* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 13
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Perceived visual angle wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
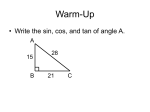
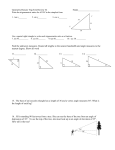
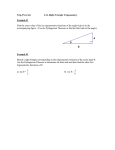
Chapter 13.1-13.5-Bradshaw Algebra 2 w/trig Test Short Answer 1. Find the values of the six trigonometric functions for angle , when AC = 10 and BC = 8. 2. Find the values of the six trigonometric functions for angle , when PQ = 60 and QR = 80. 3. Solve ABC by using the measurements , the nearest tenth and measures of angles to the nearest degree. , and . Round measures of sides to 4. Solve ABC by using the measurements , the nearest tenth and measures of angles to the nearest degree. , and . Round measures of sides to 5. A 15-m long ladder rests against a wall at an angle of from the wall? with the ground. How far is the foot of the ladder 6. The upper part of a tree, broken by wind, makes an angle of 38 with the ground. The horizontal distance from the root of the tree to the point where the top of the tree meets the ground is 20 meters. Find the height of the tree before it was broken. Rewrite the radian measure in degrees. 7. 8. Rewrite the degree measure in radians. 9. –1080° 10. 9° 11. Find one angle with positive measure and one angle with negative measure coterminal with an angle of 172°. Find the value of the given trigonometric function. 12. sin –585 13. cos 780 14. cot 210 Find the exact values of the remaining five trigonometric functions of . 15. Suppose is an angle in the standard position whose terminal side is in Quadrant III and . 16. Suppose is an angle in the standard position whose terminal side is in Quadrant IV and 17. Suppose is an angle in the standard position whose terminal side is in Quadrant II and . . Solve the given triangle. Round the measures of sides to the nearest tenth and measures of angles to the nearest degree. 18. c = 9.0, B = 40°, C = 65° 19. Q = 35°, p = 8, q = 5 Determine whether the given triangle has no solution, one solution or two solutions. Then solve the triangle. Round measures of sides to the nearest tenth and measures of angles to the nearest degree. 20. A =115°, a = 7, b = 4 21. P = 38°, p = 8, q = 6. Determine whether each triangle should be solved by beginning with the Law of Sines or the Law of Cosines. Then solve each triangle. Round measures of sides to the nearest tenth and measures of angles to the nearest degree. 22. A = 75 , b = 8, a = 13 23. A = 75 , b = 11, a = 14 The given point P is located on the unit circle. Find sin and cos . 24. P(0.8, 0.6) 25. P Chapter 13.1-13.5-Bradshaw Algebra 2 w/trig Test Answer Section SHORT ANSWER 1. ANS: 4 3 5 5 4 3 = , cos = , csc = , sec = , tan = , and cot = . 5 5 4 3 3 4 If is the measure of an acute angle of a right triangle, opp is the measure of the leg opposite , adj is the measure of the leg adjacent to , and hyp is the measure of the hypotenuse, then the following are true. sin sin cos tan csc sec cot KEY: Trigonometric Functions, Acute Angles NOT: /A/ Did you use the correct definition of trigonometric ratios? /B/ The sine, cosine, and tangent functions are reciprocals of the cosecant, secant, and cotangent functions, respectively. /C/ If x is the measure of an acute angle of a right triangle, then opp is the measure of the leg opposite x, adj is the measure of the leg adjacent to x, and hyp is the measure of the hypotenuse./D/ Correct! 2. ANS: 4 3 5 5 4 3 sin = , cos = , csc = , sec = , tan = , and cot = . 5 5 4 3 3 4 If is the measure of an acute angle of a right triangle, opp is the measure of the leg opposite , adj is the measure of the leg adjacent to , and hyp is the measure of the hypotenuse, then the following are true. sin cos tan csc sec cot KEY: Trigonometric Functions, Acute Angles NOT: /A/ Correct! /B/ If x is the measure of an acute angle of a right triangle, then opp is the measure of the leg opposite x, adj is the measure of the leg adjacent to x, and hyp is the measure of the hypotenuse./C/ The sine, cosine, and tangent functions are reciprocals of the cosecant, secant, and cotangent functions, respectively. /D/ Did you use the correct definition of trigonometric ratios? 