* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Notes Intro to Genetics
Survey
Document related concepts
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
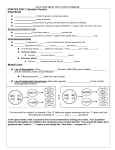
Biology Unit 8: Meiosis and Genetics Name__________________________ Date____________________Per____ Notes 3: Intro to Genetics Genetics The ______________________________ • ______________________ is the _____________________________________ from parents to their offspring. Gregor ______________________was a monk who studied genetics by observing and experimenting with pea plants (1857-1865). Known as the __________________________________________________. What information do our chromosomes hold? • Genes that code for ________________ that __________________ our individual ________________. • For example: Ear hair, Hair color, eye color, ear lobes, hair line, hitch hiker thumb, tongue rolling, behavior, predisposition for disease, etc. Mendel’s Experiments Cross pollinated pure plants with contrasting traits. P- _______________ generation F1 – __________ generation of offspring F2 = F1 crossed with F1 to get _______________ generation of offspring. Genetic Expression • ________________= inherited __________________________ that are expressed. Ex. Widows peak vs. straight hairline • Alleles = ___________________________________________________________ (you get one from mom and one from dad). • We use capital letters and lower case letters to note if they are a dominant allele or a recessive allele. W = _________________________ (Widows peak) w = _________________________ (straight hairline) Law of Dominance • When different alleles for a characteristic are inherited, the ___________ of only one (the ______________one) will be _____________________. • ______________________________________________ the expression of ____________________________ allele traits. • Examples: – Person 1 inherited WW from each parent, so this person has a widows peak – Person 2 inherited Ww from each parent, so this person has a widows peak (the dominant allele masked the recessive allele, so this person carries the allele for straight hair and can pass it on to the offspring. – Person 3 inherited ww from each parent, so this person has a straight hairline. Determining Genotypes and Phenotypes • __________________________ – the ________________________ of an organism (___________ combinations) Ex: WW – _________________________________________________ (widow’s peak) Ww – ___________________________________ (widow’s peak) ww - __________________________________________________ (straight hairline) • __________________________ – the external ___________________ of an organism (physical gene expression) Ex: the person has a widows peak or they don’t. Punnett Square • a diagram to ___________________________________________ of an offspring _________________________ _________________________________. Example: Trait: Plant ________________________ Alleles: ___________________________ Mendel’s plants: Cross: __________________________________ _________ x _________