* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CEBU INSTITUTE OF MEDICINE
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
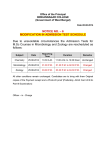
CEBU INSTITUTE OF MEDICINE MICROBIOLOGY AND P[ARASITOLOGY NAME____________________________ GROUP NO._____ ID NO. ____ DIRECTION: Each question below is followed by four possible answers. Select the one best response and mark the appropriate spaces on the answer sheet provided for. 1. The following are the most effective deterrents to progressive viral infection EXCEPT: A. interferon C. lymphocytes B. multinucleated giant cells D. specific antibody globulin (Answer: B / Reference: Microbiology p.388 / MPL 60) 2. Which of the following is true regarding endotoxin? A. become toxoids with formaldehyde C. heat labile B. causes fever D. very specific in their action (Answer: B / Reference: Microbiology p.391 / MPL 60) 3. The most important protective antibody: A. IgA B. IgE (Answer: C / Reference: Microbiology p.224 / MPL 90) C. IgG D. IgM 4. The immunoglobulin that serve as B cell antigen receptor in mature B cells: A. IgD C. IgM B. IgG D. A and C (Answer: C / Reference: Microbiology p.233 / MPL 60 ) 5. The antibody produced by the fetus in utero during fetal infection: A. IgA C. IgG B. IgE D. IgM (Answer: D / Reference: Microbiology p.206 / MPL 90 ) 6. There are immunogens that require specific recognition by the B cells and T cells. The T cell subset that regulate the activation and differentiation of B cells in the immune response: A. Helper T cells C. Cytotoxic T cells B. Delayed- type hypersensitivity T cells D. Suppressor T cells (Answer: A / Reference: Microbiology p.220 / MPL 60) 7. Following activation of the complement system, when the membrane attack is effective the end result is: A. clumping of cells C. destruction of cell B. formation of soluble complexes D. no effect on the cell (Answer: C / Reference: Microbiology p.292 / MPL 90) 8. The following events take place inside the phagocytic cells EXCEPT: A. destruction of bacteria by production of superoxide radicals B. destruction of bacteria by oxygen independent mechanisms like lysozymes C. may inhibit the replication of intracellular bacteria, fungi and protozoa D. unable to digest dead bacteria (Answer: D / Reference: Microbiology p.351 / MPL 60 ) 9. The CD8+ T cells recognize antigens in association with MHC Class: A. I C. III B. II D. IV (Answer: A / Reference: Microbiology p.303 / MPL 60) 10. The MHC class 1 genes expressed the antigens on the surface of most tissues like: A. lymphocytes C. red blood cells B. brain D. A and B (Answer: A / Reference: Microbiology p.268 / MPL 60) 11. The similarity between attenuated and inactivated vaccines: A. produce high level of antibodies B. replicate in parts of the where immunity is needed (Answer: A / Reference: Microbiology p.365 / MPL 33) C. given parenterally D. safe to administer 12. The Immunopathologic process or hypersensitivity reactions that involve the complement system: A. Immediate hypersensitivity C. Immune complex reactions B. Humorally mediated cytotoxic reactions D. B and C (Answer: D / Reference: Microbiology p.319 / MPL 60) 13. Which statement is not true of Type 4 or Delayed type Hypersensitivity reaction? A. initiated by antigen specific T cells 1 B. exemplified by tuberculin test C. histologically shows edema and numerous granulocytes D. reaction can be transferred in vivo with sensitized T cells (Answer: C / Reference: Microbiology p.322 / MPL 60) 14. Some oncofetal antigens are cell-associated but sometimes can be shed like: A. carcinoembryonic antigen C. alpha fetoprotein B. human chronic gonadotropin D. all of the above (Answer: A / Reference: Microbiology p.373 / MPL 33) 15. Failure of the maternal immune system to reject the fetus is attributed to: A. lack of antigenicity of the fetus B. humoral modification of maternal immune response C. the uterus is a privileged site D. fetus is an allograft (Answer: B / Reference: Microbiology p.381 / MPL 33) 16. The stomach under normal condition is sterile, however, bacteria may colonize in the stomach when the gastric pH is greater than: A. 2 C. 4 B. 3 D. 5 (Answer: D / Reference: