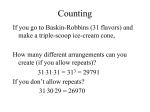* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Probability
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
Math Standards Document Probability Final Draft Hawaii School Districts Prepared by Marzano and Associates 1 Probability Summary Strand Data Analysis, Statistics, and Probability Total of Levels 3.0 Standard 14 Topic Probability Number of Elements Level 4.0-3 Level 3.0-8 Level 2.0-8 8 2 Topic/Course: Probability Strand: Data Analysis, Statistics, and Probability Standard 14: PROBABILITY: Understand and apply basic notions of chance and probability. Level 4.0 In addition to Level 3.0, in-depth inferences and applications that go beyond what was taught such as: implements an experiment and figures out the probabilities involved Level 3.5 Level 3.0 While engaged in tasks involving probability the student will: (MA.P.14.1) describe the relationship among events (inclusive, disjoint, complimentary, independent, dependent) (e.g., provide an example of inclusive, disjoint, complimentary, independent events, and dependent events) (MA.P.14.2) calculate the probability of two events under union and intersection (e.g., determine the probability of two events that are intersections and two events that are unions) (MA.P.14.5) calculate the probability of an outcome for an experiment with and without replacement (e.g., show/explain how to find the probability of events occurring with and without replacement) (MA.P.14.6) apply discrete random variables to solve for the probability of experimental outcomes (e.g., show/explain how to apply discrete random variables to solve for probability of experimental outcomes. i.e., determine the probability of rolling three 4’s in nine rolls of a number cube) The student exhibits no major errors or omissions. Level 2.5 Level 2.0 In addition to Level 3.0 performance, in-depth inferences and applications with partial success. No major errors or omissions regarding the simpler details and process and partial knowledge of the more complex ideas and processes. There are no major errors or omissions regarding the simpler details and processes as the student: recognizes or recalls specific terminology such as: o chance, probability, replacement performs basic processes such as: o recognizing or recalling accurate statements about the relationship among events (inclusive, disjoint, complimentary, independent, dependent) o recognizing or recalling accurate statements about the probability of two events under union and intersection o recognizing or recalling examples of experiments with and without replacement o recognizing or recalling accurate statements about discrete random variables being applied to solve for probability of experimental outcomes However, the student exhibits major errors or omissions regarding the more complex ideas and processes. Level 1.5 Level 1.0 Level 0.0 Partial knowledge of the simpler details and processes but major errors or omissions regarding the more complex ideas and procedures. With help, a partial understanding of some of the simpler details and processes and some of the more complex ideas and processes. Level 0.5 With help, a partial understanding of some of the simpler details and processes but not the more complex ideas and processes. Even with help, no understanding or skill demonstrated. 3 Sample Tasks for Levels 4.0, 3.0, & 2.0 Level 4.0 Ask students to implement an experiment and figure out the probabilities involved. Level 3.0 Ask students to describe the relationship among events (inclusive, disjoint, complimentary, independent, and dependent). Ask students to calculate the probability of two events under union and intersection. Ask students to calculate the probability of an outcome for an experiment with and without replacement. Ask students to apply discrete random variables to solve for the probability of experimental outcomes. Level 2.0 Ask students to recognize or recall accurate statements about relationships among events. Ask students to recognize or recall accurate statements about the probability of two events under union and intersection. Ask students to recognize examples of experiments with and without replacement. Ask students to recognize or recall accurate statements about discrete random variables being applied to solve for probability of experimental outcomes. Ask students to identify or produce definitions to the following terms: chance, probability, replacement. 4 Topic/Course: Probability Strand: Data Analysis, Statistics, and Probability Standard 14: PROBABILITY: Understand and apply basic notions of chance and probability. Level 4.0 In addition to Level 3.0, in-depth inferences and applications that go beyond what was taught such as: differentiates between using permutations and combinations differentiates between independent and dependent events Level 3.5 Level 3.0 While engaged in tasks involving probability the student will: (MA.P.14.3) differentiate between theoretical and experimental probability (e.g., compare the theoretical probability to the experimental probability of an experiment and analyze the difference between them) (MA.P.14.4) explain the difference between probability and odds and convert from one to the other (e.g., express the change of an event occurring as a probability and as odds, and describe how the representations reflect the events) (MA.P.14.7) estimate and calculate expected values (e.g., show/explain how to calculate the expected values of an experiment) (MA.P.14.8) apply permutations, combinations, and the fundamental counting principle to calculate the probability of two events (e.g., use permutations (or combinations) to determine the total number of possible outcomes and the total number of intended outcomes, and then represents the values as a ratio and simplifies) The student exhibits no major errors or omissions. Level 2.5 Level 2.0 In addition to Level 3.0 performance, in-depth inferences and applications with partial success. No major errors or omissions regarding the simpler details and process and partial knowledge of the more complex ideas and processes. There are no major errors or omissions regarding the simpler details and processes as the student: recognizes or recalls specific terminology such as: o experimental and theoretical probability, permutations, combinations, fundamental counting principle performs basic processes such as: o recognizing or recalling examples of experimental and theoretical probability o recognizing or recalling accurate statements about probability and odds o recognizing or recalling accurate statements about expected values o recognizing or recalling examples of permutations, combinations, and the fundamental counting principle However, the student exhibits major errors or omissions regarding the more complex ideas and processes. Level 1.5 Level 1.0 Level 0.0 Partial knowledge of the simpler details and processes but major errors or omissions regarding the more complex ideas and procedures. With help, a partial understanding of some of the simpler details and processes and some of the more complex ideas and processes. Level 0.5 With help, a partial understanding of some of the simpler details and processes but not the more complex ideas and processes. Even with help, no understanding or skill demonstrated. 5 Sample Tasks for Levels 4.0, 3.0, & 2.0 Level 4.0 Ask students to differentiate between using permutations and combinations. Ask students to differentiate between independent and dependent events. Level 3.0 Ask students to differentiate between theoretical and experimental probability. Ask students to explain the difference between probability and odds and convert from one to the other. Ask students to estimate and calculate expected values. Ask students to apply permutations, combinations, and the fundamental counting principle to calculate the probability of two events. Level 2.0 Ask students to recognize or recall examples of experimental and theoretical probability. Ask students to recognize accurate statements about probability and odds. Ask students to recognize or recall accurate statements about expected values. Ask students to recognize or recall examples of permutations, combinations, and the fundamental counting principle. Ask students to identify or produce definitions to the following terms: experimental and theoretical probability, permutations, combinations, fundamental counting principle. 6