* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download A large apple weighs 150 g
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
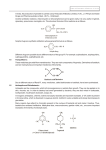
Biochemistry Calculations 1. Doritos brand potato chips have 140 Calories per serving (28.0g). a. What is the calorie value in kilojoules for a whole serving? (Remember that food calories are really kilocalories. 1 cal = 4.184 J) b. If 5.0 grams undergo complete combustion in a calorimeter filled with 200. g of water, what will be the temperature change of the water? 2. A large apple weighs 150 g. If a 15.0 g sample of the apple, on complete combustion raises the temperature of 200. g of water in a glass container by 45.3 C, calculate the calorific value of the apple. The heat capacity of the glass calorimeter = 89.1 J/C and the specific heat of water = 4.184 J/g C (419 kJ) 3. 0.010 moles of linoleic acid reacts with 5.1 g of iodine. Determine the number of double bonds present in the acid. (2) 4. Iodine index or iodine number is the number of grams of iodine that add to 100 g of a triglycerol. Calculate the iodine number of linoleic acid (C17H31COOH) based on your previous answer. (181 g) 5. The iodine number ranges for several fats is given below. Ranges are given because most are mixtures of various triglycerides. Put them in order of least saturated to most saturated. Iodine # a. Butter 30-38 b. Sunflower oil 119-138 c. Peanut oil 85-100 d. Olive oil 79-95 1. Which has more calories per gram – fats or carbohydrates? 2. When carbon is oxidized, energy is given off. When carbon is reduced, energy is absorbed. Based on this, explain the difference in energy between fats and carbohydrates. 3. For each of the following, list its function in a diet and the effect of its deficiency a. Vitamin C b. Vitamin D c. Vitamin A d. Vitamin B3 e. Vitamin B1 f. g. iodine 4. List two water soluble vitamins and 4 fat soluble vitamins 5. Discuss two solutions for the prevention of nutrient deficiencies. 6. State what is meant by dietary fiber 7. Give two examples of dietary fiber 8. Describe two reasons for the inclusion of dietary fiber in a healthy diet 9. Compare the structural properties of starch and cellulose 10. Explain why humans cannot digest cellulose 11. Describe aerobic respiration of glucose in the human body, with reference to oxidation and reduction. 12. The structures of some hormones are shown in Table 22 of the Data Booklet 13. Identify one hormone with a steroid backbone, state where it is produced and outline its specific role in the body. 14. Identify one hormone with a non–steroid backbone, state where it is produced and outline its specific role in the body. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Draw the basic structure of an amino acid Draw the basic structure of a fatty acid Draw the basic structure of a triglyceride What are the basic structural features of a carbohydrate? Explain why amino acids are often optically active 11. How many chiral centers does a molecule of glucose have? 12. Give the kind of reaction, functional group formed and other product for a. Formation of a dipeptide b. Formation of a disaccharide c. Formation of a triglyceride 13. Both carbohydrates and amino acids can form polymers. Why? 14. Give 2 example of a carbohydrate polymer 15. List the 4 levels of protein structure 16. Which level would be considered a polymer? 17. Describe the bonding involved in each level of protein structure 18. List the uses of lipids, carbohydrates and proteins in the body 19. State and explain the following physical properties: a. Solubility in water of vitamin A and C b. Solubility of mono and disaccharides c. Solubility of the amino acids d. Melting points of saturated and unsaturated fats