Microbiology p.396 / MPL 33 ) 17. The criterion used for identification of pathogenic staphylococcus is the production of: A. hemolysin C. coagulase B. catalase D. pigment (Answer: C / Reference: Microbiology p.402 / MPL 90) 18. The presumptive test used to differentiate Streptococcus pyogenes from other beta hemolytic streptococcus: A. catalase test C. bacitracin sensitivity test B. optochin sensitivity test D. oxidase test (Answer: C / Reference: Microbiology p.419 / MPL 90) 19. The most common complication of pneumococcal pneumonia: A. pleural effusion C. meningitis B. empyema D. pericarditis (Answer: A / Reference: Microbiology p.438 / MPL 60 ) 20. Streptococcus agalactiae is normal flora of various parts of the body. Infection of newborns with this bacteria is attributed to the mother harboring the organisms in the: A. pharynx C. gastrointestinal tract B. vagina D. skin (Answer: B / Reference: Microbiology p.427 / MPL 60) 21. Neisseria gonorrhoeae can be differentiated from Neisseria meningitides by: A. oxidase test C. growth in the candle jar B. fermentation of sugars D. growth on chocolate agar (Answer: B / Reference: Microbiology. p.445 / MPL 90) 22. The most common of the classic sexually transmitted disease: A. syphilis B. gonorrhea (Answer: B / Reference: Microbiology p.454 / MPL 60) C. HIV D. Herpes 23. Carriers of Neisseria meningitides harbor the organisms in the: A. throat C. eyes B. nasopharynx D. lungs (Answer: B / Reference: Microbiology p.449 / MPL 90) 24. The most common cause of acute bacterial meningitis in infancy and early childhood: A. Hemophilus influenzae type B C. Neisseria meningitides B. Streptococcus pneumoniae D. Escherichia coli (Answer: A / Reference: Microbiology p.462 / MPL 60) 25. The systemic manifestations of pertussis is attributed to: A. invasiveness of the organisms C. circulating toxin B. outer membrane proteins of the organism D. hemagglutinins (Answer: C / Reference: Microbiology . p.477 / MPL 60) 26. Reported outbreaks of diarrhea, hemorrhagic colitis and HUS has been attributed to The E. coli strain linked to this outbreak: A. EPEC C. VTEC B. EIEC D. ETEC (answer: C / Reference: Microbiology page: 548 / MPL 90) Escherichia coli. 2 27. The Escherichia coli strain identified to be the major cause(s) of traveler’s diarrhea. A. EPEC C. EAEC B. ETEC D. B and C (answer: D / Reference: Microbiology page: 548 / MPL 60 ) 28. The ability of Klebsiella pneumoniae to resist phagocytosis and the killing power of the normal serum is due to its: A. endotoxin C. capsule B. flagella D. cell wall (answer: C / Reference: Microbiology page: 549 / MPL 90) 29. Urinary tract infection caused by urease producing organisms are characterized by an alkaline pH. This cause precipitation of calcium and magnesium salts in the urine leading to production of: A. urinary calculi C. bacterial infection B. hematuria D. frequent scanty urination (Answer: A/ Reference: Microbiology page: 552 / MPL 60) 30. The ability of Salmonella to attach to host receptor cells and survive intracellularly is attributed to its: A. Vi antigen C. H antigen B. O antigen D. A and B (Answer: D / Reference: Microbiology page: 560 / MPL 60 ) 31. The best time to perform blood culture in a patient with typhoid fever is during the: A. first week of illness C. third week of illness B. second week of illness D. fourth week of illness (Answer: A / Reference: Microbiology page: 563 / MPL 90 ) 32. The source of Salmonella typhi: A. man C. eggs B. turtle D. all of the above (Answer: A / Reference: Microbiology page: 562 / MPL 90) 33. In the acute stage of shigellosis, the organisms are recovered from the: A. blood C. stool B. urine D. A and B (Answer: C / Reference: Microbiology page: 537 / MPL 90) 34. One of the following is not true of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: A. a common cause of nosocomial infection B. susceptible to chemical disinfectants C. resistant to first generation cephalosporin D. survive with a minimum nutrient with adequate moisture (Answer: B / Reference: Microbiology page: 577 / MPL 60) 35. To successfully culture Vibrio cholerae from stool of patients, the specimen should be cultured immediately or placed