* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AP Study Guide for Behavior/Ecology Unit Test
Soundscape ecology wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Deep ecology wikipedia , lookup
Nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
Ecosystem services wikipedia , lookup
Ecogovernmentality wikipedia , lookup
Human impact on the environment wikipedia , lookup
Ecological resilience wikipedia , lookup
Pleistocene Park wikipedia , lookup
Blue carbon wikipedia , lookup
Agroecology wikipedia , lookup
Natural environment wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Restoration ecology wikipedia , lookup
Cultural ecology wikipedia , lookup
Reconciliation ecology wikipedia , lookup
Lake ecosystem wikipedia , lookup
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
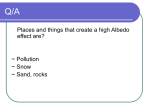
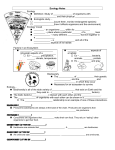
AP Study Guide for Behavior/Ecology Unit Test Chapter 52 – Population Ecology What is meant by a population? Exponential and Logistic growth patterns and reasons The meaning of N and K Carrying capacity Survivorship Curves Characteristics of r and k selection Demographic Transition and Human Populations Causes and Issues Age Structure Diagrams Ecological Footprint and comparisons for various countries Chapter 53 – Community Ecology What is meant by a community along with community interactions: Symbiosis (mutualism, parasitism and commensalism) competition, predation, herbivores, importance of carnivores, decomposers/detritivores Trophic structures and Energy Transfer and Biomass Food Chains and Food webs Invasive species and their consequences Importance of Biodiversity and reasons for loss Chapter 54 – Ecosystems What is meant by an ecosystem? Heterotrophs and autotrophs (photoautotrophs and chemoautotrophs) Primary, secondary consumers, etc. Roles/niches Herbivores and carnivores. Their roles/niches Matter and Energy movement through ecosystems and their differences Photosynthesis vs. Cell Respiration: reactants, products, organisms that do these Importance of Cyanobacteria Effect of nutrient enrichment and Eutrophication Meaning of gross and net primary production and how they are determined Ecosystem with the largest overall production vs. per area production and why Limiting Factors of Primary Production Nutrient Cycles: carbon, nitrogen, (nitrogen-fixation, denitrifying), water How fossil fuels were formed and what exactly they are Human effects on ecosystems: nitrogen cycle, carbon cycle, deforestation, biological magnification global warming vs. greenhouse effect and climate change Importance of organic farming Thermodynamic Laws and how they are applied to trophic levels