* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences Bangalore, Karnataka
Sociality and disease transmission wikipedia , lookup
Behçet's disease wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Pathophysiology of multiple sclerosis wikipedia , lookup
Sjögren syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Antimicrobial peptides wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Multiple sclerosis signs and symptoms wikipedia , lookup
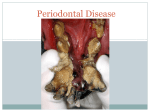
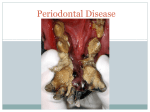
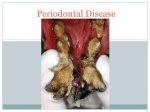
Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Sciences Bangalore, Karnataka M.D.S Periodontology Synopsis for the Registration of Dissertation M.R. Ambedkar Dental College & Hospital # 1/36, Cline Road, Cooke Town Bangalore – 05 RAJIV GANDHI UNIVERSITY OF HEALTH SCIENCES BANGALORE, KARNATAKA ANNEXURE II PROFORMA FOR REGISTRATION OF SUBJECT FOR DISSERTATION Dr. Partha Pratim Roy, 1. Name of the S/o. Shri Mrinal Kanti Roy, candidate and A.T. Mehendipir, P.O. Chandini Chowk, the address Cuttack- 753002, ODISHA 2. Name of the institution 3. Course of study and subject 4. Date of admission to the course 5. Title of the topic M.R. Ambedkar Dental College and Hospital No. 1/36 Cline road, Cooke Town Bangalore – 560005 M.D.S Periodontology 30th May, 2012 ESTIMATION OF CATHELICIDIN LL-37 LEVEL IN GINGIVAL CREVICULAR FLUID OF SMOKERS AND NON-SMOKERS SUFFERING FROM CHRONIC PERIODONTITIS- A CROSS- SECTIONAL STUDY 6. Brief resume of intended work: 6.1. Need for Study: Periodontitis is an inflammatory disease that involves microbial dental plaque, genetic and environmental factors, and it affects the supporting tissues of the teeth.1 The initiation and proliferation of periodontal disease is related to the colonization of the gingival crevice by microorganisms and their subsequent sub- gingival proliferation.2 The innate immune response has a primary role in the defense against plaqueassociated bacteria which is primarily mediated by neutrophils. Polymorphonuclear neutrophils are the first cells that migrate into the inflammatory area in response to microbial challenge and forms major defense mechanisms in the gingival crevice.1,3,4 Neutrophils produce antimicrobial peptides such as human alpha- defensins (HNPs), human beta- defensins (hBDs) and the cathelicidin LL-37 which contributes to the non- oxidative killing of microorganisms.3,4 Among antimicrobial peptides produced, human cationic antimicrobial protein of 18 kDa (hCAP18) is stored in the secondary granules of neutrophils as inactive precursor1. After the stimulation of neutrophils, cathelicidin LL-37, a peptide of 37 amino acid residues starting with two leucin residues, is released by proteolysis with proteinase. This antimicrobial peptide is an endogenous antibiotic that has a broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity and it is a chemoattractant for neutrophils, monocytes, mast cells and T-cells.1 Studies on cathelicidin LL-37 in chronic periodontitis has shown that it may play a role in the host innate immune response during periodontal inflammation. Smoking is a well established risk factor for periodontal disease. Smoking is said to have direct effect on homeostatic mechanism as well as on the periodontal microflora.4 Smokers exhibit 2.6–6 times more periodontal destruction.4 Smoking also has many significant negative effects on PMN function including impaired phagocytosis, super oxide and hydrogen peroxide generation, integrin expression, and protease inhibitor production.5 In the present view of the etiopathogenesis of periodontal disease and the effect of smoking, the study aims to assess the association between smoking and periodontal destruction. The present investigation is therefore designed to see the effect of cathelicidin LL-37 level in GCF of patients suffering from chronic periodontitis in the group of smokers and non- smokers. 6.2 Review of Literature: 1. A study was conducted in 59 subjects (39 females and 20 males: age group: 34 to 62yrs) of which 20 were with chronic periodontitis, 21 with gingivitis and 18 healthy patients to investigate the levels of cathelicidin LL-37 and IL18 in periodontal disease. The study showed significant elevation in the level of cathelicidin LL-37 in periodontal disease. 2. To analyze the neutrophil-derived antimicrobial peptides (cathelicidin LL37) in the innate immune response against periodontogenic bacteria, a study was conducted in 14 subjects with aggressive periodontitis(mean age 32.8yrs) and 17 patients with chronic periodontitis (mean age 59.1yrs) showed elevated levels of HNP1-3 and cathelicidin LL-37 in both aggressive and chronic periodontitis. But there was no correlation found between myeloperoxidase, LL-37 and HNP1-3. 3. For the evaluation of Susceptibility of various oral bacteria to antimicrobial peptides and to phagocytosis by neutrophils a study was conducted. The results indicated that immune evasion may contribute to the pathogenicity of some periodontopathic bacteria. 4. To study the difference in expression among cathelicidin LL-37 and humanβ defensins in inflammed gingival tissue, a study was conducted. The findings suggested that LL-37 displays distinct expression patterns from those of hBDs in gingival tissue. 5. To study the effect of smoking in PMN function a study was carried out in sixty subject of which 15 non-smokers, 15 light smokers, 15 moderate smokers and 15 heavy smokers. The result showed impaired PMN viability and function in periodontally healthy patients. 