* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 2, Section 2 – Features of the U
Survey
Document related concepts
Ragnar Nurkse's balanced growth theory wikipedia , lookup
Participatory economics wikipedia , lookup
Criticisms of socialism wikipedia , lookup
Economic planning wikipedia , lookup
Economic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Economics of fascism wikipedia , lookup
Post–World War II economic expansion wikipedia , lookup
Steady-state economy wikipedia , lookup
Social market economy wikipedia , lookup
Economic calculation problem wikipedia , lookup
Market socialism wikipedia , lookup
Production for use wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
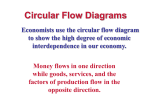
Chapter 2, Section 2 – Features of the U.S. Economy Our economic system (Capitalism) gives individuals opportunities that other systems do not. Use your text to complete the following: We can own private property How is this different from other economic systems? and enter into contracts. What are some items that are your private property? What might be considered a business’s private property? What role does a contract play in protecting property rights? We can make individual choices. List the groups that are allowed to make choices in our economy. Give examples of the types of choices that these groups can make. We can engage in economic competition. What does competition between producers encourage? What does competition between consumers encourage? We can make decisions based on self-interest. Why is this important? How does this help the economy? We can participate in an economy with limited government involvement and regulation. Who makes most production decisions in our economy? What limited role does government play in our economy? (Government involvement is what separates our capitalist system from a pure market economy where anything goes!) Economic Actors in Free Enterprise Producers use factors of production to satisfy wants and needs of society. Consumers influence production by purchasing certain goods and services, but not others. Government oversees and regulates economic activity. All three interact in a market system. The goal of this market system is to answer the questions – what, how, and for whom to produce. The system uses exchange to accomplish this goal. Economists call this market system the Circular Flow of Goods and Services. The Circular Flow Model Look at Figure 2.2 at the top of page 34. This is a very simplified view of the way the U.S. economy functions. Notice that there are two markets illustrated here. The product market is colored green and the resource market is colored gold. Also notice that the three basic economic actors are included in the chart: 1. Government (the regulators); 2. Business (producers); 3. Households (consumers). Let’s take a look at how it operates. Product Market 1. What is being exchanged between government and business? 2. What is being exchanged between business and households? 3. What is being exchanged between households and government? Resource Market 1. What is being exchanged between government and business? 2. What is being exchanged between business and households? 3. What is being exchanged between households and government?