* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Series Cicuit Lab
Josephson voltage standard wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Lumped element model wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Negative resistance wikipedia , lookup
Surface-mount technology wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
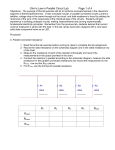
Ohm’s Law in Series Circuit Lab Page 1 of 4 Objectives: The purpose of this lab exercise will be to reinforce concepts learned in the classroom segment of Electricity/Electronics. These concepts include: series connected resistance is additive, voltage drop is additive, and current measurements through-out the circuit is the same. . Students will gain experience in building prototype circuits, making measurements and proving experimentally fundamental electricity principles. Remember from the previous lab, students learned that current must be measured in series with the load. In this lab, lamps have been replaced with a very basic solid state component know as an LED. Procedure: A. Series connected resistance 1. Read the entire lab exercise before coming to class to complete the lab assignment. 2. Record the rated resistance on the schematic diagram and in the rated resistance row of the chart. 3. Measure the resistance of each of the resistors individually and record the measurements in the space provided in the chart. 4. Connect the resistors in series according to the schematic diagram, measure the total resistance for the series connected resistances and record the measurement in the Rmeas. row and the Rtotal column. R1 R2 value value R1 Rrated Rmeas. Rcalc. R3 R4 value R2 R3 value R4 Rtotal Ohm’s Law in Series Circuit Lab Page 2 of 4 Procedure: B. Series voltage drops 1. Read the supplement containing the information regarding the LED. Keep in mind that LED’s are polarity sensitive devices and must be connected correctly in order to be operational. 2. Construct the circuit at the top of the next page using jumper wires between each of the LED’s as indicated by the schematic diagram. There is a photograph to assist you with the construction of the circuit. Set the voltage for the value outlined during the classroom introduction for this lab exercise. 3. For each measurement observe the correct meter polarity. 4. Measure the voltages across the LED’s and record the measurements in the spaces provided. 5. Measure the currents between the indicated points with the jumper wire removed and record the current measurements in the space provided in the chart. 6. For ET below add all of the measurements from the first column and record this as E T. (ET = EJ-I + EH-G + EF-E + ED-C) 7. Be sure to answer the questions at the end of this exercise as this is an excellent way to check an individual’s understanding. D1 K J D2 I H D3 G F D4 E D V1 A B 0 EJ-I EH-G EF-E ED-C EA-K IK-J EA-K II-H switch open EA-B switch open ET IG-F IE-D IA-B switch open IA-B switch closed PT C Ohm’s Law in Series Circuit Lab Page 3 of 4 Questions: 1. What has been proven about current in a series circuit? 2. Describe what happened to the circuit the instant one of the jumper wires was removed for measuring current? 3. Did the LED’s produce much heat? Explain your answer. 4. List five common applications for LED’s a. b. Ohm’s Law in Series Circuit Lab Page 4 of 4 c. d. e. 5. Describe what you know about resistance in series. 6. How much voltage did one LED drop? 7. What were the color bands on R1? 8. What were the color bands on R3? 9. List some of the advantages of using LED’s over incandescent lamps. a. b. c. 10. Describe how to identify the leads of a diode.