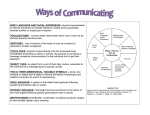
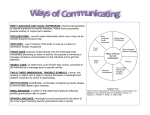
* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download NOTE: The provided figures may be useful and beneficial
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
If there are “CUES” listed within the question, please USE them and UNDERLINE them in your answer! Chapter 13 1. Use Figure 13.3 to discuss a karyotype and how it is used. (CUES: sister chromatids, genome, genetic disorders, non-disjunction) 2. Use Figure 13.7 to summarize the major steps in meiosis. Be sure to differentiate between homologous chromosomes and sister chromatids. 3. IN YOUR OWN WORDS compare & contrast mitosis & meiosis. Use Figure 13.9 in your comparison. (CUES: diploid, haploid, homologous chromosomes, sister chromatids, tetrads, clone, gamete) 4. Describe in detail how independent assortment, crossing over & random fertilization each contribute to genetic variation within a species. Chapter 14 1. Use Figure 14.3 & 14.5 to explain the genetics of how 2 same-colored flowers can produce flowers of different colors (Law of Segregation). (CUES: heterozygous, homozygous, alleles) 2. In a population of pea plants in a greenhouse, self-pollination can occur. Refer back to Concept 13.1 and explain whether self-pollination is considered asexual or sexual reproduction. Please address your reasoning for why it is one and not the other. 3. Use Figure 14.7 to describe a testcross and how it is used. (CUES: homozygous dominant, heterozygous, homozygous recessive, genotype, phenotype) 4. Use Figure 14.8 to explain Mendel's Law of Independent Assortment. (CUES: genetic variation) 5. Use Figure 14.10 to explain incomplete dominance. (CUES: genotype, phenotype) 6. Use Table 14.2 to explain blood type & multiple alleles. 7. Use Figure 14.11 to explain epistasis. 8. Use Figure 14.12 to explain the role of polygenic inheritance. 9. What is the norm of reaction? (CUES: blood type, skin color, multifactorial) 10. Explain the following recessively inherited diseases in humans: Tay-Sachs, cystic fibrosis, & sickle-cell disease. 11. Explain the dominantly inherited diseases in humans: Huntington's Disease & achondroplasia. 12. Explain the various types of genetic tests that are used for genetic counseling, including amniocentesis and CVS. Chapter 15 1. Use Figure 15.2 to explain how the Laws of Segregation & Independent Assortment lead to the following outcome: Parent w/ genotype YyRr produces gametes w/ genotypes YR, yr, Yr, & yR. 2. Explain the Inquiry & Experiment in Figure 15.4. Include in your answer an explanation regarding why only the males have white eyes. Is it possible for females to have white eyes? Provide a Punnett square as evidence to support your answer. (CUES: dominant, recessive, sex-linked.) 3. Use Figure 15.5 to explain whether the genes for body color & wing type are on the same or different chromosomes. (CUES: parental phenotype, recombinant phenotype, linked genes.) 4. Use Figure 15.6 to discuss recombination of chromosomes due to crossing over. 5. Discuss how recombination frequencies can be used to create a linkage map (Figure 15.7). (CUES: recombination frequency, map unit) 6. Use Figure 15.10 to explain transmission of sex-linked recessive traits in the following scenarios: A) Father has the sex-linked disorder B) Mother is a carrier/Father is normal C) Mother is a carrier/Father has the sex-linked disorder 7. Explain why tortoiseshell cats are almost always female. (CUES: Barr bodies, inactive X, DNA methylation.) 8. Use Figure 15.12 to explain non-disjunction. 9. Use Figure 15.14 to explain different ways chromosome can be altered. “Can Credit” Question Phenylketonuria (PKU) is an autosomal recessive genetic disorder whose symptoms can be reduced by avoiding certain foods in the diet. Explain the following: 1) the symptoms of PKU 2) what causes the symptoms 3) what foods must be eliminated in the diet in order to avoid symptoms.