* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Kingdom Plantae - Smyth County Schools
Survey
Document related concepts
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
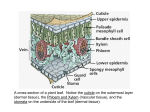
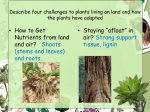
Kingdom Plantae Autotrophs (photosynthesis) Eukaryotic Multicellular By Diana L. Duckworth Rustburg High School, Campbell County Plants were first life to invade land some 400 million years ago • Three major problems to solve: • (1) How to get nutrients out of bare rock – Partnership with fungi - mycorrhizae • (2) How to keep from drying out – Developed watertight covering – cuticle – Also kept out gases – developed stomata (singular – stoma) • (3) How to reproduce without water medium – Sperm enclosed in pollen – wind or insect dispersal; prevents drying out Stomata http://www.agr.gc.ca/nlwis-snite/index_e.cfm?s1=pub&s2=ha_sa&page=73 cuticle http://www.learner.org/jnorth/spring2001/species/tulip/Update051801.html Demands of land environment led to cell differentiation & thus different tissues and enabled larger sized plants • Stems – provide support; contain vascular tissue to carry nutrients & water to leaves from roots • Roots – anchor plant in soil; take up nutrients and water • Vascular tissue – Xylem – carries water & minerals from roots – Phloem – carries food made in leaves by photosynthesis to rest of plant • Seeds – multicellular; contain embryo of plant – – – – Protection – seed coat prevents injury & dessication of embryo Nourishment – food for plant embryo as it starts to grow Dispersal – by animals or wind or water Delayed growth – can remain dormant until conditions are right to germinate • Leaves – structures specialized to carryout photosynthesis • Flowers – specialized structures to make reproduction more efficient http://www.karencarr.com/gallery_stem_diagram.html http://grandpacliff.com/Plants/Glossary-Plants.htm http://arnica.csustan.edu/photos/800/Cucurbita_vascular_tissue_LS_100x.jpg Kinds of Plants - Nonvascular • Small – no specialized structures for taking up nutrients or water; each cell for itself • Gametophyte generation is larger & photosynthetic; sporophyte non photosynthetic & grows on gametophyte • Need water for sexual reproduction – sperm swim to eggs Nonvascular Examples • Mosses – leaves arranged in spiral around stem – Have cuticle, stomata, water conducting cells • Liverworts – lack conducting cells, cuticle & stomata • Hornworts – lack conducting cells, cuticle, stomata http://www.fs.fed.us/wildflowers/interesting/lichens/whatnot.shtml Seedless Vascular Plants • Have a vascular system • Sporophyte is larger & photosynthetic • Do need water to reproduce • Have droughtresistant spores • Example: Ferns http://www.pbase.com/rak_929/image/41482294 http://eclipsetheatrecompany.wordpress.com/2008/02/29/can-you-see-the-light-part-iii/ Gymnosperms – naked seed • Produces seeds not enclosed in fruit • Gametophytes are male & female; greatly reduced – Male are grains of pollen – Female form within structures that become seeds – Have male & female cones • Wind pollination • Example - conifers http://countrysidecreek.typepad.com/photos/pictures/p1000246.html Angiosperms – Flowering Plants • Male & Female gametophytes develop within a flower – promotes pollination • Seeds are enclosed in a fruit – promotes dispersal • Seeds contain supply of food called endosperm Two kinds of angiosperms: monocots & dicots • Monocots – One seed leaf – Flowers have parts in multiples of 3 – Long narrow leaves with parallel veins – Examples – grass; corn; lilies • Dicots – Two seed leaves – Flower parts in multiples of 2, 4, 5 – Leaves with branching veins – Examples: roses – Daisies; fruits such as apples, peaches, etc. Comparison of Monocots & Dicots http://encarta.msn.com/media_461549076_761558348_-1_1/monocot_and_dicot_seeds.html