* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Presentation - ABCs of Power Conditioning (06
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Power factor wikipedia , lookup
Solar micro-inverter wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Audio power wikipedia , lookup
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Standby power wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Amtrak's 25 Hz traction power system wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
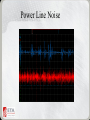
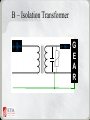
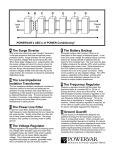
THE ABCs OF POWER CONDITIONING A Simplified Approach to Understanding Power Quality Problems and How to Solve Them. What is the origin of power quality problems? Usually they have an earthly source Hildegard, switch off the mixer, my monitor is flickering! And I don‘t mean this one . . . . Where Do Power Quality Problems Start? • Disturbances are generated external to a facility. • Disturbances are generated internal to a facility. The Four D’s of Power Disturbances • Destruction – – – – High energy Short duration Visible evidence Easy to establish cause and effect The Four D’s of Power Disturbances • Degradation – – – – – Low energy Constant exposure Cumulative damage No visible evidence Electronic rust The Four D’s of Power Disturbances • Disruption – Low energy – Interferes with operation of logic circuits – Lockups, reboots, program dumps – No trouble found system failures – Frustration The Four D’s of Power Disturbances • Dynamics – Noise that can be heard – Noise that can be seen – Noise that interferes with the enjoyment of the production, performance, or meeting How Do Power Disturbances Enter an Electronic System? There are two pathways Normal Mode Phase (hot) to Neutral Should be <10 volts Common Mode Neutral to Ground Should be < ½ volt The Nature of Power Problems • 10% of problems are outages • 90% are noise, voltage surges, harmonics, etc. • It’s what you don’t see that can kill you 10% 90% What Devices Are Used To Solve Power Problems. Which Device Is The Appropriate One To Use? SIMPLE AS A-B-C The Voltage Surge A – The Surge Diverter Clamping Level Power Line Noise AC – The Surge Diverter & Filter Common Mode Voltage • Voltage measured neutral to ground – – – – – Voltage spikes Conducted noise Radiated noise Unbalanced electrical distribution Circuit loading B – Isolation Transformer G E A R Balanced Power Transformer 60 volts H G 60 volts N Voltage Sags and Swells • Short term (less than 1 minute) decrease or increase in line voltage • Variety of causes both internal and external • Most modern loads are relatively immune D – The Voltage Regulator • Variety of technologies – – – – Ferroresonant (undesirable for modern gear) Tap switching autoformer (better) Tap switching isolation transformer (better yet) Electronic regulator with isolated output (best bet) Power Outages • Complete loss of power for seconds to hours in duration • Usually the result of a power company failure although may have internal facility causes, too. E – The Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) • Converts chemical energy stored in batteries to electrical energy to power the load • A variety of technologies (standby, line interactive, on line • Some are power conditioned some are not • BUYER BEWARE! Not All UPSs Are Alike If You Need a UPS • It should be sine wave inverter design • Inverter topology depends on the gear and application (standby or on line) • Must have an isolation transformer if you want it to also provide power conditioning An Integrated Approach • Using an integrated ABCs approach will – Prevent destruction, degradation, and disruption and safeguard dynamics – Protect from the full range of power quality problems that affect your systems – Improve system performance – Reduce operating and repair costs – Increase satisfaction Questions ?