* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Types_of_Economies - National Trail Local School District
Survey
Document related concepts
Economic planning wikipedia , lookup
Criticisms of socialism wikipedia , lookup
Economic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Ragnar Nurkse's balanced growth theory wikipedia , lookup
Fiscal multiplier wikipedia , lookup
Economics of fascism wikipedia , lookup
Steady-state economy wikipedia , lookup
Production for use wikipedia , lookup
Circular economy wikipedia , lookup
Business cycle wikipedia , lookup
Post–World War II economic expansion wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
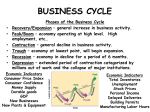
Basic Economic Questions: 1. Which goods and services should be produced? 2. How should the goods and services be produced? 3. For whom should the goods and services be produced? Types of Economies Traditional Economy Traditions and rituals answer basic economic questions What? – Little choice as to what to produce How? – Bound by tradition, follow earlier generations For Whom?- Tradition regulates who buys and sells, and where Market Economy Individuals and businesses own means of production No gov’t involvement in economic decisions What?- Consumers decide what should be produced through purchases How?- Businesses decide how to produce G&S Businesses must be competitive & produce quality products at lower prices For Whom?- People who have more money can buy more G&S People are motivated to work more Command Economy Mixed Economy Gov’t makes economic decisions No economy is purely traditional, market, or command What?- One person (dictator) or group of gov’t officials decide on what products are needed based on what they believe is important How?- Gov’t owns all means of production, it runs all businesses Controls employment and worker benefits U.S. is a mixed economy leaning toward a market economy Gov’t sets laws and regulations that businesses must follow For Whom?- Gov’t decides who will receive what is produced Wealth is shared equally among all people to ensure everyone’s basic needs are met Political Philosophies That Shape Economies Capitalism Communism Characterized by competition in the marketplace and private ownership of business Gov’t concerned about its people and cares for those who cannot care for themselves Authoritarian, gov’t controls the factors of production No private ownership of property or capital Goods owned by gov’t are available to all as needed Society is classless Typically a democratic political system Power should be in the hands of the people Usually more than one political party Examples U.S. Japan All people able to work are assigned jobs Theoretically, there is no unemployment People get paid whether they go to work or not Gov’t decides on schooling and where people live Medicare is free No financial incentive for people to increase productivity Examples Cuba China North Korea Socialism Referred to a system on its way to the communist ideal of a classless society Typically a democratic political system Increased amount of gov’t involvement in economy Main goal- meet basic needs for all and provide full employment More social services to ensure a certain standard of living to everyone Medicare is free or low cost Edu is low cost Pension systems and elderly care Businesses and individuals pay much higher taxes than capitalists countries Gov’t runs all key industries and makes economic decisions State-controlled, noncompetitive companies Examples Canada Sweden Germany GOALS OF A SUCCESSFUL ECONOMY: 1. INCREASE PRODUCTIVITY 2. DECREASE UNEMPLOYMENT 3. MAINTAIN STABLE PRICES Economic Measurements Labor Productivity Gross Domestic Product (GDP) Output per worker hour that is measured over a defined period of time Increasing productivity: Invest in new equipment or facilities Provide training and financial incentives Reduce workforce and increase responsibilities Specialization and division of labor Output of G&S produced by labor and property located within a country GDP made up of private investment, gov’t spending, personal spending, net exports of G&S, and change in business inventories Inflation Rate Rise in prices CPI PPI Unemployment Rate Jobless rate Low inflation rate (1- The higher the 5%) means stable unemployment economy rate, the greater the chances of an Double digit rate economic devastates economy slowdown As inflation increases, The lower the rate, money looses its value the greater the Controlling inflation chances of an is one of gov’ts main expansion goals When inflation is increasing, gov’t raises interest rates to discourage borrowing This slows the economy and brings inflation down Standard of Living Measurement of the amount and quality of G&S and services a nation has. Calculate standard of living by dividing the GDP by its population to get the per capita GDP THE BUSINESS CYCLE Expansion Recession Period of economic slowdown that lasts for at least two quarters Unemployment is low Economy slows Consumer confidence and Businesses lay off workers spending is high Consumer confidence and spending is low Increase in the output of G&S Little demand causes production of G&S to Businesses prosper and invest in new product decrease development and R&D Businesses have little money to invest A peak marks the end of the phase and the beginning a Depression is a prolonged recession and deep recession Time when economy is flourishing Trough Recovery Lowest point in economic activity Period of renewed economic growth Marks the transition from recession to recovery Economy stops slowing May show signs that a recovery is near GDP begins to increase Business picks up People find jobs and begin to spend Unemployment is reduced Moderate expansion of business FACTORS THAT AFFECT BUSINESS CYCLES Business Expansion Expand during recovery or expansion Invest in new properties, equipment, and inventories during expansion Hire more employees during an expansion Recession Curtail operations during recession Cut employees first during a recession Cut back on inventories to match lower demand Consumers Government Expansion/recovery Influence business cycles with policies and programs More optimistic Taxation Spend more on material goods and luxury items Raise taxes—businesses and consumer have less to spend Consumer spending accounts for 2/3 of GDP To boost the economy: Recession Reduce interest rates Fear of losing their jobs Cut taxes Fear of decrease in wages Federally funded programs Causes a loss in consumer When economy worsens: confidence Fed Reserve lowers interest rates to encourage business and consumer Reduced spending causes businesses to reduce operations spending Raise interest rates if inflation is a problem to discourage buying on credit