in a suitable transport medium because a delay in processing of the specimen might lead to. A. acidic pH of stool to which V. cholerae is sensitive to B. dehydration of clinical specimens leading to death of the microorganisms C. multiplication of coliforms which will outgrow the pathogen D. A and B (Answer: D / Reference: Microbiology page: 569 / MPL 60) 36. The following are true of Vibrio parahemolyticus: A. infection is due to ingestion of raw or poorly cooked seafood B. the short generation time allows the infective dose of 10 6 organisms to be easily attained in food C. gastroenteritis is due to potent endotoxin it releases D. A and B (Answer: D / Reference: Microbiology page: 571 / MPL 60 ) 37. Laboratory identification of H. pylori is based on: A. tissue sections showing gram negative filamentous rod B. positive urease test C. demonstration of the organism in silver stain tissue section D. B and C (Answer: D / Reference: Microbiology page: 679 / MPL: 60 ) 38. The most common vehicle of transmission of human listeriosis in both adults and neonates: A. sick person C. food B. sick animal D. water (Answer: C / Reference: Microbiology page: 483 / MPL 60) 39. The systemic manifestations of diphtheria is essentially due to: A. endotoxins C. invasiveness of the organisms 3 B. exotoxins D. metachromatic granules (Answer: B / Reference: Microbiology page: 488 / MPL 90) 40. The simple staining procedure used in the laboratory to demonstrate the metachromatic granules of Corynebacterium diphtheriae: A. safranin staining C. carbol fuchsin staining B. crystal violet staining D. methylene blue staining (Answer: D / Reference: Microbiology page: 488 / MPL 60 ) 41. The difference in the body response to primary and secondary tuberculosis is due to: A. resistance C. virulence of the organisms B. delayed hypersensitivity D. A and B only (Answer: D/ Reference: Microbiology page: 506 / MPL 60) 42. The biochemical test used to identify the culture of Mycobacterium tuberculosis: A. oxidase test C. catalase test B. niacin test D. urease test (Answer: B/ Reference: Microbiology page: 511 / MPL 90) 43. The usual source of secondary or re-infection tuberculosis: A. endogenous C. exogenous B. organisms from BCG vaccine that became virulent D. none of the above (Answer: A / Reference: Microbiology page: 506 / MPL 90) 44. The mode of transmission of Mycobacteria associated with non tuberculous infections: A. man to man C. inhalation of contaminated soil B. reservoir animal to man D. ingestion of contaminated food (Answer: C / Reference: Microbiology page: 512 / MPL 60) 45. The MOTT which cause one of the common complication of AIDS: A. M. kansasii C. M. marinum B. M. avium-intracellulare D. M. fortuitum (Answer: B / Reference: Microbiology page: 515 / MPL 90) 46. Mycobacterium leprae has been successfully grown in: A. tissue culture C. Lowenstein Jensen medium B. footpads of mice D. Petragnani medium (Answer: B / Reference: Microbiology page: 516 / MPL 90 ) 47. Diagnosis of leprosy is made by demonstration of acid fast bacilli in smears of the skin, nasal scrapings and ear lobes. The bacilli are difficult and often impossible to detect in: A. tuberculoid leprosy C. borderline leprosy B. borderline lepromatous leprosy D. lepromatous leprosy (Answer: A / Reference: Microbiology page: 518 / MPL 90 ) 48. Nocardia asteroides in sputum smears appears as: A. filamentous and branching C. partially acid fast B. gram positive D. all of the above (Answer: D / Reference: Microbiology page: 534 / MPL 90) 49. Bacteroides fragilis is known to be: A. highly susceptible to penicillin B. normal flora of the vagina and cervix C. associated primarily with intrabdominal infection or septicemia D. B and C (Answer: C / Reference: Microbiology . p.631 / MPL 60) 50. The specimen that can be processed for anaerobic culture: A. throat swab C. blood B. stool D. sputum (answer: C / Reference: Microbiology page: 629 / MPL 60 ) 51. The most frequent anaerobic organism isolated from clinical specimens: A. Bacteroides fragilis C. Prevotella B. Porphyromonas D. Fusobacterium (Answer: A / Reference: Microbiology page: 631 / MPL 90) 52. The following are true of Fusobacterium nucleatum