* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What does the “PASSIVE” device mean
Electrification wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Transformer wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Power factor wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Power over Ethernet wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Transformer types wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Resonant inductive coupling wikipedia , lookup
Surface-mount technology wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic core wikipedia , lookup
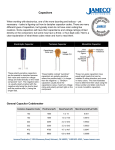
Aluminum electrolytic capacitor wikipedia , lookup
Niobium capacitor wikipedia , lookup
Tantalum capacitor wikipedia , lookup
Capacitor plague wikipedia , lookup
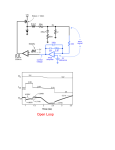
AE1M13VES 16th. January 2014 first name: surname: 1. What does the “PASSIVE” device mean? it can be just resistor, capacitor or inductor, no other devices, device, where output power (Pout) is lower (or equal) than the input power (Pin), device, where input power (Pin) is lower (or equal) than the output power (Pout), all the semiconductor devices, e.g. LED, thyristors etc. 2. What does the “LINEAR” device mean? device, that can be described by means of simple linear formulas and their combinations, device, that can generate harmonic signals and their combinations (intermodulation), device, which behavior is determined by differential equations with both time and coordinate variables, device that exhibits linear dependence between temperature and its resistivity. 3. Which elements (and their combinations) are not often used for common resistors: Gold (Au), Carbon (C), oxides of Pt + Ni, oxides of Fe + Cr + Ni. 4. In which units is given the temperature coefficient of resistivity (TCR)? -1 K-1 K/W J/kg 5. How can we define the dissipation factor (D)? it is an angle between current I flowing trough the capacitor and applied voltage V, it is an angle between voltage V on the capacitor and voltage on the parasitic inductance L of the outlets, it is an parameter responsible for total power losses in the capacitor, it is a self resonance frequency; above this limit capacitor starts to be “more inductance” than the capacitor. 6. Which important materials are used for electrolyte capacitors? Aluminum (Al) or Tantalum (Ta), solution of KOH or H2SO4, Stainless steel (Fe), other ferromagnetic metals (Ni, Cr, Etc.), Carbon (C), Silicon-carbide (SiC). 7. Electrolyte capacitors are typically used: for high voltage and high frequency applications (low power losses needed), as charge accumulators thanks to big specific capacity, as variable capacitors for tuned RF applications, for filtering in AC/DC converters, in power sources. AE1M13VES 16th. January 2014 first name: surname: 8. Variable capacitors are typically made and designed as: rotating parts with an air (dielectric) gap, foil capacitors based on plastic dielectric (PE, PA, PVC, etc.), rolled capacitors with metallization on both electrodes, ceramic capacitors made from ferroelectric (FexOy) or similar dielectric with large permittivity. 9. Inductors, coils and transformers can be made: as a simple air-winding - without any magnetic circuit, only from ferromagnetic cores (Fe, Ni, Cr), only from dia/paramagnetic cores (Al, Mn, Cu), from a copper winding wounded on some ferromagnetic core. 10. Quality factor (Q) of inductor can be defined as: ratio between imaginary and real part of the inductor’s impedance, an angle between flowing current in inductor and voltage on the inductor’s outlets, an product of absolute and relative permeability of used ferrite material, maximum magnetic flux in the middle of the magnetic core.