* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Genes and Natural Selection
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Pathogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Essential gene wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
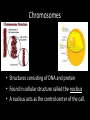
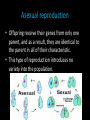
Genes and Natural Selection BY: Shanelle Cabral Sierra Jacoby Brenen Basaldua Who started this • Darwin proposed his theory of evolution, cell division, genes, and chromosomes had not yet been discovered Deoxyribonucleic acid • “DNA” • Double stranded molecule with the shape of a helix. • Contains genetic information known as “genes”. • Capable of copying itself so that the information can be passed from one generation to another. Genes • Is a unit of heredity information • Contains the chemical instructions for making proteins, and these proteins are largely responsible for the structure and function of organisms. Chromosomes • Structures consisting of DNA and protein • Found in cellular structure called the nucleus • A nucleus acts as the control center of the call. Asexual reproduction • Offspring receive their genes from only one parent, and as a result, they are identical to the parent in all of their characteristic. • This type of reproduction introduces no variety into the population. Sexual reproduction • Genes are randomly assorted into new combinations during the formation of sex cells • Sex cells (eggs, sperm, pollen, etc.) are called gametes. • A gene pool is all of the genes in a given population that exist at a given time Fitness • Measured in terms of the number of its own genes that are presented in the next generation of a population.