* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download July 2010
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Electric power system wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Wireless power transfer wikipedia , lookup
Power factor wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Induction motor wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Brushed DC electric motor wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
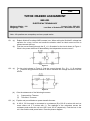
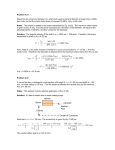
DME TUTOR MARKED ASSIGNMENT BET-022 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS Maximum Marks : 100 Weightage : 30% Course Code : BET-022 Last Date of Submission : November 15, 2010 Note : All questions are compulsory and carry equal marks. Q.1 (a) Define the following terms : (i) Factor of Safety (ii) Shear Stress and Shear Strain (iii) Modulus of Elasticity (iv) Resilience (v) Strain Energy (b) A tensile test is carried out on a bar of mild steel of diameter 2.25 cm. The bar yields under load of 8 x 104 N; it attains a maximum load of 15 x 10 4 N breaks finally at a load of 7 x 10 4 N. Estimate (i) tensile stress at yield point (ii) ultimate Stress (iii) average stress at breaking point if the diameter of the neck is 1.2 cm. Q.2 (a) A Steel tube 3.2 cm internal diameter, 0.25 cm thick and 4 m long is covered and lined throughout with copper tubes of 0.508 cm thick. The three tubes are firmly united at their ends. This compound tube is subjected to tension and stress produced in the steel tube is 60 MPa. Determine (a) the elongation of the tube, (b) stress in the copper tube, (c) load carries by the combined tubes. Take Es = 2.1 1011 Pa and Ec =1.1 1011 Pa. (b) The efficiencies of longitudinal and circumferential joints in a cylindrical drum are 75% and 40% respectively. The drum is 2250 mm long with wall thickness 12 mm. Find the safe air pressure if the allowable stress in the shell material is 120 MPa. Q.3 (a) Discuss the various types of beam with suitable examples. (b) A beam 8.0 m long made of wood with a square cross-section (400 mm) is floating in sea water. Two equal just sufficient weights are placed on the beam at 2.0 m away from each end to immerse in the sea. Find the magnitude of the weights. Also draw S.F.D and B.M.D for the beam. Take unit weight of timber and sea water 6400 N/m and 10200 N/m respectively. Q.4 (a) A simply supported beam having circular cross-section of diameter 0.01778 m is loaded by the two concentrated load of 88.96 KN each applied 0.3048 from the ends of the beam. Determine the maximum flexural stress in the beam. (b) Write some important points showing some characteristics of shear force and bending moment diagrams. Q.5 (a) (b) Q.6 (a) (b) Q.7 (a) A beam of hollow square cross-section (5 cm x and 5 cm) with 0.6 cm uniform thickness is subjected to shearing force 50 KN in the direction of one of the diagonal of the cross section. Determine maximum shearing stress developed and draw shearing stress distribution across the section. Discuss the assumptions made in case of pure symmetrical bending. Derive differential equation of deflection curve in a beam. Draw the shear stress distribution diagram for a channel section (12 cm x 6 cm x 1.5 cm) of a beam subjected to shear force 50 KN at a Section. Also find the ratio between the maximum and minimum shear stresses. Derive the following expression, considering the theory of torsion. T G . J L (b) A solid circular shaft transmits 75 KW power at 200 r.p.m. Find the suitable diameter of the shaft if the twist in the shaft not to exceed 10o in 2 meters length and shear stress is limited to 50 MPa. Take G = 100 MPa. Q.8 (a) A flat steel bar, 25 mm wide by 6mm thick and 1 m long is bent by couples applied at the ends so, that the mid point deflection is 20 mm. compute the stress in the bar and magnitude of the couples. E = 200 GPA. (b) Determine Euler’s Crippling load for I-section just 40 cm x 