* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download WHAT INTERNATIONAL MARKETING IS:
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
Ambush marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Bayesian inference in marketing wikipedia , lookup
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Grey market wikipedia , lookup
Market analysis wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Dumping (pricing policy) wikipedia , lookup
Market segmentation wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Perfect competition wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Darknet market wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Segmenting-targeting-positioning wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Services marketing wikipedia , lookup
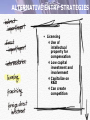
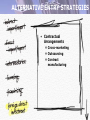
• International Marketing Understand the importance of international marketing Appreciate the opportunities and challenges offered by international marketing Recognize the effect of the global environment on international marketing activities Understand the process of market selection Recognize the process of internationalization. Appreciate the different forms of market entry Comprehend the international adjustment of the marketing mix Understand the steps necessary for the implementation of an international marketing strategy WHAT INTERNATIONAL MARKETING IS: • International marketing is the process of planning and conducting transactions across national borders to create exchanges that satisfy the objectives of individuals and organizations. PLANNING FOR INTERNATIONAL MARKETING • How will my product fit into the international market? • What marketing adjustments are or will be necessary? • What threats from global competition should I expect? • How can these threats be turned into opportunities? Top 25 Multinational Firms • TABLE 3.1 Opportunities • TABLE 3.1 • Integrate global knowledge • Expand long-run production • Lengthen and rejuvenate product life cycles THE INTERNATIONAL MARKETING ENVIRONMENT • Cultural Environment • Socioeconomic Environment • Legal and Political Environment THE INTERNATIONAL MARKETING ENVIRONMENT Cultural Environment Socioeconomic Environment Political/Legal • International marketer surveys: Depth of traditional beliefs and attitudes and dominant cultural elements Power of opinion leaders and change agents Communication from different media Cultural Environment • Four Dimensions of Culture Degree of Individualism Level of Equality Uncertainty Avoidance Material Achievement Four Dimensions of Culture Cultural Environment Socioeconomic Environment • Population Age Distribution Income Infrastructure Socioeconomic Environment Cultural Environment Socioeconomic Environment Political/Legal • Population and its characteristics Aging of world populations for example • Economic Integration NAFTA, EU, MERCOSUR Socioeconomic Environment Socioeconomic Environment Political/Legal • Elderly population boom changes U.S. market characteristics Growth Rate Cultural Environment 3.5 3 2.5 2 1.5 1 0.5 0 1910- 1930- 1950- 1970- 1990- 2010- 20301930 1950 1970 1990 2010 2030 2050 Decades Source: http://www.census.gov/ Legal and Political Environment • Legal and Political Issues Facing Marketers Intellectual Property Rights World Trade Organization (WTO) Common Law Code Law Antidumping Laws Legal and Political Environment Cultural Environment Socio-Economic Environment Political/Legal • Host country Minimum wage legislation Regulatory measures Lack of enforcement • Home country Import/Export restrictions, etc. Legal and Political Environment Cultural Environment Socio-Economic Environment Political/Legal • Intellectual property rights • Common law Vs Code law Tradition/ precedence vs comprehensive written statutes Often a mixture of two systems Legal and Political Environment Cultural Environment Socio-Economic Environment Political/Legal • International Law • World Trade Organization Defines economically acceptable practices for its member nations Intent is to provide stable markets INTERNATIONAL MARKET SELECTION • Identification of Potential Markets • Selectively expanding Screening Process in Target Market Choice • Figure 3.3 Market potential Level of sales that might be available to all marketers in an industry in a given market. Sales potential Share of the market potential that a particular marketer may hope to gain over the long run. Expansion – Concentration versus Diversification • Concentration – market development strategy that involves focusing on a smaller number of markets • Diversification – marketing development strategy that involves expansion to a relatively large number of markets. THE INTERNATIONALIZATION PROCESS Major Motivations to Internationalize Proactive Profit advantage Unique products Technological advantage Exclusive information Tax benefit Economies of scale THE INTERNATIONALIZATION PROCESS Major Motivations to Internationalize Competitive pressures Overproduction Declining domestic sales Excess capacity Saturated domestic markets Proximity to customers/ports Reactive ALTERNATIVE ENTRY STRATEGIES • Indirect Exporting and Importing • Direct Exporting and Importing • Licensing (Franchising) • Foreign Direct Investment ALTERNATIVE ENTRY STRATEGIES • First Tier Direct exporting/importing Indirect exporting/importing Licensing and franchising • Second Tier Foreign