* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Linear Pair Postulate
Survey
Document related concepts
Cross product wikipedia , lookup
Riemannian connection on a surface wikipedia , lookup
Tessellation wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Golden ratio wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
Four color theorem wikipedia , lookup
Riemann–Roch theorem wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Noether's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Brouwer fixed-point theorem wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
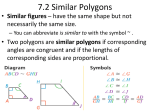
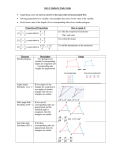
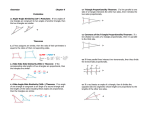
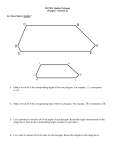
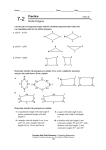
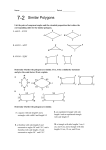
CROSS PRODUCT PROPERTY The product of the means equals the product of the extremes GEOMETRIC MEAN It is the square root of the product. SIMILAR POLYGONS The corresponding angles are congruent. The corresponding sides are proportional PERIMETERS OF SIMILAR POLYGONS If two polygons are similar, then the ratio of their perimeters is equal to the ratios of their corresponding side lengths. This is the scale factor. CORRESPONDING LENGTHS IN SIMILAR POLYGONS If two polygons are similar, then the ratio of any two corresponding lengths in the polygon is equal to the scale factor of the similar polygons. WAYS TO SHOW TRIANGLES ARE SIMILAR AA (Angle – Angle) Similarity Postulate SSS (Side – Side – Side) Similarity Theorem SAS (Side – Angle – Side) Similarity Theorem TRIANGLE PROPORTIONALITY THEOREM If a line parallel to one side of a triangle intersects the other two sides, then it divides the two sides proportionally. CONVERSE OF THE TRIANGLE PROPORTIONALITY THEOREM If a line divides two sides of a triangle proportionally, then it is parallel to the third side. THEOREM 6.6 If three parallel lines intersect two transversals, then they divide the transversals proportionally THEOREM 6.7 If a ray bisects an angle of a triangle, then it divides the opposite side into segments whose lengths are proportional to the lengths of the other two sides.