6.3 Objectives of the Study : To study the effect of smoking on level of cathelicidin LL-37 in periodontal diseases. To estimate the level of cathelicidin LL-37 in gingival crevicular fluid in smokers and non smokers with chronic periodontitis. To correlate the role of cathelicidin LL-37 on periodontal clinical parameters in smokers and non-smokers with chronic periodontitis. 7. Methodology : 7.1. Source of Data : The study group will consist of subjects belonging to both sexes. Subjects will be selected from the out- patient department of M. R. Ambedkar Dental College and Hospital, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India. Written informed consent will be obtained from all patients. 30 smokers with chronic periodontitis and 30 non-smokers with chronic periodontitis will be compared with 30 healthy patients. Group I: 30 healthy non-smoker patients Group II: 30 non-smokers with chronic periodontitis Group III: 30 smokers with chronic periodontitis Inclusion Criteria : 1. Study subjects should be >25 Years of age. 2. Patients suffering from chronic periodontitis i.e. a) Bleeding on probing b) Probing pocket depth of ≥ 5 mm c) Clinical attachment level of ≥ 3 mm d) Smokers smoking more than 5 cigarettes/day for over a year are included in the study. Exclusion Criteria: 1. Patients with systemic diseases that can impair immune response such as diabetes mellitus, HIV, immunological disorder and hepatitis. 2. Subjects who have undergone periodontal therapy in the past 6months. 3. Patients on any systemic antibiotics, NSAIDS, steroid therapy and any other drugs which is known to affect the periodontal status. 4. Former smokers are excluded from the study. 5. Smokers smoking other than cigarettes are excluded from the study. 7.2. Methods of Data collection: The whole-mouth clinical parameters including probing depth, clinical attachment level, plaque index (OHI), bleeding on probing (Ainamo and Bay) and gingival inflammation (Loe and Silness) will be recorded in all patients. Gingival crevicular fluid collection will be done from sites having probing depth > 5mm and clinical attachment loss >3mm. 3µl GCF will be collected by extra crevicular method using micro-capillary pipettes. All samples will be stored at -70о C. Cathelicidin LL-37 level will be estimated using enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) method. Values obtained from the test will be recorded, computed and subjected to statistical analysis. 7.3. Does the study require any investigations to be conducted on patients or other human/animals? Yes 7.4. Has ethical clearance been obtained from your institution in case of 7.3? Yes 8. List of References: 1. Oya Turkoglu, Gulnur Emingli, Necil Kutukculer, Gul Atilla. Gingival Crevicular Fluid Levels Of Cathelicidin LL-37 and Interleukin-18 in Patients With Chronic Periodontitis. J Periodontol 2009:80;969-976 2. M. Puklo, A. Guentsch, P.S. Hiemstra, S. Eick, J. Potempa. Anlysis of neutrophil-derived antimicrobial peptides in gingival crevicular fluid suggests importance of cathelicidin LL-37 in the innate immune response against periodontogenic bacteria. Oral Microbiol Immunol 2008;23;328-335 3. Ji S, Hyun J, Park E, Lee B-L, Kim K-K, Choi Y. Susceptibility of various oral bacteria to antimicrobial peptides and to phagocytosis by neutrophils. J Periodont Res 2007; 42: 410–419. 4. I. Hosokawa, Y. Hosokawa, H. Komatsuzawa, R. B. Goncalves, N. Karimbux, M. H. Napimoga, M. Seki, K. Ouhara, M. Sugai, M. A. Taubman and T. Kawai. Innate immune peptide LL-37 displays distinct expression pattern from beta-defensins in inflamed gingival tissue. British Society for Immunology, Clinical and Experimental Immunology2006, 146: 218–225 5. A.Guntsch, M.Erler, P.M.Preshaw, B.W.Sigusch, G.Klinger, E.Glockmann. Effect of smoking on crevicular polymorphonuclear neutrophil function in periodontally healthy subjects. J Periodont Res;2006;41;184-188. CONSENT FORM I, __________________, aged______ yrs, son/daughter/wife /husband of ________________ hereby authorize Dr PARTHA PRATIM ROY, working at M.R.AMBEDKAR DENTAL COLLEGE AND HOSPITAL, to perform any diagnostic examination and collection of gingival crevicular fluid. The nature of the condition and any possible complications of the procedure have been explained to me in the language i understand by my doctor. I also agree that if any untoward incident happens, which is beyond the doctor’s control, no responsibility will be attached to the doctor(s)/hospital/ staff. I also agree and give my full consent to participate in the study conducted in Department of Periodontics, Ambedkar Dental College and Hospital, the nature of the study have been explained to me by my doctor (s). I declare that I am of sound mind and I am giving this consent with my own free will after having read and understood the contents of the consent form. Name of the procedure: Measurement of the clinical parameters and collection of gingival crevicular fluid. Signature of the patient/person giving consent: WITNESS SIGNATURE 1. 2. Date: SIGNATURE OF THE CANDIDATE REMARKS OF THE GUIDE NAME AND DESIGNATION OF DR. JAYANTHI.D THE GUIDE PROFESSOR, DEPARTMENT OF PERIODONTICS, M.R. AMBEDKAR DENTAL COLLEGE, BANGALORE-05 SIGNATURE OF THE GUIDE CO-GUIDE SIGNATURE HEAD OF THE DEPARTMENT SIGNATURE REMARK OF THE PRINCIPAL SIGNATURE DR. MOHAMED FAIZUDDIN