* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Honors Chemistry
Nuclear chemistry wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Bent's rule wikipedia , lookup
Resonance (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Lewis acid catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Atomic nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Bioorthogonal chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Nucleophilic acyl substitution wikipedia , lookup
Computational chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical reaction wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Metastable inner-shell molecular state wikipedia , lookup
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Chemistry: A Volatile History wikipedia , lookup
Inorganic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Coordination complex wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Electronegativity wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital diagram wikipedia , lookup
Photoredox catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Atomic orbital wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Periodic table wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular theory wikipedia , lookup
Organosulfur compounds wikipedia , lookup
Extended periodic table wikipedia , lookup
Stoichiometry wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Hypervalent molecule wikipedia , lookup
Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
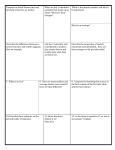
1 1st Semester Final Study Guide Glencoe: Honors Chemistry Chapters 1-6, 8-11 and 25 Chapters 1 & 2: Intro to Chem & Data Analysis 1. What is the difference between a number and a quantity? Give an example of a quantity. 2. Give the SI units and their abbreviations for the following: length, mass, time, temperature and amount of substance. 3. Give the SI prefixes and their relationship with the base unit. Table 1-2. 4. How many centimeters are in 3.1232 x 1016 nanometers? 5. What are significant figures? How many SF are in 4.500060 cm? 0.0036030 ft? 3.980200 x 1017 mm? 6. What is the rule for SF in calculations such as multiplication, division, addition and subtraction? What is 0.760 cm + 367.8 cm? What is 609 g / 1020 mL? 7. What is the density of a 7.9 lb rock that occupies 78 L of water? 8. Using dimensional analysis: How many mm are in 789.5 inches? How many torr are in 103.5 kPa? How many K are in 203.78C? 9. Distinguish difference between a chemical and physical change? Give examples. 10. Draw a picture at the molecular level for a solid, liquid and gas. Describe the movement of atoms/molecules in each. Chapter 3: Matter 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Define the following: atom, molecule, ion, mixture, element and compound. What is a pure substance? Distinguish between a homogenous and a heterogeneous mixture. Give examples of both. What are the seven diatomic molecules? What is a binary compound? What the difference between a nonmetallic and metallic (ionic) compound? How are they named? (See notes in “Naming Compounds”.) 7. What are the names of SO6 and Mg(NO3)2? What are the formulas for ammonium hydroxide, nitrogen pentoxide and copper (II) chloride? Study the entire ion sheet. (See notes in “Naming Compounds”.) 1 2 Chapter 4 & 5: The Structure of the Atom & Electrons in an Atom 1. 2. 3. 4. What are the 3 subatomic particles of the atom? What did Dalton’s Atomic Theory say? What as Thomson’s Plum Pudding Theory? Describe Rutherford’s gold foil experiment. How did it improve on Dalton’s and Thomson’s theories? 5. What is an isotope? 6. How can the number of protons be determined? Neutrons? Electrons? 7. Determine the # of p+, no and e- in the following: oxygen-14, 356210XY34- and Astatine. 8. Draw a wave. Label the wavelength and amplitude on your drawing. 9. What are the colors that make up white light? 10. Give the different waves of the magnetic spectrum. 11. Which wave has more energy: red or blue? Short or long? Microwave or x-ray? 12. What does Bohr’s Model say about the hydrogen atom? 13. What does it mean when an electron is excited? What happens when the excited electron returns to the ground state? 14. What are the 4 sublevels of orbitals that can determine the shape of the orbitals? 15. In order to give an electron an address it must be a given a quantum number with 4 different parts. What are these 4 numbers? 16. Write the electron configurations for the following: carbon, beryllium, chloride ion and magnesium ion. Draw the diagram for the magnesium ion. Chapter 25: Nuclear Chemistry 1. What are the 3 types of radiation? What are the particles emitted from each? 2. Write the nuclear equation for the bombardment of uranium with beta particles (show equations for both positron and electron bombardment.) 3. Titanium-51 decays by negative emission with a half-life of 6 minutes. How much of a 48.0 gram sample would be left after one hour? 4. Compare and contrast some characteristics of fusion and fission. 5. Why would a tracer with a shorter half-life be more beneficial than one with a long halflife? Ch 6: The Periodic Table 1. What are some characteristics of nonmetals? Where are they located? What are their charges in ion form (trends)? 2. What are the electron configurations for S, Co, Ba, K+ and Br-? What is the scheme for remembering the e- configurations? 3. What are the 6 different chemical families in the periodic table? 4. What are the trends for charges of ions when looking at the periodic table? 5. Which region of the periodic table has metals? Nonmetals? Semimetals? 6. Define isoelectronic. What element is isoelectronic with Ba2+? 7. Draw a rectangle to show the periodic table. Draw dots to show increasing trends of electronegativity, atomic and ionic radius and ionization energy. 2 3 Chapter 8 & 9: Ionic & Covalent Bonding 1. 2. 3. 4. Where are the 3 different types of bonds? What are the differences between them? How is the bond determined to be any of the three? What type of bond is present in CaCl2, CO2, SO2 and NH3? What is the difference between a polar and a nonpolar molecule? Give an example of each. 5. What are the different molecular shapes? Give one example for each. Chapter 10: Chemical Reactions 1. What are the four indications that a chemical reaction has taken place? 2. List the 5 types of reactions. 3. What shows that a reaction will take place in a single replacement reaction? Double replacement reaction? What charts or graphs must be used? 4. Chapter 10 Problems #14, 17, 21, 26. Highlight the numbers for each of these problems. Chapter 11: The Mole 1. What does a mole measure? 2. What is the molar mass of CO2 and NH4NO3? 3. Conversion of mass to moles: How many moles are in 3.9 kg CaSO4? 3.99 mg LiNO3? 790 cm3 water? 4. How many molecules are in 1 mol of NaOH? 2.5 mol CO2? How many ions are in Ca(OH)2? 5. What are the units for molarity? (Pages 464-466.) How many grams of copper (II) sulfate are needed to prepare a 3.00L of a 1.50 M solution? 6. Calculation of % mass. What are the %’s of each element’s mass in NaNO3? 7. What is the empirical formula of a sulfur oxide compound that is 50% sulfur by mass? 8. A 0.725 gram sample of oxalic acid was found to contain 0.194 grams of carbon, 0.016 grams of hydrogen and 0.516 grams of oxygen. If the molar mass of oxalic acid is 90.04 g/mol, what is the molecular formula? 3