants. The pollen is able to travel between plants in many different ways, wind, animals, birds, and insects (BEES). Once the eggs are fertilized they become seeds. The petals fall and in some species the ovary develops into the fruit. CONTROL OF PLANT DEVELOPMENT Plant development involves growth (increase in the number and size of cells) and differentiation (change in the form or function of the cells) INTERNAL FACTORS PLANT GROWTH REGULATOR (PLANT HORMONES) Chemical produced by plant cells that regulates growth and development 5 common plant hormones: 1. AUXINS Promotes the elongation cells Stimulate the growth and ripening of fruit Inhibit dropping of fruit and leaves 2. GIBBERELLINS Promote cell division and elongation Cause fruit to enlarge 3. CYTOKININS Stimulate cell division and leaf growth Extend the life of cut flowers 4. ABSCISIC ACID inhibitor of growth coordinate stress response induce closing of stoma – reduce rate of transpiration 5. ETHYLENE Controls timing of flower death, fruit ripening, leaf and fruit loss Associated with the colour change and sweetness of fruit EXTERNAL FACTORS Plants must be able to respond to external factors such as temperature, the amount of light and amount of moisture Changes in these factors may result in changes in the amounts of plant growth regulators There are 2 examples of environmental responses: 1. TROPISM 2. PHOTOPERIODISM TROPISM Changes in growth pattern or movement in response to directional environmental stimuli o Thigmotropism Response to touch o Phototropism Response to light Example – plant stretches towards light o Gravitropism Response to gravity Allows plants to orientate themselves appropriately to their environment PHOTOPERIODISM Plant development that varies with the amount and quality of light Amount of daylight triggers changes that are linked to seasonal changes and the reproductive cycle of the plant PEST CONTROL ALWAYS COMPETITION AFFECTING THE GROWTH OF PLANTS Host of Fungi, insects and other organisms feed on and in plants Look for ways to eliminate or control these competitors; Effective pest control is required PESTICIDES A chemical used to kill pests o Insecticides – kill insects o Fungicides – kills fungus o Herbicides – kills plants (weeds) Broad Spectrum Pesticides o Kills a large variety of species Selective Pesticides o Kills only limited or specific species PESTICIDE SAFETY Pesticides are regulated to protect human health and natural environments Legislation governs the sale, use and storage of pesticides; Risks on human health have led to the elimination of a number of pesticides BIOACCUMULATION PROCESS BY WHICH THE CONCENTRATION OF A COMPOUND INCREASES THROUGH THE FOOD CHAIN THE CHEMICALS DO NOT BREAK DOWN SO THEY PERSIST IN THE ENVIRONMENT INTEGRATED PEST MANAGEMENT A PEST MANAGEMENT STRATEGY THAT USES A COMBINATION OF CAREFUL MONITORING, NATURAL BIOLOGICAL CONTROLS AND LIMITED APPLICATIONS OF SYNTHETIC PESTICIDES All pests have natural predators o Lady bugs o Wasps WHY DO HUMANS GROW PLANTS? 1. FOOD corn, tomatoes grains – corn, rice, beans herbs – basil, oregano 2. MEDICINE Codeine o analgesic (pain killer) o made from the plant Papaver somniferum 3. PULP AND PAPER 937 tons of paper is used each day (not including food products such as wrappers) 4. FUEL Source of heat in wood burning stoves, fireplaces 5. CONSTRUCTION MATERIALS Wood is the most common building material – Homes, furniture, etc. 6. CLOTHING Fibres / Fabric – cotton, rayon 7. DECORATION Annuals - Live only for 1 growing period Biennials - Live for 2 growing periods Perennial- Long living, live for a number of growing period WORKING WITH PLANTS Plants are an important part of our lives. There are many careers associated with the growing and caring of plants. Arboriculture The cultivation of trees and shrubs Arborists – people who work with Arboriculture Forestry Technology One of Canada’s largest industries Measure forest resources Forest fires, Firefighting methods, Prescribed burns Horticulture The science and art of cultivating fruits, vegetables, flowers and ornamental plants Work in nurseries, greenhouses, garden centres, landscaping firms Hydroponics A technique for growing plants in solution rather than soil Common in commercial greenhouses because it reduces pathogens and pests that live in soil Turf Management Growing and maintaining lawns Golf courses, sports fields, public parks, private residences