* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electronics Analog-to
Survey
Document related concepts
Quantization (signal processing) wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Television standards conversion wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Time-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
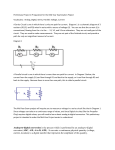
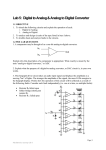
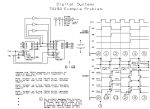
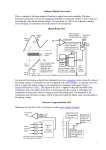
Electronics Analog-to-digital converter An analog-to-digital converter (abbreviated ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts continuous signals to discrete digital numbers. The reverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC). Typically, an ADC is an electronic device that converts a voltage to a binary digital number. However, some non-electronic devices, such as shaft encoders, can be considered as ADCs. Resolution The resolution of the converter indicates the number of discrete values it can produce. It is usually expressed in bits. For example, an ADC that encodes an analog input to one of 256 discrete values has a resolution of eight bits, since 28 = 256. Resolution can also be defined electrically, and expressed in volts. The voltage resolution of an ADC is equal to its overall voltage measurement range divided by the number of discrete values. Some examples may help: Example 1 o Full scale measurement range = 0 to 10 volts o ADC resolution is 12 bits: 212 = 4096 quantization levels o ADC voltage resolution is: (10-0)/4096 = 0.00244 volts = 2.44 mV Example 2 o Full scale measurement range = -10 to +10 volts o ADC resolution is 14 bits: 214 = 16384 quantization levels o ADC voltage resolution is: (10-(-10))/16384 = 20/16384 = 0.00122 volts = 1.22 mV In practice, the resolution of the converter is limited by the signal-to-noise ratio of the signal in question. If there is too much noise present in the analog input, it will be impossible to accurately resolve beyond a certain number of bits of resolution, the "effective number of bits" (ENOB). While the ADC will produce a result, the result is not accurate, since its lower bits are simply measuring noise. The S/N ratio should be around 6 dB per bit of resolution required.