20 cm x 1 cm and 5 m long which is used as a column with both ends fixed. E = 2.0 X 105 MPa. Q.9 (a) (b) Q.10 (a) (b) Discuss the Buckling Load and Slenderness Ratio. An Allowable axial load for a column of a length l with both ends fixed is 30 KN. Three different columns made of same material, same length and section having the following end conditions : (i) Both the ends are hinged, (ii) one end is fixed other end is free and (iii) one end is fixed, other end is hinged. What are the allowable loads for the three columns with conditions given above? Discuss the Euler Theory of column. A Thin cylindrical Shell of diameter 500 mm and wall thickness t is subjected to an internal pressure of 2 N/mm2. Determine the thickness of the cylinder according to the maximum principal stress taking factor of safety as 3, if the yield strength of the material. DME TUTOR MARKED ASSIGNMENT BCE-025 ELEMENTARY CIVIL ENGINEERING Maximum Marks : 100 Weightage : 30% Course Code : BCE-025 Last Date of Submission : November 15, 2010 Note : All questions are compulsory and carry equal marks. Q.1 (a) (b) Q.2 (a) (b) Q.3 (a) (b) Q.4 (a) (b) Q.5 (a) (b) Q.6 (a) (b) Q.7 (a) Explain in detail the terms PERT and CPM used in construction planning. Write a note on curing of concrete. Discuss the common building stones and their uses. Discuss and draw the double Flemish and English bond for double brick. Explain in brief the construction of Cement Concrete road. Discuss the commonly used paints in building constructions. Discuss the types of hot rolled bars. Discuss the different types of valves with sketch, used in water works practice. Give a brief account of the sealants and joints fillers used in building construction. Explain in brief plate load test with the help of a neat sketch. What are the various features to be considered while locating window. Enlist the different types of stairs with labeled sketches. What are the types of doors? Draw labeled sketch. (b) Write significance of wind-rose diagram with reference to airport engineering. Q.8 (a) What is revetted joint? Explain the types of the revetted joint with neat sketch. (b) Q.9 (a) (b) Q.10 (a) (b) What is bulking of sand? Explain with sketch. Write a difference between determinate and indeterminate structures. Discuss the stages of survey in a highway alignment. What is meant by foundation? Explain the functions of foundation. Explain orthographic projection with suitable example. DME TUTOR MARKED ASSIGNMENT BEE-031 ELECTRICAL TECHNOLOGY Maximum Marks : 100 Weightage : 30% Course Code : BEe-031 Last Date of Submission : November 30, 2010 Note : All questions are compulsory and carry equal marks. . Q.1 (a) Explain Kirchhoff’s voltage AND currents Law. When writing the Kirchhoff’s voltage law equation for a loop, how do we handle the situation when an ideal current source is present around the loop. (b) Find the current flowing through the RL = 1 k Ω resistor for the circuit shown in Figure 1. What is the power delivered or absorbed by the independent current source? Figure 1 Q.2 (a) For the circuit shown in Figure 2, find the current through R2 = RL = 1 k Ω resisters (Ia – b).Branch using Norton’s theorem & hence calculate the voltage across the current source. Figure 2 (b) Q.3 (a) (b) Give the statements of the following theorems. (i) Superposition Theorem (ii) Thevenin’s Theorem. Explain and prove Maximum power transfer theorem. A 200 V, 50 Hz supply is connected to a resistance (R) of 20 Ω in series with an iron cored choke coil (r in series with L). The readings of the voltmeters across the resistance and across the coil are 120 V and 150 V respectively. Find the loss in the coil. Also find the total power factor. Draw the phasor diagram. Q.4 (a) Find the input voltage at 50 Hz to be applied to the circuit shown in Figure 3 such that the current in the capacitor is 8 A? Figure 3 (b) Q.5 (a) (b) Explain the condition of resonance in RLC series circuit. Enlist the effect of resonance in