* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download cw3cb_WK8_HW1 - East Penn School District
Ultrafast laser spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Surface plasmon resonance microscopy wikipedia , lookup
Optical flat wikipedia , lookup
Optical rogue waves wikipedia , lookup
Dispersion staining wikipedia , lookup
Optical amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Nonlinear optics wikipedia , lookup
Ellipsometry wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Fiber Bragg grating wikipedia , lookup
Refractive index wikipedia , lookup
3D optical data storage wikipedia , lookup
Optical coherence tomography wikipedia , lookup
Optical aberration wikipedia , lookup
Optical fiber wikipedia , lookup
Nonimaging optics wikipedia , lookup
Harold Hopkins (physicist) wikipedia , lookup
Silicon photonics wikipedia , lookup
Birefringence wikipedia , lookup
Anti-reflective coating wikipedia , lookup
Optical tweezers wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric optics wikipedia , lookup
Photon scanning microscopy wikipedia , lookup
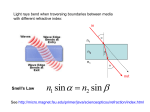
Mrs. Carole Wilson’s WebQuest: INTRODUCTION You cannot watch television without seeing the Verizon FiOS® guy telling the cable guy how superior FiOS is to cable TV. What exactly is FiOS? According to the Verizon website, FiOS is not an acronym for anything. It just means that optical fibers are used to carry the television signal to the home instead of copper wiring. Optical Fibers are based upon physics concepts that you are studying in class. In this WebQuest you will learn about optical fibers and their uses. TASK You will read each section by clicking on the blue links ( BLUE ) provided below and then answer the questions or complete the activities given. You may record your answers in one of two ways: 1. Save this Word document on your home computer or on your account on the student server, answer the questions in the document, print out the completed version, and turn it in. 2. Write answers on your own paper and turn them in. Note - Some websites require a username and password. If you do not remember the Emmaus High School username and password for any site, check with your instructor. You may have to enter your username and password more than once to get the page to open. Alternate links are provided for the websites that require a password and username in case you cannot access them. PROCESS AND RESOURCES COMMUNICATION BY LIGHT 1. 2. Briefly describe how light was used to communicate in the following instances: a. The beginning of the Revolutionary War b. The heliograph Heliograph site 2 c. The photophone Based upon what you read in the links above and in this link what advantage or advantages do you think optical fibers provide over the other methods for communication by light signals. THE PHYSICS BEHIND OPTICAL FIBERS You have already learned about refraction and Snell’s law. In this link the simulations are listed in the left hand column. Scroll down and click on the one entitled Refraction and total internal reflection. This simulation allows you explore refraction by varying the index of refraction in both medium 1 and medium 2 and the angle of incidence. You should: 1. Listen to the audio introduction. 2. Explore the simulation on your own. 3. Read the student notes and answer any investigation questions by using the simulation. 4. Complete the self-test. You may refer to your notes or textbook in addition to the material in this WebQuest. 5. Record answers to any questions in the listed sections below. Now explore this refraction simulation. Investigation Questions – Use the simulation to explore the answers to these questions. 1. The angles are measured from the normal. What direction is the normal relative to the interface between medium 1 and medium 2? 2. In general, when light passes from one medium to a second medium that has a higher index of refraction ( n2 > n1 ), does the light bend towards the normal or away from the normal? What happens when the second medium has a lower index of refraction than the first ( n2 < n1 )? 3. There is one particular angle of incidence that always results in the same angle of refraction, no matter what the indices of refraction are. What is this angle? 4. Set n1 > n2 . The critical angle will be displayed. If the angle of incidence is less than the critical angle, some of the light refracts into the second medium. When the angle of incidence exceeds the critical angle, however, what happens? This is known as total internal reflection. 5. Are there any refraction questions you have which you could not answer by exploring the simulation? If so, record them here. Self-Test Questions – The simulation may be helpful in answering some of these questions. 1. There are two cases in which the angle of refraction is the same as the angle of incidence. What are they? 2. The situation where n2 = n1 is a special case. What happens with the reflected ray in this situation? How does the angle of refraction compare to the angle of incidence? 3. Refraction occurs because light has wave properties. When light passes from one medium to a second medium with a larger index of refraction, what happens to the speed, wavelength, and frequency of the light? 4. If n1 > n2 and the angle of incidence is exactly equal to the critical angle, what is the angle of refraction? Combining this information with Snell’s law, derive an expression for the critical angle in terms of n1 and n2. 5. What is a practical application of total internal reflection? DESCRIPTION OF OPTICAL FIBERS 1. Parts of Optical Fibers - List the parts of an optical fiber, the material that makes up each part, and the function of each part. 2. Optical Fibers 101 – Go to this educational website provided by Corning, a manufacturer of optical fibers, and answer the following questions. a. How much of a difference in refractive index is there between the core and the cladding of the fiber? Which one has the higher index of refraction? Why doe that part have the higher index of refraction? b. What is a single-mode fiber? What is the advantage of a single-mode fiber? c. What is a multimode fiber? What is the advantage of a multimode fiber? d. When light rays enter the optical fiber from the air what happens to the light rays? e. What is the Numerical Aperture of an optical fiber? Upon what properties does it depend? f. What is attenuation? Is attenuation a limitation of using optical fiber compared to other technologies? g. What is dispersion? What problem does dispersion cause? What must be included in a fiber optic system because of dispersion? USES OF OPTICAL FIBERS Now that you know what optical fibers are and how they work you will explore some uses of optical fibers. Explore the following links and then list at least 3 different uses of optical fibers. For each use you list briefly describe in the space below how the optical fibers are used and the advantage(s) of using optical fibers. Uses of Optical Fiber (Timbercon Source) Uses of Optical Fiber (WorldbookOnline) Communications 1 Communications 2 Medical Uses of Optical Fiber o Use in Endoscopy o Endoscopy 2 o Arthroscopy Dental Uses Industrial Uses o Fiberscope o Borescope Biological Use