* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Civics and Economics – Goal 7 – The learner will investigate how
Survey
Document related concepts
Fei–Ranis model of economic growth wikipedia , lookup
Steady-state economy wikipedia , lookup
Rostow's stages of growth wikipedia , lookup
History of macroeconomic thought wikipedia , lookup
Economics of digitization wikipedia , lookup
Supply and demand wikipedia , lookup
History of economic thought wikipedia , lookup
Ragnar Nurkse's balanced growth theory wikipedia , lookup
Chicago school of economics wikipedia , lookup
Production for use wikipedia , lookup
Macroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Ancient economic thought wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
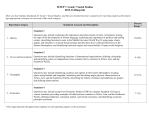
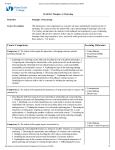
Civics and Economics – Goal 7 – Investigating how and why individuals and groups make economic choices (microeconomics). Objective 7.01: Describing the basic factors of production such as land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurial skills and their impact on economic activities. MAJOR CONCEPTS: Four Factors of Production Basic Economic Questions Efficient Use of Production TERMS YOU WILL NEED TO KNOW: Economics Wants Needs Land Renewable Natural Resources Nonrenewable Natural Resources Labor Capital Entrepreneurship Productivity Objective 7.02: Explaining how scarcity influences producers and consumers to make choices MAJOR CONCEPTS: Scarcity Decision Making Process TERMS YOU WILL NEED TO KNOW: Limited Resources Decision-making Model Services Goods Wages Salary Consumer Producer Pricing Objective 7.03: Compare examples of tradeoffs and opportunity costs of economic choices. MAJOR CONCEPTS: Wants vs. Needs Tradeoffs Opportunity Costs TERMS YOU WILL NEED TO KNOW: Immediate Gratification Incentives Fixed Costs Variable Costs Total Costs Marginal Costs Objective 7.04: Analyze the impact of specialization, division of labor, consumption, and production increases on economic activities MAJOR CONCEPTS: Specialization Division of Labor TERMS YOU WILL NEED TO KNOW: Assembly Line Technologies Robotics Invention Innovation Mass Production Factory Agribusiness Unskilled Workers Automation Consumption Production Business Organizations Specialization Human Capital Productivity White Collar Blue Collar Skilled Workers Objective 7.05: Explaining the impacts of investments on human, capital, productive, and natural resources. MAJOR CONCEPTS: Productivity Investment 1 TERMS YOU WILL NEED TO KNOW: Capital Goods Consumer Goods Consumer Price Index (CPI) Producer Price Index (PPI) Output vs. Input Recycling Education and Training Objective 7.06: Comparing and contrasting how different economic systems address key economic factors. MAJOR CONCEPTS: What to Produce How to Produce It TERMS YOU WILL NEED TO KNOW: Market Economy Mixed Market Economy Command Economy For Whom to Produce It Mixed Economy Traditional Economy Goal 8: Analyzing features of he economic system of the United States. 8.01: Comparing characteristics of command, market, and mixed economies. 8.02: Describing how the free enterprise system encourages private ownership of property and promotes individual initiative. MAJOR CONCEPTS: Mixed Market Economy Economic Goals of the Free Enterprise System ESSENTIAL TERMS: Private Property Voluntary Exchange Patents Copyrights Full Employment Efficiency Productivity Specialization Division of Labor Security Equity Consumer Sovereignty 8.03: Explaining the circular flow of economic activities and haw interactions determine the prices of goods and services. MAJOR CONCEPTS: Factor Market Product Market ESSENTIAL TERMS: Circular Flow of Economic Activity Economic Interdependence Wages Salary 8.04: Illustrating how supply and demand affects prices. MAJOR CONCEPTS: Law of Demand Equilibrium Price/Market Price Law of Supply Law of Supply AND Demand Influences upon Supply and Demand ESSENTIAL TERMS: Demand Curve/Schedule Supply Curve/Schedule Personal Income Disposable Income Complimentary Goods Substitute Good 8.05: Predicting how prices change when there is either a shortage or surplus. MAJOR CONCEPTS: Influences on Prices ESSENTIAL TERMS: Surplus Shortage Consumer Tastes Minimum Wage Inflation Deflation Wage and Price Control Interest Rates 2 Trickle-Down Effect Supply Side Economics 8.06: Explaining how changes in the level of competition can affect price and output levels. MAJOR CONCEPTS: Basic concepts of Capitalism/Free Market ESSENTIAL TERMS: Buyers and Sellers Horizontal Merger Monopoly Vertical Merger Oligopoly Conglomerates Competitive Market Mergers Multinational Conglomerates 8.07: Identifying and Describing the roles and functions of various economic institutions and business organizations. MAJOR CONCEPTS: Types of Business Organized Labor ESSENTIAL TERMS: Sole Proprietorship Partnership Corporation Cooperative Franchise Limited Liability Unlimited Liability Limited Life Unlimited Life Small Business Administration (SBA) Stock Stock Market Dividend Bond Craft Union Industrial Union Collective Bargaining Mediation Arbitration Lockout Strike Social Security Act of 1935 (FDR) National Labor Relations Act, 1935 Fair Labor Standards Act, 1938 Taft-Hartley Act, 1947 Anti-Trust Laws Labor Union 8.08: Evaluating the investment decisions made by individuals, businesses, and the government. MAJOR CONCEPTS: Fiscal Policy Monetary Policy Banking System Types of Insurance ESSENTIAL CONCEPTS: Timed Deposit Investment Spending Demand Deposit Capital Investment Credit Cards Life - Insurance Debit Cards Medical Mutual Funds Comprehensive Commercial Bank Liability Savings & Loan Associations Tight Money Credit Unions Easy Money (FDIC)Federal Deposit Insurance Commission 8.09: Describing the role of money in trading, borrowing, and investment. MAJOR CONCEPTS: Types of Money Function of Money ESSENTIAL TERMS: Collateral Money Barter Coins Currency Check Legal Tender Credit Reserve Requirement Medium of Exchange Pension Funds Mutual Funds 3