* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evolution ppt - Duplin County Schools
Survey
Document related concepts
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Sociobiology wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Saltation (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
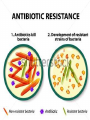
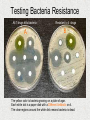
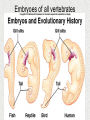
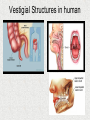
Evolution Fossils indicated that living things have changed. Several scientists had ideas to explain how living organism could change. 1. Lamarck • French scientist • Late 1700 early 1800’s • “Acquired Traits” Theory traits are not determined by genes but by “need”. Ex. Giraffe necks grow longer because they needed to stretch to reach the leaves higher up in the tree. Lamark “Acquired Traits” 2) Charles Darwin • English scientist • Developed his theory of “natural selection” in the mid 1800’s • Was a naturalist on the HMS Beagle (traveled around the world, mostly the southern hemisphere) for 5 years. • Notice organisms had same similarities even when they lived far apart. • Kept records, collected specimens, and published “The Origin of Species”. Voyage of the HMS Beagle Galapagos Islands Galapagos Islands played a big role in Darwin’s thinking! Darwin’s Finches • Good example of how evolution occurs • Each Galapagos Island has its own unique species of finch • Each finch had a head and body well-adapted for life on that island • The finches were different species, but looked similar Adaptive Radiation Evolutionary Tree (cladogram) •Darwin realized that the finches had a common ancestor •He proposed that originally a few seed-eating finches had flown to the islands from mainland. Over millions of years, the finches adapted to the foods available on each island – and evolved into separate species. Adaptive radiation is a type of Divergent Evolution Adaptive radiation is a type of divergent evolution where a group of organisms quickly diverges into new species. Galapagos Tortoises Adaptive Radiation Darwin’s ideas that served as a basis for theory of natural selection 1. All organisms produce more offspring than can survive. 2. Population numbers remain fairly constant over long periods of time. 3. Organisms in a species show wide variation. 4. Some variations are inherited and passed on to the next generation. Units of Variation • Genes carry inheritable characteristics, also source of random variation – crossing over • Mutations cause variation – missing letters in DNA Then Darwin made 2 deductions: 1. Since most offspring don’t survive, all organisms must have to struggle for survival. (Others are eaten, or die of disease.) 2. The ones who survive and reproduce will pass on their genes. Survival of the Fittest! Mutations play big role in natural selection Rabbit Tale Maybe once upon a time all rabbits had short ears and managed OK. Then one day a mutant with big ears was born. She was always the first to dive for cover. Pretty soon, she had babies; some inherited her big ears. They all dived for cover as fast as their mom – faster than the short earred rabbits. Eventually, only the big earred rabbits are left. Natural Selection Nature selects those that are best adapted to survive. “Survival of the Fittest” Any adaptive advantage (a favorable trait) that an organism has is passed to offspring. Example of evolution through natural selection Cockroaches Over the centuries, as man and cockroaches have shared homes, cockroaches have become smaller and flatter – easier access to hiding places. (Large, fat ones more easily stomped.) Another example – Antibiotic Resistance by natural selection • Someone gets sick • Give them antibiotics • 99% of the bacteria are killed; only the antibiotic resistant mutants survive • They thrive and flourish • Person gets sick again • Bacteria cannot be killed by antibiotics What is this graph telling us? Testing Bacteria Resistance All 7 drugs kills bacteria A Resistant to 4 drugs B The yellow color is bacteria growing on a plate of agar. Each white dot is a paper disk with a Different Antibiotic on it. The clear regions around the white disk means bacteria is dead. Evidence of Evolution • • • • • Fossils Similarity of embryos Homologous and analogous structure Vestigial structures Similarities in macromolecules Fossils – tell us that organisms that once lived on Earth are not here any more. Embryoes of all vertebrates are similar – common ancestor Homologous Structures – similar structures with similar functions. Suggest a common ancestor. Vestigial Structures • Examples: appendix, wisdom teeth, human tail bone • Interpretation: the vestigial structure was functional in some ancestor of the modern organism • Snakes have pelvic bones; they are known to be the descendants of four-legged reptiles. Vestigial Structures in Animals Vestigial Structures in human Similarities in Macromolecules • Natural Selection Beneficial mutations new genetic traits (adaptive traits) advantage in a changing environment produce more offspring with those traits. • Through time these adaptive traits become more common in a population. • Evolution is the change in genetic makeup of a population through successive generations. • New species can be formed, or if they cannot adapt they will die off or become extinct. • Biodiversity is a result of the ongoing processes of evolution and extinction. Adaptive Radiation Many related species evolve from a single ancestral species Examples: Galapagos tortoises, Darwin’s finches, Hawaii Honeycreepers. Adaptive Radiation Lonesome George Near losses… The cheetah, Acinonyx jubatus, is the sole member of its genus. Twenty thousand years ago, cheetahs roamed four continents. About 10,000 years ago - because of climate changes - all but one species of the cheetah became extinct. With the drastic reduction in their numbers, close relatives were forced to breed and the cheetah became genetically inbred. This means all cheetahs are closely related.