* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Homework 3
Survey
Document related concepts
Financialization wikipedia , lookup
Adjustable-rate mortgage wikipedia , lookup
Continuous-repayment mortgage wikipedia , lookup
Pensions crisis wikipedia , lookup
Fractional-reserve banking wikipedia , lookup
Stagflation wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative easing wikipedia , lookup
Monetary policy wikipedia , lookup
History of the Federal Reserve System wikipedia , lookup
History of pawnbroking wikipedia , lookup
Credit card interest wikipedia , lookup
Present value wikipedia , lookup
Interest rate swap wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
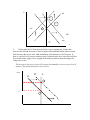
Homework 3 Economics 503 Foundations of Economic Analysis Assigned: Session 6 Due: Session 7 1. Construct an AS-AD model of the economy. Begin by assuming the economy is in a long-run level of equilibrium with the aggregate supply curve crossing the aggregate demand curve at the level of potential output. Use the model to describe how each of the events will change the macroeconomic equilibrium in the short-run. Suppose that policymakers allow the self correction mechanism to bring GDP back to the long-run equilibrium. Use the model to describe how each of the events will change the economy in the long-run. Illustrate with diagrams. a. An increase in the level of GDP of a leading trading partner. P AS lt st AS' o AD' YP AD Y b. The central bank increases the money supply. P AS lt st AS' o AD' YP AD Y 2. In December 2010, China increased their reserve requirement. Assume this increases the demand for reserves. Draw a graph of the interbank market when a central bank increases the reserve ratio while maintaining a fixed money level of reserves. If there is a given level of reserves and the reserve to deposit ratio rises, what effect will this have on the money supply. Draw a graph of the money market to show the impact of a rising reserve ratio. The increase in the reserve ratio will increase the demand for reserves at any level of deposits. The equilibrium interest rate will rise. iIBOR D D' S 2 i* 1 The money multiplier would be reduced by an increase in the reserve to deposit ratio. The liquidity available from the national banking system would be reduced and money market interest rates will rise. M S P i** 2 i* MS P S 1 M P i D Real Balances 3. Estimate the current real interest rate in Hong Kong. There are two steps: 1) get the nominal interest rate; and 2) estimate the future inflation rate. a. To measure current interest rates, i, Use the end of period 12 Month HIBOR (Hong Kong Interbank Offered Rate) rate from December, 2011 found in Table 6.3.1 of the Hong Kong Monetary Authorities Monthly Statistical Bulletin from January, 2012. This can be found at this webpage: HKMA Monthly Statistics 0.75% or i = .0075 b. To estimate the future inflation rate, πt+1, use the % growth of the Composite Consumer Price Index for November, 2011 relative to November, 2010 from Hong Kong Statistics from Bureau of Census and Statistics. This can be found on this webpage Hong Kong Department of Census and Statistics . CPI 102.4 108.2 Nov 2010 Nov 2011 tE1 t Pt Pt 1 108.2 102.4 .0566 Pt 1 102.4 rt it tE1 .0075 .0566 .0491 4. For the country of Elbonia, there is a saving curve which shows the relationship between national supply of loanable funds from the private sector at any real interest rate: S = 300*r . The private sector level of demand for loanable funds is also a function of the interest rate, D = 20-100*r. a. Assume government savings is 0. Assume Elbonia’s loanable funds market is closed so supply and demand for loanable funds are equal. Solve for the equilibrium real interest rate and quantity in the loanable funds market. Supply and demand are equal so S = 300*r = 20-100*r = D. 20 300r 20 100r 400r 20 r .05 so S = 300r = 15. 400 b. Assume that Elbonia is part of a global capital market and the world real interest rate is rW = .06. Calculate Elbonian supply of loanable funds, demand for loanable funds and capital inflows. S = 300*.06 = 18.; D = 20-100*.06 = 14. So KA =-4. c. The Elbonian government runs a deficit and has government savings of -20. Calculate, supply and demand of Elbonian loanable funds at an interest rate of rW = .06. What are capital inflows. Now, D = 20-100r+20 = 40-100r = 34, so KA = 16.