* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Light and Optics Unit
Survey
Document related concepts
Reflector sight wikipedia , lookup
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Nonimaging optics wikipedia , lookup
Image intensifier wikipedia , lookup
Anti-reflective coating wikipedia , lookup
Night vision device wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Chinese sun and moon mirrors wikipedia , lookup
Optical telescope wikipedia , lookup
Ray tracing (graphics) wikipedia , lookup
Mirrors in Mesoamerican culture wikipedia , lookup
Image stabilization wikipedia , lookup
Johan Sebastiaan Ploem wikipedia , lookup
Retroreflector wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
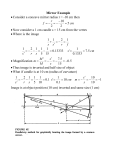
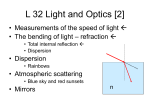
Light and Optics Unit Part 1 (Chapter 11. 2, 11.4-11.9) For the test, you should: know the ray model of light understand and apply the terms transparent, translucent, and opaque understand and apply the terms specular and diffuse reflection Reflection from a Plane Mirror understand and apply the terms angle of incidence, angle of reflection, normal, incident ray, reflected ray be able to explain (and draw) how an image is formed in a plane mirror (also what type of image it is, where it is, and understand that it is laterally inverted) be able to draw the mirror image of a word Curved Mirrors understand and apply the terms center of curvature, focus, focal length, principal axis, and vertex as they apply to curved mirrors understand the difference between concave (converging) and convex (diverging mirrors) be able to locate the image of an object using ray diagrams and describe its characteristics using SALT (size, attitude, location, type) be familiar with the characteristics of an image (using SALT) based on the location of the object without drawing the diagram (example: objects inside the focal length always make upright, large, virtual images - see table on pg.499) be able to use the mirror equation to determine the characteristics of an image 1 1 1 f d0 bject dimage Magnification : M himage hobject dimage dobject NOTE: focal length is negative if the mirror is diverging distance of image is negative if image is virtual height of image is negative if inverted be able to state, explain, and draw applications of concave mirrors: headlights, telescopes, satellite dishes, parabolic cooker, makeup mirrors, and flashlights convex: rearview mirrors and security mirrors Types of Light: be able to identify the different sources of light from the definition (e.g. incandescence, electric discharge, phosphorescence, fluorescence, chemiluminescence, bioluminescence, triboluminescence) Electromagnetic Spectrum: be able to characterize the different types of the electromagnetic spectrum based on their characteristic wavelengths and frequency and detail their uses (e.g. shortest wavelength or highest frequency, what are uses for each type )