3. ANS: , , If the measures of one side and one acute angle are known, you can determine the measures of all sides and angles of the triangle by using trigonometric functions. KEY: Solve Triangles, Right Triangles NOT: /A/ Did you interchange the values of b and c? /B/ Correct! /C/ Use the measures of one side and one acute angle to find the other measures./D/ Did you use the trigonometric functions to find the missing measures? 4. ANS: , , If the measures of one side and one acute angle are known, you can determine the measures of all sides and angles of the triangle by using trigonometric functions. KEY: Solve Triangles, Right Triangles NOT: /A/ Did you use the trigonometric functions to find the missing measures? /B/ Correct!/C/ Did you interchange the values of p and q? /D/ Use the measures of the side and acute angle to find the missing measures. 5. ANS: 7.5 m Write an equation using a trigonometric function that involves the ratio of length and 15. KEY: Right Triangles, Real-World Problems NOT: /A/ Correct! /B/ Did you write an equation using a trigonometric function that involves the ratio of the length of the ladder and the distance of the foot of the ladder from the wall? /C/ Use cos 60 to find how far is the foot of the ladder from the wall. /D/ Did you use the correct trigonometric function? 6. ANS: 41.006 m Write an equation using a trigonometric function that involves the ratio of and 20. KEY: Right Triangles, Real-World Problems NOT: /A/ Did you use the correct trigonometric function? /B/ Did you write an equation using a trigonometric function? /C/ Use the tan function to find the height of the lower part of the tree. /D/ Correct! 7. ANS: 10 To rewrite the radian measure of an angle in degrees, multiply the number of radians by . KEY: Radian Measure, Degree Measure NOT: /A/ One radian is around 57 degrees. /B/ Did you multiply the number of radians correctly by the conversion factor? /C/ One degree is about 0.0175 radian. /D/ Correct! 8. ANS: 45 To rewrite the radian measure of an angle in degrees, multiply the number of radians by . KEY: Radian Measure, Degree Measure NOT: /A/ One degree is about 0.0175 radian. /B/ One radian is about 57 degrees. /C/ Correct!/D/ Did you multiply the number of radians correctly by the conversion factor? 9. ANS: To rewrite the degree measure of an angle in radians, multiply the number of degrees by . KEY: Radian Measure, Degree Measure NOT: /A/ Did you multiply the number of degrees correctly by the conversion factor? /B/ One degree is about 0.0175 radian. /C/ One radian is about 57 degrees./D/ Correct! 10. ANS: To rewrite the degree measure of an angle in radians, multiply the number of degrees by . KEY: Radian Measure, Degree Measure NOT: /A/ One degree is about 0.0175 radians. /B/ Did you multiply the number of degrees correctly by the conversion factor? /C/ Correct! /D/ One radian is about 57 degrees. 11. ANS: 532°, –188° In degree measure, coterminal angles differ by an integral multiple of 360 . KEY: Coterminal Angles NOT: /A/ In degree measure, coterminal angles differ by an integral multiple of 360 degrees. /B/ Correct! /C/ When two angles in the standard position have the same terminal sides, they are called coterminal angles. /D/ Did you add or subtract the given angle with an integral multiple of 360 degrees? 12. ANS: First, find the reference angle . Then, find the value of the trigonometric function for . Then, using the quadrant in which the terminal side of lies, determine the sign of the trigonometric function value of . KEY: Sine, Cosine NOT: /A/ Did you find the reference angle of the given angle?/B/ Use a reference angle to find the value of the given trigonometric function. /C/ Correct! /D/ Find the sine of the given angle, not tan. 13. ANS: First, find the reference angle . Then, find the value of the trigonometric function for . Then, using the quadrant in which the terminal side of lies, determine the sign of the trigonometric function value of . KEY: Sine, Cosine NOT: /A/ Use a reference angle to find the value of the given trigonometric function. /B/ Find the cos of the given angle, not tan. /C/ Did you find the reference angle of the given angle?/D/ Correct! 14. ANS: First, find the reference angle . Then, find the value of the trigonometric function for . Then, using the quadrant in which the terminal side of lies, determine the sign of the trigonometric function value of . KEY: Tangent, Cotangent NOT: /A/ Use a reference angle to find the value of the given trigonometric function. /B/ Correct!/C/ Find the cot of the given angle, not tan. /D/ Did you find the reference angle of the given angle? 