* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genetics Lecture Guide
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
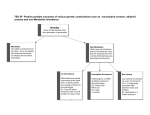
Genetics Lecture Guide Lecture 6: Bombay Phenotype & Epistasis 1) When, where and how was the Bombay Phenotype discovered? 2) What does it mean to be homozygous recessive for FUT1? 3) Who can individuals with the Bombay Phenotype receive blood transfusions from? 4) Explain the term ‘epistasis’ and how the Bombay Phenotype is an example of epistasis. 5) Mice also exhibit epistasis in regards to their fur color. Write the possible F2 genotypes and phenotypes in the table below: F2 Ratio Genotype Phenotype Phenotypic Ratios 9/16 9/16 agouti 3/16 4/16 albino 3/16 3/16 black 1/16 6) Mouse color is dependent on 2 different genes that interact (A- and B-). Draw the possible gene pathways below: 7) Use the branch diagram method to try out this cross: F1: Aabb x AaBb