* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Variation - Elgin Academy
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Fetal origins hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Selective breeding wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
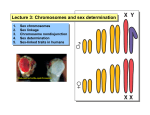
Standard Grade Biology Topic 6 Learning Outcomes Inheritance Variation At the end of this topic you should be able to : o state that a group of interbreeding organisms producing fertile offspring is called a species o state that variation can occur within a species o give examples of continuous and discontinuous variation o explain the terms continuous and discontinuous variation Standard Grade Biology Topic 6 Learning Outcomes Inheritance What is Inheritance? GENERAL o state that genetic information from parents determines certain characteristics o give examples of inherited information in plants and animals o understand the meaning of the terms phenotype, genotype, dominant, recessive and true breeding o identify generations as P, F1 and F2 o state that each body cell has 2 matching sets of chromosomes (diploid or 2n) o state that sex cells are called gametes and they have only 1 set (haploid or n) o state that the reduction from 2n to n occurs during gamete formation o 2 haploid gametes unite at fertilisation to form a diploid zygote o state that genes are parts of chromosomes o state that a characteristic is controlled by 2 forms of a gene o state that each parent supplies 1 allele for each gene to the gamete o state that sex is determined by special chromosomes X and Y o state that in humans, female gametes contain one X chromosome and male gametes an X or a Y o explain how sex is determined with reference to the X and Y chromosomes CREDIT o o o o o be able to carry out a monohybrid cross predict the phenotype ratio in the F2 of a monohybrid cross state that the different forms of a gene are called alleles explain a monohybrid cross in terms of genotypes explain the difference between observed and expected results Standard Grade Biology Topic 6 Learning Outcomes Inheritance Genetics and Society GENERAL o give 2 examples of an improved characteristic from selective breeding eg increased yield, disease resistance or increased growth o describe 1 human condition caused by chromosome mutation eg Downs syndrome o state that amniocentesis can detect chromosome characteristics before birth CREDIT o describe 2 examples of enhancement (improvement) through selective breeding o give an example of an advantageous mutation to man o give an example of a factor which can influence the rate of mutation