the circuit. Draw the complete phasor diagrams of a single phase transformer when : (i) the load in the secondary is purely resistive, and (ii) secondary load power factor is leading. In Figure 4, the ideal transformer has turns ratio 2 : 1. Draw the equivalent circuits referred to primary and referred to secondary. Calculate primary and secondary currents and the input power factor and the load power factor Figure 4 Q.6 (a) An ideal autotransformer steps down a 400 V, single phase voltage to 200 V, single phase voltage. Across the secondary an impedance of (6 + j8) Ω is connected. Calculate the currents in all parts of the circuit. (b) A 4-pole, lap wound, DC machine has total number of 800 armature conductors and produces 0.03 Wb flux per pole when field is excited. If the machine is driven by a prime mover at 1000 rpm, calculate the generated EMF across the armature. If the generator is loaded to deliver an armature current of 50 A, Calculate the prime mover and electromagnetic torques developed at this load current. Neglect frictional torque. Q.7 (a) A d.c motor takes an armature current of 50 A at 220 V. The resistance of the armature is 0.2 Ω. The motor has 6 poles and the armature is lap wound with 430 conductors. The flux per pole is 0.03Wb. Calculate the speed at which the motor is running and the electromagnetic torque developed. (b) Derive the expression for the generated voltage in a d.c generator. Write down the expression for electromagnetic torque in a d.c motor. Q.8 (a) (b) Draw and explain the Torque- Slip characteristic of 3-phase Induction Motor. Give the various methods of starting of single phase motor. Explain any one of them. Q.9 (a) Explain the working principle of synchronous motor with neat sketch. Give its applications. (b) The armature of 8 pole, 3-phase,50 Hz alternator has 17 slots and has 10 conductors per slot. There are 0.04 Wb entering the armature from 1 pole.Assume the flux to be distributed sinusoidal along the air gap. Calculate the induced EMF per Phase. Q.10 (a) (b) Show the phasor diagram of alternator for Leading power factor. Give the advantage of rotating field generator. DME TUTOR MARKED ASSIGNMENT BET-034 MACHINE DRAWING Maximum Marks : 100 Weightage : 30% Course Code: BET- 034 Last Date of Submission: November 30, 2010 Note : All questions are compulsory and carry equal marks. Q.1 (a) What are the two systems of placing dimensions on a drawing? Explain them with suitable sketches. (b) Explain the difference between Isometric projection and oblique projection with suitable diagrams. Q.2 (a) Draw the front view, side view and top view of the hexagonal prism with 50 mm side and 200 mm height. Assume one face of the prism is parallel to vertical plane. (b) Describe about the sectional view with suitable examples. Q.3 (a) Two 8 mm thick plates are bolted by passing the 10 mm major diameter bolt through 11 mm diameter hole. The nut is tightened on top. Draw the dimensioned front view. (b) Draw a bolted joint in section (front view) between circumference of a cylinder and cover. Cylinder diameter = 400 mm. Number of bolts 12. Pitch circle diameter of bolts = 480 mm, M 20 bolts with d = 20mm, p = 2.5 mm and d1 = 17.3 mm is tube used. Q.4 Draw two suitable views of Eye Foundation bolt (D = 25 mm) of Figure 1. Figure 1 Q.5 (a) (b) Q.6 (a) Two 20 mm thick plates are joined in double riveted but joint. Find the rivet hole diameter, margin, pitch and back pitch for chain riveting, draw the front sectional view and plan. What is welded joint? Explain the types of the welded joint with neat sketch. Explain with the help of sketches, the use of (i) a woodruff key and (ii) a cone key. (b) On a 35 mm diameter shaft carries a pulleys of 900 mm diameter whose hub tapers from 75 mm at the arm to 70 mm at the edge end is 80 mm long. Four arms, elliptic in section from a1 = 26 mm to a = 20 mm and b1 = 12 mm to b = 30 mm. Show the assembly of pulleys with gib headed key and with part of shaft whose