* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Type of Infectious Agent
Survey
Document related concepts
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Chagas disease wikipedia , lookup
Schistosoma mansoni wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
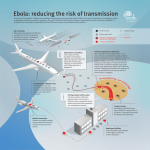
Ebola virus disease wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Brucellosis wikipedia , lookup
Cryptosporidiosis wikipedia , lookup
Tuberculosis wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Plasmodium falciparum wikipedia , lookup
Leishmaniasis wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
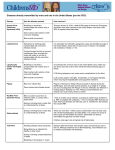
Type of Infectious Agent Disease Examples Modes of Transmission Methods of Prevention How the Agent Reproduces How the Agent is Treated Bacteria Tuberculosis airborn In the lungs antibiotics Strep throat Skin contact Keep infected individual in controlled area syphillis Surface contact Washing hands Sexual contact Not sharing food or drink In the throat Skin contact Not engaging in sexual activities with an infected person Viruses Rhinovirus Rotavirus influenza Airborn and skin contact, sharing objects with infected surfaces like phones and toys. Hand-to-mouth contact Airborn Contaminated water Infected individuals should cough into sleeve and do not share things that come in contact with mouth or nose Throughout the body No treatment for the common cold or rotavirus Antiviral medications for flu Washing hands Washing hands after using restroom and after changing child’s diaper. Skin contact Fungus Histoplasmosis Ringworm Athlete’s Foot Spores become airborn and are inhaled Skin to skin contact Wearing masks during demolition and landscaping. Wash hands Lungs Skin Antifungal drugs feet Wear shoes in public areas Wearing contaminated clothing, shoes Walking barefoot in public areas Protozoa Malaria Giardiasis Cryptosporidiosis Blood to blood through mosquitoes, needles, and blood transfusions. Person to person, infected water, Bug spray Not sharing needles. Being in an area that does not have malaria. Washing hands Avoiding Damages red blood cells Antimalarial drugs Intestines Medication Anti-motility drugs, and fluid replacement therapy. contaminated water and people Helminthes Ascariasis Trichinosis tapeworm Prions CreutzfeldtJakob Disease Come in contact with soil mixed with infected human feces Prevented by cleaning food before eating it Food or water contamination avoid undercooked, infected meat (pork, bear, walrus, or horse) Protein mutation caused by genetics Avoid exposure to infected tissue during a medical procedure Being exposed to contaminated tissue In intestines and lungs Anti-parasite medications Muscles and blood stream Stomach and intestines Proteins No treatment