EXCEPT: A. most common species isolated from clinical specimens B. organisms appear as thin bacilli with pointed ends microscopically C. frequent flora of the urogenital tract D. important agent in oral infection (Answer: C / Reference: Microbiology page: 632 / MPL 60 ) 53. The anaerobic organism which is not a pigment producer: 4 A. Porphyromonas C. Prevotella B. Fusobacterium D. Bacteroides (Answer: D / Reference: Microbiology page: 621 / MPL 60 ) 54. The disease that is not attributed to Clostridium perfringens: A. wound infection C. food poisoning B. pseudomembranous enterocolitis D. clostridial myonecrosis (Answer: B / Reference: Microbiology p.637 / MPL 60) 55. The signs and symptoms of tetanus is attributed to its: A. endotoxin C. exotoxin B. production of hyaluronidase D. invasiveness (Answer: C / Reference: Microbiology p.645 / MPL 60) 56. The statements that are true with reference to Bacillus cereus infection: A. clindamycin is the drug of choice C. manifest as food poisoning B. enterotoxin is a determinant of pathogenicity D. all of the above (Answer: D / Reference: Microbiology p.618 / MPL 60 ) 57. Leptospirosis is acquired through: A. ingestion of contaminated food C. skin penetration of organisms B. inhalation of microorganism D. sexual contact (Answer: C / Reference: Microbiology p.672 / MPL 90 ) 58. Mycoplasma spp. is resistant to: A. erythromycin C. minocycline B. penicillin D. doxycycline (Answer: B / Reference: Microbiology page: 736 / MPL 90 ) 59. A syphilitic person with grnulomatous lesion in the mouth is: A. in the second stage of the disease C. highly infectious B. positive for VDRL D. FTA-ABS positive (Answer: D / Reference: Microbiology p.662 / MPL 60) 60. The most common complication of Varicella is: A. bacterial superinfection of the skin C. cerebellar ataxia B. postherpetic neuralgia D. pneumonia (Answer: C / Reference: Microbiology page: 960 / MPL 60 ) 61. Which of the following is the common feature of herpesvirus? A. ability to establish latency in the body after primary infection B. ability to produce rashes in infected individuals C. ability to cause cancer in humans D. ability to affect nerve cells in humans (Answer: A / Reference: Microbiology page: 955 / MPL 60) 62. Which of the following is true regarding adenovirus infection? A. it may cause hemorrhagic cystitis B. it is the most common viral respiratory pathogen in children C. it is rarely associated with the common cold syndrome D. it causes pneumonia that is less severe than that caused by parainlfuenza (Answer: C / Reference: Microbiology page: 969 / MPL 60 ) 63. A 25-year old patient had his blood tested for Hepatitis B yielding the following results: HBs Ag (+) Anti-HBs (-) HBe Ag (-) Anti-HBe (+) Anti-HBc (+) What is the most likely interpretation of the above results? A. Early recovery phase from acute Hepatitis B B. Has received Hepatitis B vaccination C. Chronic Hepatitis B carrier state D. Early acute Hepatitis B (Answer: C / Ref: Baily & Scott ‘s Diagnostic Microbiology, 11 th ed p. 849 / MPL 60) 64. Poliovirus is spread from person to person thru: A. inhalation of aerolized droplet C. sexual transmission B. fecal-oral route D. skin penetration (answer: B / Reference: Microbiology page: 981 / MPL 90 ) 5 65. A 7 year old male patient was brought to the OPD reporting symptoms of mild fever and cough preceding the onset of macular rash which appeared first on the face, then on the neck, trunk and extremities. The rashes appeared to be discrete and rarely coalesce, Postauricular lymphadenopathy was also noted. The most likely condition the patient has is: A. rubella C. varicella B. rubeola D. roseola (Answer: A / Reference: Microbiology page: 9509,965,1013,1016 / MPL 60 ) 66. Which of the following is true regarding dengue virus? A. It is a DNA virus that causes fever and sometimes rash B. It belongs to the family of Filoviruses causing hemorrhagic fever like Ebola virus C. There are 3 serotypes thus there area 3 chances of having dengue in a lifetime D. Subsequent infection with another dengue serotype is more severe than the previous one (Answer: D / Reference: Baily & Scott ‘s Diagnostic Microbiology, 11 th ed page: 806-807 / MPL 60 ) 67. The leading cause of diarrhea in the first 2 years of life among cases seen in hospitals and health centers world wide. A. rotavirus C. Entamoeba histolytica B. Escherichia coli D. Shigella flexneri (Answer: A / Ref: Readings on Diarrhea, 2nd printing June 1990 p. 19 / MPL 90) 68. The period of communicability for mumps usually lasts for about: A. 24 hours C. 3-6 days B. 48 hours D. 7-10 days (Answer: D / Reference: Microbiology page: 1007 / MPL 33) 69. The incubation period of measles is: A. 1-2 days C. 7-9 days B. 3-6 days D. 10-14 days (Answer: D / Reference: Microbiology page: 1012 / MPL 60 ) 70. The cornerstone of human rabies prevention in most areas of the world is: A. killing of stray dogs and cats B. vaccination of domestic dogs and cats C. spaying of female dogs and cats D. vaccination of persons with pet dogs and cats (Answer: B / Reference: Microbiology page: 1029 / MPL 60) 71. Which of the following statements is correct regarding influenza vaccine? A. protection is conferred as early as 1 month after vaccination B. it should also be given to caregivers of elderly individuals in nursing homes. C. protection will last for 10-15 years D. at present the vaccines are monovalent (Answer: B / Reference: Microbiology page: 496-497 / MPL 60) 72. Confirmatory test for Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV): A. Western blot C. Southern blot B. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) D. ELISA test (Answer: A; Ref: Baily & Scott ‘s Diagnostic Microbiology, 11th ed p. 832 / MPL 60) 73. The leading cause of posttransfusion heaptitis is: A. Hepatitis A C. Hepatitis C B. Hepatitis B D. Hepatitis D (Answer: C / Reference: Microbiology page: 1043 / MPL 90 ) 74. Routine fungal cultures are incubated at: A. 28oC C. 37oC o B. 35 C D. 42oC (Answer: A / Reference: Microbiology page: 1087 / MP :90 ) 75. The most common pathogenic species of Aspergillus for humans: A. Aspergillus niger C. Aspoergillus terreus B. Aspergillus fumigatus D. Aspergillus flavus (Answer: B / Reference: Microbiology p.1147 / MPL 60) 76. The fungi whose identification is based on microscopic picture of the skin scrapings and not on culture of the fungus. A. Microsporum canis C. Malassezia furfur B. Exophiala werneckii D. Epidermophyton floccosum (Answer: C / Reference: Microbiology p.1131 / MPL 60) 77. The frequent cause of tinea pedis: A. Microporum canis C. Epidermophyton floccosum B. Trichophyton mentagrophytes D. Candida albicans (Answer: B / Reference: Microbiology p.1130 / MPL 60) 6 78. The appearance of pseudohyphae or true hyphae along with budding yeast cells in tissue is pathognomonic for: A. Aspergillosis C. Mucormycosis B. Cryptococcosis D. Candidiasis (Answer: D / Reference: Microbiology p.1142 / MPL 90) 79. The most frequent cause of opportunistic mycosis: A. Candida albicans C. Aspergillus spp. B. Cryptococcus neoformans D. Penicillium spp (Answer: A / Reference: Microbiology page: 1043 / MPL 90 ) 80. The most important source of Cryptococcus infection in man: A. pigeon excreta C. infected person B. infected dogs D. contaminated food (Answer: A / Reference: Microbiology p. 1144 / MPL 90 ) 81. Diarrheic stools of patients suspected with Entamoeba histolytica infection must be examined within: A. 15 minutes C. 3-5 hours B. 30 minutes to 60 minutes D. anytime (Answer: B / Reference: Parasitology p.104 / MPL 60) 82. For diagnosis of amoebiasis, ideally stool exam should be done: A. examinations of 3 specimens every other day C. daily for 3 days B. examinations of 3 specimens every 2nd or 3rd day D. weekly for one month (Answer: B / Reference: Parasitology p.119 / MPL 60) 83. The incorrect statement regarding Trichomonas vaginitis A. this is usually acquired through sexual intercourse B. female patients are usually symptomatic C. in men the infection is usually asymptomatic D. diagnosis is based on recovery of the cystic stage from genital discharges (Answer: D / Reference: Parasitology p.50-51; MPL 60 ) 84. True relapse in malaria is: A. due to activation of surviving erythrocytic parasites B. due to activation of hypnozoites C. seen in Plasmodium falciparum infection D. seen in carriers of Plasmodium malariae (Answer: B / Reference: Parasitology p. 197 / MPL 33) 85. The clinical manifestations of malaria is attributed to: A. destruction of parasitized red blood cells C. appearance of gametocytes B. released of merozoites from hepatocytes D. merozoites enter the RBC (Answer: A / Reference: Parasitology p.194 / MPL 60 ) 86. The nematode whose larva does not undergo lung migration: A. Ascaris lumbricoides C. Capillaria philippinensis B. Necator americanus D. Strongyloides stercoralis (Answer: C / Reference: Parasitology p. 246 / MPL 90) 87. The filariform larva is not the infective stage to man of: A. Necator americanus C. Ascaris lumbricoides B. Ancylostoma duodenale D. Strongyloides stercoralis (Answer: C / Reference: Parasitology p. 278. / MPL 90) 88. Demonstration of Enterobius vermicularis eggs is best done by: A. direct fecal examination C. rectal swab B. scotch tape method D. concentration method (Answer: B / Reference: Parasitology p. 304 / MPL 90) 89. Allergic manifestations of ascariasis include asthma, and urticaria are seen in the following conditions: A. pulmonary migration of the parasite C. intestinal phase of ascariasis B. when pulmonary phase wanes D. all of the above (Answer: D / Reference: Parasitology . p.314 / MPL 60 ) 90. The microfilaria of Wuchereria bancrofti are best recovered from the: A. blood C. CSF B. lymph D. urine (Answer: A / Reference: Parasitology p.362 / MPL 90) 91. The intermediate host of Schistosoma japonicum in the Philippines: A. Oncomelania quadrasi C. Bortia asperata B. Pila luzonica D. Gyraulus convexiusculus (Answer: A / Reference: Parasitology p.416-417 / MPL 60) 7 92. The current treatment for schistosomiasis: A. Thiabendazole C. Praziquantel B. Mebendazole D. Metronidazole (Answer: C / Reference: Parasitology p.424 / MPL 90 ) 93. The infective stage to man of Echinostoma ilocanum is: A. encysted metacercaria in snail C. cercaria B. encysted metacercaria in fresh water fish D. embryonated operculated egg (Answer: A / Reference: Parasitology p.458 / MPL 60) 94. Heterophyes heterophyes infection can lead to cardiac failure as a result of the: A. adult fluke producing granuloma in the heart B. metacercaria developing to adult worm in the heart C. eggs blocking the vessels leading to the heart D. eggs cause myocarditis (Answer: D / Reference: Parasitology p.479; MPL 33) 95 . Paragonimus westermani infection can mimick pulmonary tuberculosis and other pulmonary problems. Laboratory diagnosis of Paragonimus westermani infection is by demonstration of the eggs from the: A. sputum C. stool B. urine D. A and C (Answer: D / Reference: Parasitology p.466; MPL 60) 96. Cysticercus cellulosae is the larva of: A. Diphyllobothrium latum C. Taenia solium B. Hymenolepis nana D. Taenia saginata (Answer: C / Reference: Parasitology p.516 / MPL 60) 97. Diphyllobothrium latum is transmitted through ingestion of: A. fresh water fish with plerocercoid larva C. water contaminated with eggs B. fresh water fish with procercoid larva D. water with infected Cyclops Reference: Parasitology . p.497; MPL 60) (Answer: A / 98. The only human tapeworm which does not require an intermediate host: A. Hymenolepis diminuta C. Echinococcus granulosus B. Hymenolepis nana D. Multiceps multiceps (Answer: B / Reference: Parasitology p.511 / MPL 60) 99. A child with a pet dog, passed out gravid proglottids with genital atrium on each lateral margin. This cestode is: A. Hymenolepis nana C. Raillietina garrisoni B. Bertiella studeri D. Dipylidium caninum (Answer: D / Reference: Parasitology . p.508 / MPL 60 ) 100. The cestode whose proglottids detach from the worm singly and are capable of independent motion crawling out of the anus during the daytime while the patient is active: A. Diphyllobothrium latum C. Taenia solium B. Hymenolepis nana D. Taenia saginata (Answer: D / Reference: Parasitology p.521 / MPL 60) References: MICROBIOLOGY: 1. Textbook in Microbiology: Zinsser Microbiology 20th edition Joklik, Willet, Amos, Wilfert 2. Bailey & Scott’s Diagnostic Microbiology, 11 th ed Baron, Finegold 3. Readings on Diarrhea, 2nd printing June 1990 PARASITOLOGY: 1. Textbook in Parasitology: Clinical Parasitology 9th ed. Beaver, Jung, Cupp 8