* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What IS A VOLCANO?
Axial Seamount wikipedia , lookup
Itcha Range wikipedia , lookup
Mount Meager massif wikipedia , lookup
Mount Garibaldi wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pinatubo wikipedia , lookup
Craters of the Moon National Monument and Preserve wikipedia , lookup
Level Mountain wikipedia , lookup
Llullaillaco wikipedia , lookup
Mount St. Helens wikipedia , lookup
Lascar (volcano) wikipedia , lookup
Potrillo volcanic field wikipedia , lookup
Olympus Mons wikipedia , lookup
Volcanology of Io wikipedia , lookup
Cascade Volcanoes wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pleasant Caldera wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Mount Edziza volcanic complex wikipedia , lookup
Mount Pelée wikipedia , lookup
Shield volcano wikipedia , lookup
Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field wikipedia , lookup
Nevado del Ruiz wikipedia , lookup
Mount Vesuvius wikipedia , lookup
Cerro Azul (Chile volcano) wikipedia , lookup
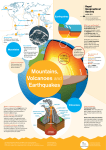
How do volcanoes affect the lithosphere, plate boundaries, & the atmosphere? VOLCANOES Unit 5 EEn.2.1.1 How do volcanoes affect the lithosphere, plate boundaries, & the atmosphere? A volcano is a place where lava reaches the surface. - The Vents - is the main conduit through which magma moves towards to get to the surface. The Crater - sits at the top of a volcano and is the location where much of the lava, gas, rock fragments and ash are ejected from. There are three types of Volcanoes 1. Shield Volcano: A gently-sloped mountain. Forms when layers of basaltic lava accumulates during nonexplosive eruptions. 2. Cinder Cone: A volcano made of cinders that are blown into the air. • • • Are smaller volcanoes Its magma consists of more water & silica than what is found in shield volcanoes Large amounts of gas 3. Composite: A volcano built of alternating layers of cinders and lava. • Composite magma consists of large amounts of silica, water, and gases. • Are more violently explosive Mount Shasta is a composite volcano. Over the last 10,000 years, Mt. Shasta has erupted on average once every 800 years. During the 3,500 years the volcano has erupted about once every 300 years. Diamond Head is an eroded Cinder (Tuff) Cone. Diamond Head formed when hot magma rising up a conduit hit ocean water, causing large explosions that threw exploded magma particles (tuff) into a broad ring. Compare Magma & Lava Magma is molten rock which is still underground in vents. On the other hand, lava refers to molten rock which has found its way to the ground after an eruption. Lava occurs in active volcano while magma occurs in an inactive one. At the core of the earth is hot molten rock, magma. The molten rocks erupt through a volcano and come out as lava. The temperature of magma is extremely high while that of lava are lower as it cools down when it comes out under the atmosphere. The varying amount of heat causes a difference in their viscosity; magma's viscosity is lower due to immense heat inside earth. What are Lahar? • Lahar is an Indonesian term that describes a hot or cold mixture of water and rock fragments flowing down the slopes of a volcano and (or) river valleys. It’s mud. When moving, a lahar looks like a mass of wet concrete that carries rock debris ranging in size from clay to boulders. • Can lead to increased deposition (sediments on the ground/bottom of a body of water) of sediments • Can destroy streams, valleys, & communities What are Lahar? Volcanic effects on lithosphere, & plate boundaries Convergent plate boundaries are locations where lithospheric plates are moving towards one another. The plate collisions that occur in these areas can produce earthquakes, volcanic activity and crustal deformation. This results in destruction of the lithosphere. Volcanic effects on lithosphere, & plate boundaries Convergent Plate Boundary Oceanic and Continental Plates The buoyant magma chambers begin a slow ascent through the overlying materials, melting and fracturing their way upwards. If a magma chamber rises to the surface without solidifying, the magma will break through in the form of a volcanic eruption. This will destroy the oceanic lithosphere. Volcanic effects on lithosphere, & plate boundaries Convergent Plate Boundary - Oceanic When a convergent boundary occurs between two oceanic plates one of those plates will subduct beneath the other. Normally the older plate will subduct because of its higher density. Magma begins ascending by melting and fracturing its way through the overlying rock material. Magma break through to form a volcanic eruption cone.