* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AP Biology: Chapter 53-Community Ecology Give the definition and
Survey
Document related concepts
Soundscape ecology wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
Biogeography wikipedia , lookup
Overexploitation wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Introduced species wikipedia , lookup
Occupancy–abundance relationship wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Storage effect wikipedia , lookup
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Reconciliation ecology wikipedia , lookup
Ecological succession wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
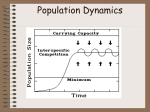
AP Biology: Chapter 53-Community Ecology 1. Give the definition and an example (if appropriate) for the following terms: a. Community b. Interspecific interaction c. Interspecific competition d. Competitive exclusion e. Ecological niche f. Resource partitioning g. Character displacement 2. Describe Gausse’s experiment with Paramecia. 3. Fill in the chart of interspecific interactions: Interaction Effects on population density Example Predation Herbivory Parasitism Disease Mutualism Commensalism 4. Describe several defense mechanisms to predation in plants. 5. Define and give an example of the following animal defenses: a. Cryptic coloration b. Aposematic coloration c. Batesian mimicry d. Mullerian mimicry 6. What is meant by the “trophic structure” of a community? 7. What does a food web show that isn’t indicated by a food chain? 8. What limits the length of a food chain? 9. Define a dominant species, invasive species, and keystone species. 10. Explain why keystone species are so important to a community. 11. Define ecological succession. 12. What is the difference between primary and secondary succession? 13. Explain how each of the following biogeographic areas affect community biodiversity: a. Equatorial-Polar Gradients b. Area Effects c. Island Equilibrium Model