Direct Investment Joint ventures Contract manufacturing ALTERNATIVE ENTRY STRATEGIES • Indirect Exporting and Importing Intermediary used to deal with foreign customers or firms Low management commitment Often unintended or unaware ALTERNATIVE ENTRY STRATEGIES • Direct Exporting and Importing Control international activities better Can lead to further growth with trading partners Must find customers, markets ALTERNATIVE ENTRY STRATEGIES • Intermediaries Importers/Exporters frequently use them • Export Management Companies (EMC) • Trading Company ALTERNATIVE ENTRY STRATEGIES • Licensing Use of intellectual property for compensation Low capital investment and involvement Capitalize on R&D Can create competition ALTERNATIVE ENTRY STRATEGIES • Franchising Grant by parent company to independent entity to do business in a prescribed manner Sell franchiser’s products using name and marketing techniques or business approach Franchise must offer high uniqueness with high standardization ALTERNATIVE ENTRY STRATEGIES • Foreign Direct Investment Generally large MNC due to capital and risk factors Need for wide market access remedied by acquisition Circumvent barriers to trade Government incentives ALTERNATIVE ENTRY STRATEGIES • Full Ownership often desirable and often impossible • Joint Venture collaboration between 2+ organizations Share assets, risks, profits Partner brings local expertise, influence ALTERNATIVE ENTRY STRATEGIES • Strategic Alliances Informal or formal arrangements between 2+ companies with common objective Flexible to environmental conditions Pooling of expertise ALTERNATIVE ENTRY STRATEGIES • Contractual Arrangements Cross-marketing Outsourcing Contract manufacturing Complementary Strengths Create Value • Figure 3.4 COMPREHENSIVE VIEW OF INTERNATIONAL EXPANSION • Figure 3.5 International Expansion • 3 Factors to Market Approach Market Characteristics Government regulations Customer characteristics, expectations, and preferences Purchase patterns State of economic development Competitive offerings Climate and geography International Expansion • 3 Factors to Market Approach Market Characteristics Government regulations Customer characteristics, expectations, and preferences Purchase patterns State of economic development Competitive offerings Climate and geography Product Characteristics Product constituents Brand Positioning Packaging Country of origin International Expansion • 3 Factors to Market Approach Market Characteristics Government regulations Customer characteristics, expectations, and preferences Purchase patterns State of economic development Competitive offerings Climate and geography Product Characteristics Company Considerations Product constituents Brand Profitability Positioning Market opportunity Packaging Policies Country of origin International Expansion International Expansion • Mandates most marketing-mix adjustments • Government regulations are most prevalent Standards (language, ISO 9000, etc.) • Product positioning changes International Expansion • Global products Only changes possible are to positioning Product timing based on economic growth • Price competition Foreign exchange factor Extra costs incurred (shipping, etc.) International Expansion • Climate and geography Food product distribution is different in many countries International Expansion • Cannot contain features/ingredients in violation of law/custom • Standardization applied most successfully in culturally similar markets • Promotional features and packaging often varied International Expansion • “Is it worth it?” • Can the company justify internationalization? Adjusting the Marketing Mix • Standardized Approach • Multi-domestic Approach • Globalization Approach Factors Affecting Marketing-Mix Adjustments • Figure 3.6 Product Decisions • Design • Branding • Packaging • Labeling Promotion Decisions • Positioning • Copy Promotion Decisions • Figure 3.7 Distribution Decisions • Tactical and Market-by-market Pricing Decisions • Price Escalation Due to Costs • Foreign-exchange Rates IMPLEMENTING MARKETING PROGRAMS WORLDWIDE • Management Process • Organization Structure IMPLEMENTING MARKETING PROGRAMS WORLDWIDE Headquarters Division C Division B Division A IMPLEMENTING MARKETING PROGRAMS WORLDWIDE • Management Process Information flows between headquarters and country organizations Information flows between country organizations Headquarters Division C Division B Division A IMPLEMENTING MARKETING PROGRAMS WORLDWIDE • Management Process Personnel exchange Headquarters coordinates and leverages combined resources Centralized marketing strategy with local marketing augmentations Certain marketing-mix aspects are left localized (distribution channels, etc.) IMPLEMENTING MARKETING PROGRAMS WORLDWIDE • Organization Structure Matrix style has replaced the country division model Product groups coordinate efforts at headquarters Supplemental Material International Expansion • 3 Ways to Approach International Markets Make no special provisions International Expansion • 3 Ways to Approach International Markets Make no special provisions Adapt to local conditions in each target market (multidomestic approach) International Expansion • 3 Ways to Approach International Markets Make no special provisions Adapt to local conditions in each target market (multidomestic approach Incorporate differences into a regional/global strategy to allow for local implementation (globalization approach)