15. ANS: sin , csc , sec , tan , and cot If the quadrant that contains the terminal side of in the standard position and the exact value of one trigonometric function of are known, then the values of the other trigonometric functions of can be obtained using the function definitions. KEY: Reference Angles, Trigonometric Functions NOT: /A/ Did you use the correct signs of the trigonometric functions for Quadrant III? /B/ The angle is in Quadrant III and not in Quadrant II. /C/ Use function definitions to find the remaining five trigonometric functions. /D/ Correct! 16. ANS: cos , csc , sec , tan , cot If the quadrant that contains the terminal side of in the standard position and the exact value of one trigonometric function of are known, then the values of the other trigonometric functions of can be obtained using the function definitions. KEY: Reference Angles, Trigonometric Functions NOT: /A/ Correct! /B/ The angle is in Quadrant IV and not in Quadrant I. /C/ Did you use the correct signs of the trigonometric functions for Quadrant IV? /D/ Use function definitions to find the remaining five trigonometric functions. 17. ANS: cos , csc , sec , tan , cot If the quadrant that contains the terminal side of in the standard position and the exact value of one trigonometric function of are known, then the values of the other trigonometric functions of can be obtained using the function definitions. KEY: Reference Angles, Trigonometric Functions NOT: /A/ The angle is in Quadrant II and not in Quadrant I. /B/ Use function definitions to find the remaining five trigonometric functions. /C/ Did you use the correct signs of the trigonometric functions for Quadrant II? /D/ Correct! 18. ANS: A = 75°, a = 9.6, b = 6.4 Let be any triangle with , , and representing the measures of sides opposite angles with measurements , , and respectively. Then, KEY: Solve Problems, Law of Sines NOT: /A/ Correct! /B/ Did you interchange the values of the sides? /C/ Apply the Law of Sines to solve the triangle./D/ Did you apply the Law of Sines to solve the triangle? 19. ANS: P = 90°, R = 55°, r = 6.6 Let be any triangle with , , and representing the measures of sides opposite angles with measurements , , and respectively. Then, . KEY: Solve Problems, Law of Sines NOT: /A/ Did you apply the Law of Sines to solve the triangle? /B/ Correct! /C/ Did you interchange the values of the sides? /D/ Apply the Law of Sines to solve the triangle. 20. ANS: one solution; c 4.0; B 31°; C 34° Determine whether the given triangle has zero, one or two solutions. Find the measure of angle C and the value of c. KEY: Solve Triangles NOT: /A/ Did you interchange the values of angles B and C?/B/ Correct! /C/ Did you calculate the value of C correctly? /D/ Did you use the Law of Sines correctly? 21. ANS: one solution; r 8.0; Q ; R 115 Find whether the given triangle has one, two or zero solution and then find the values asked in the question by applying appropriate formula. KEY: Solve Triangles NOT: /A/ The sum of the measures of the angles of a triangle is 180./B/ Correct! /C/ Did you use the Law of Sines? /D/ Did you find the value of r and the corresponding angle correctly? 22. ANS: Law of Sines; B 37 , C 69 , c 13.0 Use the Law of Sines when two sides and an angle opposite one of them are given. KEY: Solve Triangles, Law of Sines, Law of Cosines NOT: /A/ What is the Law of Sines?/B/ Did you use the correct law? /C/ Did you interchange the angles? /D/ Correct! 23. ANS: Law of Sines; B 49 , C 56 , c 12.0 Use the Law of Sines when two sides and an angle opposite one of them are given. KEY: Solve Triangles, Law of Sines, Law of Cosines NOT: /A/ Did you use the correct law? /B/ What is the Law of Sines?/C/ Correct! /D/ Did you interchange the angles? 24. ANS: sin = 0.6; cos = 0.8 If the terminal side of an angle in the standard position intersects the unit circle at P(x, y), then cos = x and sin = y. KEY: Trigonometric Functions, Unit Circle NOT: /A/ Correct! /B/ Did you write the answers in the correct order? /C/ Did you change the sign of the coordinates? /D/ Check the sign of the coordinates. 25. ANS: sin = ; cos = If the terminal side of an angle and sin = y. in the standard position intersects the unit circle at P(x, y), then cos =x KEY: Trigonometric Functions, Unit Circle NOT: /A/ Did you write the answers in the correct order? /B/ Correct! /C/ Did you change the sign of the coordinates? /D/ Check the sign of the coordinates.