* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1) You push your lawnmower (mass = 15 kg) across
Survey
Document related concepts
Classical mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Center of mass wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Variable speed of light wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
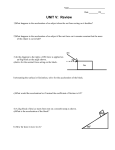
AP Physics: Newtons Laws and Force Diagrams 1) Object slides without friction. Solve for Weight and acceleration in terms of m, g, θ. a. Calculate the acceleration on the weight for m = 20 kg g = 9.8 m/s² and θ = 60 º 2) Static friction prevents sliding. Solve for Weight and acceleration in terms of m, g, θ. 3) You push your lawnmower (mass = 15 kg) across the lawn at constant speed. To do so, you must exert 120 N of force. The handle makes a 35° angle with the horizontal. a. In the space under the figure, sketch a force diagram to represent this situation. b. What is the x-component of the force you apply? c. How does this compare to the frictional force which opposes your effort? Explain. d. What is the value of the normal force? 4) A man pulls a 50 kg box at constant speed across the floor. He applies a 200 N force at an angle of 30°. a. Sum the forces in the x-direction. What is the value of the frictional force opposing the motion? b. Sum the forces in the y-direction. What is the value of the normal force? 5) A man pushes a 2.0 kg broom at constant speed across the floor. The broom handle makes a 50° angle with the floor. He pushes the broom with a 5.0 N force. a. Sum the forces in the y-direction. What is the value of the normal force? b. Sum of the forces in the x-direction. What is the value of the frictional force opposing the motion? c. If the frictional force were suddenly reduced to zero, what would happen to the broom? 6) Derive the “a” acceleration system and the Tension (T) in terms of m, g, θ. 7) A passenger of mass m= 72.2 kg stands on a bathroom scale in an elevator. We are concerned with the scale readings when the cab is stationary, and when it is moving up or down. (a) Find the general solution for the scale reading, whatever the vertical motion of the cab. (b) What does the scale read if the cab is stationary or moving upward at a constant 0.50 m/s? (c) What does the scale read if the cab accelerates upward at ? and downward at 8) A 5.0 kg salmon is weighed by hanging it from a fish scale attached to the ceiling of an elevator. What is the apparent weight of the salmon, moves with an upward acceleration of of , if the elevator (a) is at rest, (b) , or (c) moves with a downward acceleration ? 9) A trained sea lion slides from rest with constant acceleration down a 3.0 m long ramp into a pool of water. If the ramp is inclined at an angle of above the horizontal. (a) Find the acceleration the sea lion has down the plane. (b) Find how long the sea lion takes to make a splash in the pond. 10) 1) A block of mass slides on a frictionless tabletop. It is connected to a string that passes over a pulley and suspends a mass . Find the acceleration of the masses and the tension in the string. Atwood's Machine 11) The figure shows two blocks connected by a cord that passes over a massless, frictionless pulley. The lighter block has a mass m = 1.3 kg and the heavier block has a m = 2.8 kg. Find the magnitudes of the accelerations of the two blocks and the magnitude T of the force on each block from the cord. 12) In the figure a crate of dilled pickles with mass makes an angle of moves along a plane that with the horizontal. The crate is connected to a crate of pickled dills with mass by a taut, massless cord that runs over a frictionless, massless pulley. The dills descend with constant velocity. (a) What are the magnitude and direction of the frictional force on the pickles from the plane? (b) What is ? 13) To hang a 6.20 kg pot of flowers, a gardener uses two wires–one attached horizontally to a wall, the other sloping upward at an angle of the tension in each wire. and attached to the ceiling. Find AP Physics Application of Newton’s Laws Circular Motion 14) A 1200 kg car rounds a corner of radius r = 45 m. If the coefficient of static friction between the tires and the road is car can have in the corner without skidding? , what is the greatest speed the 15) The figure represents a stock car of mass m = 1600 kg traveling at a constant speed v = 20 m/s around a flat, circular track of radius R = 190 m. For what value of between the track and the tires of the car will the car be on the verge of sliding off the track? 16) If a roadway is banked at the proper angle, a car can round a corner without any assistance from friction between the tires and the road. Find the appropriate angle for a 900 kg car traveling at 20.5 m/s in a turn of radius 85.0 m. 17) While driving along a country lane with a constant speed of 17.0 m/s, you encounter a dip in the road. The dip can be approximated as a circular arc, with radius of 65.0 m. What is the normal force exerted by a car seat on a 80.0 kg passenger when the car is at the bottom of the dip? 18) In a 1901 circus performance, Allo "Dare Devil" Diavolo introduced the stunt of riding a bicycle in a loop-the-loop. Assuming that the loop is a circle with radius R = 2.7 m, what is the least speed v Diavolo could have at the top of the loop to remain in contact with it there? Applications of Newton’s Laws and Circular Motion 19) 20) 21)