* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Study Guide Module 3
Survey
Document related concepts
Positional notation wikipedia , lookup
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Law of large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Minkowski diagram wikipedia , lookup
Location arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
Proofs of Fermat's little theorem wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
P-adic number wikipedia , lookup
Cartesian coordinate system wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
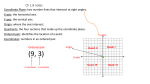
Name____________________________________________ Study Guide- Module 3 Integers Absolute Value Compare integers Rational Numbers Coordinate geometry Reflections Integers: Positive and negative whole numbers including zero. The Number Line Negative Numbers (-) Positive Numbers (+) (The line continues left and right forever.) The further to the right a number is the greater it is! The opposite of a positive number is a negative Ex. the opposite of 4 is -4 The opposite of a negative number is a positive Ex. The opposite of -6 is 6 Zero is its own opposite! Opposite Integers (2 numbers that are the same distance from zero on a number line): Opposite of 3 is –3 Opposite of 10 is –10 Absolute Value (the distance from zero): *Absolute value is represented by 2 bars. │ -3 │ = 3 │ 3 │= 3 Opposite of –1200 is 1200 Comparing Integers: -2 < 4 -7 < -5 │-14 │ > 11 Rational Numbers: A rational number is a number that can be in the form p/q where p and q are integers and q is not equal to zero. Number 5 1.75 .001 0.111... √2 (square root of 2) Coordinate Geometry This is a coordinate plane. It has two axes and four quadrants. The two number lines form the axes. The horizontal number line is called the x-axis and the vertical number line is called the y- As a Fraction 5/1 7/4 1/1000 1/9 Rational? Yes Yes Yes Yes ? NO ! axis. The center of the coordinate plane is called the origin. It has the coordinates of (0,0). Locations of points on the plane can be plotted when one coordinate from each of the axes are used. This set of x and y values are called ordered pairs. Assuming one box equals one unit follow the examples below: Ex: (x, y) Quadrant I If you have to plot the point (1, 2) Always start at the origin and move to the right one and up two This is in the first quadrant! Ex: (-x, y) Quadrant II If you plot the point (-3, 2) Always start at the origin and move to the left three and up two This is in the second quadrant! Ex: (-x,-y) Quadrant III If you have to the plot the point (-4,-1) Always start at the origin and move to the left four and down one This is in the third quadrant! Ex: (x,-y) Quadrant IV If you have to plot the point (5, -6) Always start at the origin and go to the right five and down six This is in the fourth quadrant! You can also plot points that are on the x and y axis….. Ex: (0, 5) This means stay at zero but move up five (5, 0) This means move to the right five and stay at zero. These are examples of x and y intercepts!!!!! Reflections: Reflection in the x-axis. A reflection in the x-axis can be seen in the picture below in which A is reflected to its image A'. The general rule for a reflection in the x-axis: (A,B) (A, −B) Reflection in the y-axis. A reflection in the y-axis can be seen in the picture below in which A is reflected to its image A'. The general rule for a reflection in the y-axis: (A,B) (−A, B)