diameter increases to 45 mm from 35 mm suddenly with radius of 5 mm at the corner. The width of the pulleys is 1000 mm with 9 crown of 3 m. Rim thickness at edges, 8 mm. Q.7 (a) Make a neat dimensioned sketch of a flanged joint for two 100 mm diameter C.I. Pipes. (b) What is bearing? Explain the types of the bearing with neat sketch? Q.8 The details of screw jack are given in Figure 2. Assemble the parts and draw elevation plan side view of the assembly. Figure 2 DME TUTOR MARKED ASSIGNMENT BME-052 BASICS OF THERMAL ENGINEERING Maximum Marks : 100 Weightage : 30% Course Code : BME-052 Last Date of Submission : November 15, 2010 Note : All questions are compulsory and carry equal marks. Q.1 (a) What is thermodynamics? Explain the first law of thermodynamics with suitable example. (b) State explains Zeroth law of thermodynamics. Distinguish between intensive properties and extensive properties by giving examples. (5 + 5 = 10) Q.2 A system receives 200 kJ of heat at constant volume. Then it is cooled at constant pressure, when 50 kJ of work has done on the system while it rejects 70 kJ of heat. Supposing the system is restored in the initial state by an adiabatic process, how much work will be done by the system? (10) Q.3 (a) Steam initially at 1.5 MPa, 300oC expands reversibly and adiabatically in a steam turbine to 40oC. Determine the ideal work output of the turbine per kg of steam. Show the process on T-s and h-s diagram. (b) A pressure cooker contains 1.5 kg of dry saturated steam at 5 bar. Find the quantity of heat which should be removed to reduce the quality of steam to 60% dry. (5 + 5 = 10) Q.4 What is a boiler? How the boilers are classified? Describe the working of Cochran boiler with neat diagram. Also explain some of its applications. (10) Q.5 (a) What is rankine cycle? Describe the effects of pressure and temperature on rankine cycle. (b) Steam enters the turbine of reheat rankine cycle at 5 MPa, 400 oC. After expansion in the turbine to 4 bar it is taken to a reheater and heated at 400oC and sent to the low pressure turbine. If the condenser pressure is 10 KPa, determine the cycle efficiency. (3 + 7 = 10) Q.6 (a) What is a condenser? What are the types of condensers? Using a neat sketch, explain the construction and working of surface condenser. (b) Briefly describe the construction and working of any one type of induced draft type cooling tower. (5 + 5 = 10) Q.7 (a) What are the functions of air pre-heater, economizer and re-heater in a power plant? Explain in detail the feed water-steam circuit. (b) Define conduction, convection and radiation? What is a black body? Also explain the Stefan-Boltzmann law of thermal radiation. (5 + 5 = 10) Q.8 (a) What is solar energy? Give some applications of solar energy. Describe the construction of solar flat plate collector. (b) Draw neat sketch of a tidal power plant and explain the construction and working. Also list the advantages and limitations of a tidal power plant. (5 + 5 = 10) Q.9 (a) (b) When a stationary mass of gas was compressed without friction at constant pressure its initial state of 0.4 m3 and 0.105 MPa was found to change to final state of 0.20 m3 and 0.105 MPa. There was a transfer of 42.5 kJ of heat from the gas during the process. Find, how much did the internal energy of the gas change? A cylinder containing the air comprises the system. Cycle is completes as follows : (i) 82000 Nm of work is done by the piston on the air during compression stroke and 45 kJ of heat are rejected to the surroundings. (ii) during expansion stroke 100000 Nm of work is done by the air on the piston. Calculate the quality of heat added to the system. (4 + 6 = 10) Q.10 (a) If a barometer stands at 760 mm and condenser vacuum is at 710 mm and temperature is 30oC, calculate the mass of air per kg of uncondensed steam. (b) Steam enters a condenser at 36oC and with barometer reading 760 mm. If the vacuum of 695 mm is produced, find the vacuum efficiency. Use steam tables.